Introduction
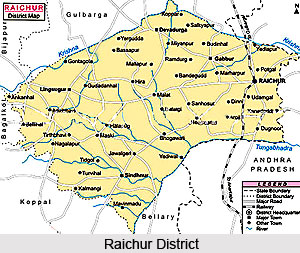 Raichur District is situated in the state of Karnataka. The district has a rich historical past, steeped in the conquests, achievements and works of art of various dynasties that have held sway here at one time or another. Though initially part of the princely state of Hyderabad, Raichur District is now a constituent district of the Mysore state. The district has protected and preserved a rather rich cultural tradition and legacy, which has grown here since the early times. A number of beautiful temples, forts and mathas are found strewn all over the place, all of which have been the vessels of great heights in artistic skills and learning.
Raichur District is situated in the state of Karnataka. The district has a rich historical past, steeped in the conquests, achievements and works of art of various dynasties that have held sway here at one time or another. Though initially part of the princely state of Hyderabad, Raichur District is now a constituent district of the Mysore state. The district has protected and preserved a rather rich cultural tradition and legacy, which has grown here since the early times. A number of beautiful temples, forts and mathas are found strewn all over the place, all of which have been the vessels of great heights in artistic skills and learning.
Location of Raichur District
Raichur district lies between 15 degrees 09 minutes and 16 degrees 34 minutes North latitude and 75 degrees 46 minutes and 77 degrees 35 minutes East longitude. Situated in the state of Karnataka, the Raichur District is bounded on the North by the Gulbarga District, on the West by the Bijapur District and Dharwad District and on the East by the Mahbubnagar district of Andhra Pradesh. On the South lies the Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh, and the Bellary District. The two rivers, the Krishna River and the Tungabhadra River form the entire North and Southern boundaries of the district.
History of Raichur District<
 History of Raichur district recounts a very rich narrative full of the tales of Kings and legends. The district of Raichur has a hoary past. It has had an eventful and rich beginning from the days of the Mauryan King Ashoka. A number of edicts, rocks and other records, temples, forts and battlefields bear testimony to this fact. It has already yielded hundreds of inscriptions, ranging right from the Mauryan period upto the end of the Muslim period, in a variety of languages like Sanskrit language, Prakrit language, Kannada language, Arabic language and Persian language and belonging to almost all the dynasties that ruled over the Deccan. The most important places from this point of view are Maski, Koppal, Kuknur, Mudgal and Raichur.
History of Raichur district recounts a very rich narrative full of the tales of Kings and legends. The district of Raichur has a hoary past. It has had an eventful and rich beginning from the days of the Mauryan King Ashoka. A number of edicts, rocks and other records, temples, forts and battlefields bear testimony to this fact. It has already yielded hundreds of inscriptions, ranging right from the Mauryan period upto the end of the Muslim period, in a variety of languages like Sanskrit language, Prakrit language, Kannada language, Arabic language and Persian language and belonging to almost all the dynasties that ruled over the Deccan. The most important places from this point of view are Maski, Koppal, Kuknur, Mudgal and Raichur.
The earliest recorded history of the district can be traced right back to the 3rd century B.C. The fact that three minor rock edicts of Ashoka are found in this district proves that this area was included in the dominions of the great Mauryan King Ashoka (273-236 B.C.). Of these, one rock edict has been found at Maski in the Lingasugur taluk and the other two at Koppal. During this time, the region was under the governance of the Viceory or Mahamatra of Ashoka.
Early in the Christian era, the district appears to have been a part of the kingdom of the Satavahana dynasty. The Vakatakas, who reigned during the 3rd and 4th centuries A.D., seem to have held sway over Raichur for sometime after which it appears to have been included in the Kadamba dominions. The Chalukyas of Badami are the next dynasty of importance that ruled over the place. According to an inscription from Aihole, Pulikeshin-II having defeated the Pallava Dynasty occupied this area and made it a province in his empire under the governance of his son Adityavarma.
Later on, the entire region of the present Raichur district was included in the dominions of the Rashtrakutas. The rulers of the Rashtrakuta dynasty rose to power sometime in the eighth century as could be gathered from the inscriptions of that period found in this district. According to an inscription from Manvi taluk, one Jagattunga, a subordinate ruler under the Rashtrakuta king Krishna-II, was ruling the province of Adedore Eradusavirapranta, i.e., the area constituting the present Raichur district. Nripatunga, a Rashtrakuta king, has described Koppal in his Kannada work, Kavirajamarga, as the great `Kopananagara`.
Numerous inscriptions of the Chalukyas of Kalyani, found in the various parts of the district, testify to the fact that this region was under their sway for a considerable length of time between the 10th and 12th centuries A.D. It is learnt from an inscription found at Naoli in Lingsugur taluk that during the reign of Chalukya Vikramaditya-V, the Adedore-pranta, i.e., the Raichur region, was being ruled by his younger brother Jagadekamalla-I. Another inscription from Maski describes the place as a capital and makes a reference to the reign of Jayasimha. There were, however, frequent wars between the Chola kings of the south and the Chalukyan kings of Kalyani for supremacy over the Raichur region and the territory had passed into the hands of the Cholas for a brief period.
The Haihayas and Sindas also seem to have ruled some parts of this region for sometime. Later, after the fall of the Chalukyas, Raichur passed into the hands of the Kalachuri kings. They were followed by the Kakatiyas in the 13th century. From an inscription on the fort-wall of Raichur, referred to earlier, it is learnt that the original fort was built by one Gore Gangayya Reddy, a general of the Kakatiya queen Rudramba Devi of Warangal, in 1294 A.D., at the command of the latter.
In the recent past, the Raichur district was a part of the princely state of Hyderabad. Since the 1st of November 1956, it is a constituent district of the Mysore state.
Geography of Raichur District
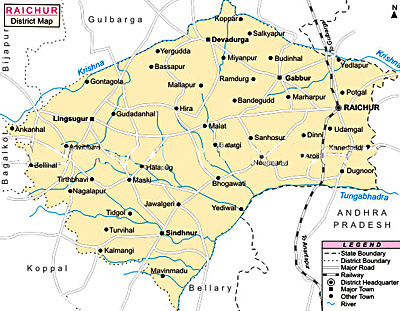 Geography of Raichur District deals with the landforms of Raichur District, where the soil has the rich content of black soil. Raichur District is situated in the state of Karnataka in between the Tungabhadra River and the Krishna River.
Geography of Raichur District deals with the landforms of Raichur District, where the soil has the rich content of black soil. Raichur District is situated in the state of Karnataka in between the Tungabhadra River and the Krishna River.
Latitudinal Extent of Raichur District
Raichur District lies between 15 degrees 9 minutes and 16 degrees and 34 minutes North latitude and 75 degrees 46 minutes and 77 degrees 35 minutes East longitude. The general slope of the district is from the north-west towards the south-east, its average height above the Mean Sea-Level being just 1,311 feet.
Extension of Raichur District
Raichur district is bounded on the North by the Gulbarga district, on the West by Bijapur district and Dharwad district, on the East by the Mahbubnagar district of Andhra Pradesh, and lying on the South are the districts of Kurnool and Bellary. The two rivers, the Krishna and the Tungabhadra, form the entire northern and southern boundaries of the district. The geographical area of the district, according to the Central statistical organization of the Government of India, is 14,013 Sq Kilometres which works out to 5410 sq. miles.
Climate of Raichur District
The climate of Raichur district is characterised by dryness for the major part of the year and a very hot summer. The year may be divided broadly into four seasons. The hot season begins by about the middle of February and extends to the end of May, South-west monsoon is from June to end of September. October and November are the post monsoon or retreating monsoon months and the period from December to the middle of February is the cold season. The coldest month is that of December, with the mean daily maximum temperature being around 29.3 Degree Celsius and the mean daily minimum at 17.7 Degree Celsius. May is the hottest month, the mean daily maximum temperature being 39.8. The heat is oppressive till the onset of the south-west monsoon by about the first week of June. Thereafter the weather becomes slightly cooler and continues to be so till the end of the South-west monsoon season. Day temperatures show a slight increase in October. From November, both day and night temperatures gradually decrease till December.
The low and highly variable rainfall renders the district liable to drought. The region around Lingsugur gets the least amount of rainfall in the district while towards the south as well as the east, rainfall increases. During the south-west monsoon months, viz., June to September, the district receives the highest rainfall. In the post-monsoon months of October and November also, the district receives some rain. The variations in the annual rainfall from year to year are large as is the case in the neighbouring districts. Skies are moderately to heavily cloud in the south-west monsoon months. In the post-monsoon months, clouding is somewhat less. Clear or lightly clouded skies are common in the rest of the year.
Soil of Raichur District
The undulating black cotton soil strips, cut by numerous nalas, characterise the region of the Dharwad schists, which is now practically denuded of trees and presents a monotonous landscape, while the gneissic region is generally more or less broken and covered with a thin mantle of red loamy soil. Gneissic hills and sedimentary formations, which cover a small belt of the region adjoining the confluence of the Krishna River and the Tungabhadra River, occupy more or less flat plateaus.
Landform of Raichur District
Regionally viewed, the hills in the area present some structural features which are of interest in relation to the geology of the area: 1) Taking the most south westerly group, the hills of Karigudda, Manvi and Rabhinakal show a continuity along roughly north-west south-east directions: 2) from Sirwar and Yermasagar, running in a roughly south-east direction, may be recognised the hill of Madhugiri, Neermanvi, Gorkal, Kurvi and the one two miles west of Kamalahatti; 3) between Masarakal and Gabbur, a number of gneissic hills are seen at Kakarga, Jinnapur, Hungundabad, Ramdurga, Jagatkal, Khardigud, Maladkal and Gabbur. The hills around Uttanur are seen to be in line with the south-western group of hillocks in the above areas also the hill-clusters around Kalmala and Kallur, are seen to be situated in the same north-west and South-east disposition as that of the group of gneissic hills enumerated above; and 4) the hills around Raichur, which constitute a prominent landmark in the area, may also be seen roughly to display north-west and south-east trends.
Culture of Raichur District
Culture of Raichur district is a rich blend of the art, architecture and literature of various famous ruling dynasties that held sway here. The temples and mathas that were built by these ancient rulers were the centres of cultural, literary and social activities. The rulers of some of the most powerful kingdoms- like the Chalukyas and Rashtrakutas, of Viajayanagara and of the Bahmanis and Adil Shahs, which arose in the vicinity of the district, were great patrons of arts and letters. A galaxy of eminent personalities, who shone in the cultural field, hailed from this district. There were independent Bhakti movements pioneered by Sharanas and Haridasas who were dedicated souls and many of whom have left a deep impress on the literature and culture of the Kannada society. A brief history in the development and spread of the literary art and culture of the place is discussed below.
In the 11th century, Naoli in the Lingsugur taluk was known for two reputed vachanakaras, namely, Shankara Dasimayya and Dhakkeya Marayya. They were the beginners of the vachana style which produced, in the following centuries, a unique treasure of Kannada literature. Significant contributions were made towards the Vachanakaras by Ayadakki Marayya, Ayadakki Lakkamma and Bibbi Bacharasa in the 12th century. In the 16th century, Lingannacharya of Kallur wrote Vararamya-Ratnakara in Bhamini-shatpadi metre.
The mathas were re-organised during the reign of the Vijayanagara Kings, and the cultivation of arts and letters received a great impetus. The great Haridasa tradition was propagated in Raichur district by several eminent saints like Vijayadasa, Gopaladasa and Jagannathadasa in the 17th and 18th centuries. They are well known for having written a great number of devotional and mystical songs. A number of famous dasas followed these saints, and they are renowned for their Sanskrit and Kannada works and treatise. They include Praneshadasa, Vasudeva Vitthala, Panganama Thimmanna Dasa, Kallur Subbannacharya, Guru Pranesha, Sreesha Pranesha Vitthala etc, all of whom strove earnestly to continue the Haridasa tradition.
A great number of Veerashaiva writers arose in the 18th century. The most famous names in this field include Sangavibhu of Ganekal who wrote Kumara Vijaya and three Shatakas; Ganamathadarya, the author of Bhakti-Sudharasa, Kudlur Basavalinga Sharma etc. Famous writers of the 19th century include Veerabhadra Kavi, Gugal Parappayya, Mariswamy etc. The late Kaviratna Chenna kavi and Maski Basavappa Sastry were famous for their Puranas.
Concerted efforts have been made by many people for the preservation, protection and propagation of the literary traditions of the place. The research work of Gorebala Hanumantha Rao of Lingsugur in the field of Dasa Sahitya (the literature of Dasas), has brought to light the works of several Dasas who strove hard to propagate the Dasa tradition. He brought out more than 50 works containing keertanas of several Dasas. It was also discovered that there were Harijans and Muslims too among the Dasas.
In the 1920s and 1930s, the literary and cultural activities gained a considerable momentum through the strenuous efforts of Pandit Taranath (1891-1942), an eminent thinker, linguist and social worker, who hailed from South Kanara District but spent many active years of his life in the Raichur region. He attracted a number of devoted followers whom he inspired to work earnestly for the country. He wrote Dharma Sambhava, Dharmada Tirulu and other thought- provoking works. He was highly proficient in Ayurveda also and trained many youth in this medical science. He founded the Hamdard High School at Raichur.
The late Kallinatha Shastri Puranik wrote many well-known Puranas, like his father Kaviratna Chenna kavi. He has also authored many plays, songs and other works. Late Prof. D.K.Bhimasen Rao of Bidgi in Manvi taluk, who worked as the Head of the Kannada Department of Osmania University, was responsible for fostering Kannada movement in Hyderabad through Kannada Sahitya Mandir and Nizam Karnatak Sahitya Parishat. Late Sri Manvi Narasinga Rao, who worked for the cause of Kannada through Kannada Sahitya Mandir, Hyderabad, contributed to the Kannada literature Saraswati Tatva (a collection of essays) and Kannada Yatre (a travelogue), etc. He was mainly responsible for organizing the Nizam Karnatak Sahitya Parishat. Considerable contributions have been made by a number of other people who sought to revive and preserve the artistic culture of the place. These include Pandit D.M.Sharma, Dr.S.M.Hunashal, Sri Annadanayya Puranik, Sri Jaithirth Rajpurohit, Sri Chandrashekhara Sastry, Sri Gadwal Shankarappa etc.
It is therefore evident from the above discussion that the literary legacy of Raichur district is a rather rich one. Raichur district thus has rich cultural traditions and has been playing an important role in the field of literary activities since early times.
Education In Raichur District
 Education in Raichur district has seen a sustained effort in making education a fundamental right that can be achieved by all. This reflects the increased national commitment towards achieving the goal of Universality of Elementary Education (UEE).
Education in Raichur district has seen a sustained effort in making education a fundamental right that can be achieved by all. This reflects the increased national commitment towards achieving the goal of Universality of Elementary Education (UEE).
There has been a demand from parents for attention to the education of their children. Simultaneous efforts were taken to focus on the Universality of primary education. The district has made steady progress in achieving Universality of elementary education, though the progress has been uneven in different blocks. Increasing enrolment, retention and achievement at the primary stage has in turn generated growing demand for upper primary education. Consequently, achievement of UEE depends now, along with continuing efforts at the primary stage, on a focus on the upper primary stage.
As regards higher education, the district has good facilities. There are colleges of engineering, medicine, nursing, dental sciences, post graduate courses, agricultural sciences, business management etc catering to the needs of higher education.
The district has 1465 primary schools having classes I to V of which 524 are higher primary schools having classes I to VII. This is inclusive of Government Schools / Aided Schools / Unaided schools.
There are 1308 Anganwadi centres run by the Department of Women and Child Development. The HPS schools consist of classes I - VII and thus the number of schools providing access to primary schooling are 1465. To move towards the national norm of elementary education, eighth standard is added to 56 Upper primary schools during 2003-04. However majority of UPS remain at the seventh standard level.
There are 1086 habitations in the district. According to the household survey most of the habitations having a population of 200 and above and child population of 15 and above are provided with access for primary schools within a distance of 1 km. Some of the towns and big villages may have more than one school. Each primary school is serving on an average a population of 1125 in the district and an upper primary school is serving on an average 3086 populations in the district. During 2002-03 Class V was added to Primary schooling and classes VI and VII were put under Upper Primary Schooling. As a result there is a revision of number of primary and upper primary schools in the district.
The Educational Administrative machinery at the district level is headed by the Deputy Director of Public Instruction (DDPI). He is assisted by a team of 2 Educational Officers, 5 Subject Inspectors and one Superintendent of physical Education, all of whom provide academic guidance at the district level. The D.D.P.I. takes up the academic and administrative inspections of the institutions in the district and also provides educational leadership to the entire district.
At the level of the blocks, the Block Educational Officer (B.E.O.) leads the administration of the educational machinery. He is supported by a team of 5 Educational Co-ordinators and Educational Assistants. They pay visits to the schools in their jurisdiction and provide guidance for improvement of educational quality in the schools. The BEOs are assisted by the Block Resource Coordinators in the planning, implementation and supervision of the activities under Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan. The BRCs have 5 resource persons - 2 from the high school cadre and 3 from the primary cadre. These resource persons provide training, academic guidance and on job support to the teachers in their respective blocks.
At the cluster level there is a Cluster Resource Person (CRP) who provides academic guidance and on job support to the teachers in their clusters.
In order to look to give academic support to the teachers of primary schools, the District Institute of Education and Training (DIET) has been set up. The Institute also sees to the training needs of teachers working in both the districts of Raichur and Koppal. It is headed by the Principal of the DDPI cadre, and re-designated as ex-Officio DDPI (Development). There are a total of seven units that form part of the DIET. These are- Pre Service Teachers Education (PSTE); District Resource Unit (DRU); Inservice Training, Field Interaction and Co-ordination (IFIC); Curriculum, Material Development and Evaluation (CMDE); Educational Technology (ET); Work Experience (WE); Planning and Management (P and M)
Each unit is headed by a Senior Lecturer and assisted by one or two Lecturers. DIET functions as the academic nucleus of the district in identifying the training needs of teachers, the teaching learning and evaluation processes and accordingly designs the need-based interventions in the development of training packages, training design and provide academic support to the teacher fraternity. As the district has Block Resource Centres and Cluster Resource Centres, the DIET also functions to coordinate the activities of these sub-district structures in providing training and academic guidance to the teachers. The DIETs also take up the action research studies in the district with a view to bringing out innovative ideas and practices in the field of education, and they share the same among the teacher fraternity.
Temples of Raichur District
 Temples of Raichur district in Karnataka are some of the architectural marvels of south India. Raichur, on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, was the princely state of Mysore during the rule of Tipu Sultan, later coming under the Kingdom of the Nizam.
Temples of Raichur district in Karnataka are some of the architectural marvels of south India. Raichur, on the banks of the Tungabhadra River, was the princely state of Mysore during the rule of Tipu Sultan, later coming under the Kingdom of the Nizam.
Gabbur is one of the religious quarters of the district and has several old temples and inscriptions. In the old days, it was a center of education and was also known as Gopuragrama. The most important of the temples of Raichur district are those of Male-Shankara, Venkateshwara, Ishwara, Bangara Basappa and Hanuman. In addition to these, there are several ruined temples of Raichur district, two or three mathas, a few cisterns and a gateway called the Chandi-gage with a temple on either side of it. The Male-Shankara temple, one of the well known sacred site of this district is built of rough grey stone and has a high plinth. The carving in the temple is plain on description of the roughness of the stone. There are two inscriptional tablets at the northern and western entrances and there is a large reservoir in front of the temple.
The temple of Venkateshwara is a popular one amongst the temples of Raichur district and consists of three shrines, two of them containing the images of Vishnu and the third a linga. The carving on the outer walls of this temple represents elegant figures of various deities and animals, those of the elephants being particularly striking. On the eastern side of the temple, there is a large cistern, with beautifully carved granite steps all round, called Sat baoli or seven cisterns. One of the mathas here is called Ganni Gudi Matha. It has a magnificently carved door. There is a tank, which is now in carcass. The Bangara Basappa temple has a shrine with an image of Ganesha, two Nandis (one is of fairly large in size and the other is a small one) and an inscriptional flank. Gabbur has enclosure walls round it, which were built in different periods and are in different states of decay. The square form of their bastions is considered to be Islamic in design.
Anegundi, 135 km from Raichur, has some splendid temples from the Vijayanagar era such as the Ranganatha Temple and the Huchchappayana Matha. The Pampa Sarovara, the Kamal Mahal and Nava Brindavana enshrine the mortal remains of famous saints. Markandeshwara Temple is one of the oldest temples of Raichur district at Kallur. Lord Shiva in the form of Markandeshwara is the chief deity here. The shrine is distinguished for its beautifully carved pillars. Narada Temple at Naradagadde is one of the most beautiful temples of Raichur district. Built on Naradagadde, a picturesque island in the Krishna River, this temple is dedicated to the Celestial Sage, Narada. Naradagadde is also known as Kuruvapur and was built on the site where Sage Narada performed penance. The temples of Raichur district are famous in south India for their outstanding architecture.
Tourism In Raichur District
 Tourism in
Tourism in
Places of historical interest are found in abundance in the Raichur district. Kallur, in Manvi taluk, is a large village, about 13 miles from Raichur. The village is surrounded on all sides by granite hills except the east and derives its name from the abundance of the boulders on these hills.
The village and the hills around are full of antiquities. The present village, which is a modern growth, is surrounded by an old wall, which appears to be a work of the 13th or 14th century A.D., though the five gates appear to be of Muslim period.
Two of them, which are not in much use, have no names. The other three are called after the towns to which they lead, namely, Manvi Darwaza, Kalmala Darwaza and Raichur Darwaza. The gates are more or less in a ruined condition. The superstructure of the Raichur Darwaza, which has been pulled down to construct the Chavadi in the village, contained a wooden inscription in the Kannada language. According to this inscription, which now forms part of the ceiling of the chavadi building, the gateway was constructed by Agha Khusru, a well known Adil Shahi dignitary. There are six temples in and around the village. Out of these, the Markandeshwara temple seems to be the oldest temple in the village and its hall has some pillars of black polished stone with beautiful carvings on them. A number of inscriptions have been found in this village, most of them belonging to the period of the Chalukyas of Kalyana.
Another interesting feature of Kallur is that there are many large and well-built wells. Five of these wells are very spacious, which have been built of solid masonry and have flights of steps leading to their base. It is not known when and by whom they were constructed. The largest well is 50 feet into 50 feet on the surface and about 120 feet deep and contains sweet water.
 Gabbur, in Deodurg taluk, was a centre of education in the old days. Found here are a number of temples and inscriptions. Gabbur was also known as Gopuragrama in the olden times. According to inscription dated 1109 A.D., belonging to the reign of Vikramaditya VI of the Chalukyas of Kalyana, now placed in the Hyderabad Archaeological Museum but originally belonging to a Jain Temple at Gabbur, the place (then called Gobbur or Hiriya Gobbur) was an agrahara town in the 12th century A.D. The same record states that it had also a Jain temple called Brahma-Jinalaya or Nagara-Jinalaya.
Gabbur, in Deodurg taluk, was a centre of education in the old days. Found here are a number of temples and inscriptions. Gabbur was also known as Gopuragrama in the olden times. According to inscription dated 1109 A.D., belonging to the reign of Vikramaditya VI of the Chalukyas of Kalyana, now placed in the Hyderabad Archaeological Museum but originally belonging to a Jain Temple at Gabbur, the place (then called Gobbur or Hiriya Gobbur) was an agrahara town in the 12th century A.D. The same record states that it had also a Jain temple called Brahma-Jinalaya or Nagara-Jinalaya.
Deodurg is the headquarters town of the taluk of the same name and is about 34 miles west of Raichur. It was formerly a stronghold of Bidar chieftains and has an old fort. Nearby, there is a hill, which contains talc.
Gurugunta, in Lingsugur taluk, was the chief town of a small principality (samsthana) of Naiks related to the chiefs of Kankgiri and Shorapur. In the old days, these chiefs owed allegiance to Vijayanagara kings or the Adil Shahi dynasty of Bijapur. The Gurugunta samsthana had survived under the Nizams and was merged in the district in 1949.
Jaladurga, in Lingsugur taluk, is an island fort situated picturesquely in the Krishna River, about eight miles from Lingsugur. It was an important fort of the Adil Shahs of Bijapur. The fort at Mudgal has a long history of dynastic rule behind it.
A number of places containing tools and items from pre historic times are also found at Raichur district. Maski, in Lingsugur taluk, is highly interesting from the points of view of prehistory and protohistory. It must have been a town of considerable size and importance in the remote past, as is evident from the traces of its iron and gold workings covering a large area, and from the references made to it in a number of inscriptions ranging from the 10th to the 16th century A.D. There is an abundance of artefacts found at the various sites located here. Among these sites, the so-called fields of Sultan Muhammad were found to be particularly rich in antiquities. These are believed to constitute the old town of Maski which was accessed from the riverside through a gorge amidst a ring of hills which surround the site. The hills have several spurs, the highest of which has a Shaivite temple which, from its architecture, appears to be of the 13th century A.D. On two other spurs near the gorge, are two other temples - one goldsmith`s and the other weaver`s. Weaving and gold-smelting are still the principal industries of the place. Neolithic implements like stone axes, hammers, flakes and cores and plain pottery were discovered at Lingsugur, and pre historic items were also found along the slopes of the hillocks at Kottekal. Artefacts, iron slag and pieces of ancient pottery have also been found at Kavital in the Manvi taluk.
Tourist places in Raichur
 Raichur Fort in Raichur District
Raichur Fort in Raichur District
This fort is situated only about 2 km from Raichur Railway Station. The Kakatiya rulers constructed this monumental fort in 1294. The massive stone slab extending 41 ft in length is a main attraction here. It is situated near the bus stand at Raichur. A record in Telugu can be seen in this slab.
Ekminar Mosque of Raichur District
This mosque was built during the days of Mohammed Shah Bhamini. But the largest Mosque of Raichur is the Jama Masjid.
Itagi in Raichur District
It is situated about 40 km from Gadag District. The ancient temple with visibly the best of Kalyani Chalukya architecture is situated in Itagi. Mahadeva Dhandanayaka built this temple, which is renowned for its intricately carved entrance. The ethereal sculpture here makes a lasting impression. The architecture has drawn historic comparisons with that of the temples at Halebid.
Another important monument of Itagi in Raichur is the `Saraswati Mutt`, the students` residence. The famous temple complex of `Navalinga` is situated about 10 km from Raichur at Kukanur. It is dedicated to Lord Shiva.
The wonderful architectural structures of the Rashtrakuta Dynasty can also be seen here. The temples of the Kalyani Chalukyas are also found here. These are the ancient temples dedicated to Lord Mahamaya, Lord Kaleswara and Lord Mallikarjuna.
Koppal in Raichur District
Earlier, Koppal was the capital of the provincial Kingdom of Shilaharas, a feudatory to the Kalyani Chalukyas. This place has a magnificent citadel. It is also a holy place of the Jains. The Lord Shiva temple called the Male Malleswara temple is situated at Palligundu here. The inscriptions of Ashoka can also be seen at Palligundu and Govimatha. Koppal is well known for its traditional colourful lacquer ware.
Hutti in Raichur District
This place of Raichur is renowned for its gold mines. It is situated about 18 km from Lingasugar.
Pilgrimage Tourism In Raichur District
 Pilgrimage tourism in Raichur District is a very enriching experience as there are a number of places of worship located here in the district. Naradagadde, Kurugadda, Jitamitragadde, Manvi, Mahamalleshappa, Devarbhupur, Kadlur and Balaganur are the most important centres of pilgrimage situated in the district of Raichur.
Pilgrimage tourism in Raichur District is a very enriching experience as there are a number of places of worship located here in the district. Naradagadde, Kurugadda, Jitamitragadde, Manvi, Mahamalleshappa, Devarbhupur, Kadlur and Balaganur are the most important centres of pilgrimage situated in the district of Raichur.
One of the most important pilgrim centres for the Hindus in the district is Naradagadde, which is about 15 miles from Raichur. It is surrounded by the Krishna River and the place is held to be very sacred. The annual fair held in the month of Phalguna, i.e., about March, attracts thousands of pilgrims. The island of Kurugadde near Devarsugur is a well known festival centre for the Smartas. The island, along the course of the Krishna River, houses a temple where the presiding deity is Sripada Srivallabha. The place is visited by pilgrims all throughout the year. Jitamitragadde, another island in the river course of the Krishna, is a sacred place for the Hindus who visit the place all the year round for a holy bath.
Gabbur, in the Deodurg taluk, is famous for the many ancient temples found here. The most important of the temples are those of Male-Shankara, Venkateshwara, Ishwara, Bangara Basappa and Lord Hanuman. In addition to these, there are several ruined temples, two or three mathas, a few cisterns and a gateway called the Chandi-gage with a temple on either side of it. The Male-Shankara temple is built of rough grey stone and has a high plinth. The carving in the temple is plain on account of the roughness of the stone. There are two inscriptional tablets at the northern and western entrances and there is a large cistern in front of the temple. The temple of Venkateshwara consists of three shrines, two of them containing the images of Lord Vishnu and the third a linga. The carving on the outer walls of this temple, representing figures of various deities and animals, are elegant, the figures of elephants being particularly striking. On the eastern side of the temple, there is a large cistern, with beautifully carved masonry steps all round, called Sat baoli or seven cisterns.
One of the mathas here is called Ganni Gudi Matha. It has a beautifully carved door. There is a tank, which is now in ruins. The Bangara Basappa temple has a shrine with an image of Lord Ganesha, two images of Nandi (one is of fairly large in size and the other is a small one) and an inscriptional tablet. Gabbur has enclosure walls round it, which are of different periods and in different states of decay. The square form of their bastions is considered to be Muslim in design. Found at Kavital in Manvi taluk is a temple called Tryambakeshwara dating back to the medieval period. The temple has three shrines, two of which contain lingas. The exterior of the temple is plain, but the masonry work is very impressive.
Gandhal, in Raichur taluk, which is situated about 20 miles south of Raichur, has a well known temple of Panchamukhi Prana Devaru (Hanuman with five faces) on a hillock. Visitors to Mantralaya (now in Andhra Pradesh) make it a point to visit this temple also. Matmari, in Raichur taluk, is looked upon as a holy place. It has a temple dedicated to Veerabhadra and the well-known Matha of Sri Saviradevaru Channaveera Shivacharya Swami is nearby.
The district is also of religious significance due to the many fairs, festivals and Jatra that are held here. A well known place of pilgrimage for the Hindus is at Manvi. A number of fairs and festivals are held here. Of these, the most important ones are the Karemma Jatra which is held for about two days in the month of January, amd the Yellama Jatra which is held for about seven days in the month of February. Also of significance is the Mahamalleshappa Jatra held usually about January and the Sanjeevaraya Jatra held about December. Manvi is also the birth-place of Jagannatha Dasa who is noted for having spread the Bhakti cult. In the Lingsugur Taluk, the Amareshwara Jatra is held for about three days in the month of March. It is a very popular jatra which attracts a large number of people. This fair is held at Devarbhupur and is particularly popular with the Veerashaivas of the district.
The Kadlurayya fair at Kadlur held in the month of Margashira in December attracts a good number of people. Hanumanji Jatra at Balaganur, Sindhanur taluk, held in Vaishakhain the month of May, lasts for three days. A cattle show is also held as an adjunct to the religious fair.
The Syed Shams Alam Hussainali Urus held about August is a great Muslim festival. Muslims from all over the district and also from outside congregate at Raichur on this occasion to offer prayers.



















