About Sabarmati River
 Sabarmati River is a west-flowing Indian river. It is considered to be a monsoon-fed river and is associated with the history of India and Indian mythology. It is believed that Lord Shiva brought Goddess Ganga to Gujarat which triggered the birth of Sabarmati.
Sabarmati River is a west-flowing Indian river. It is considered to be a monsoon-fed river and is associated with the history of India and Indian mythology. It is believed that Lord Shiva brought Goddess Ganga to Gujarat which triggered the birth of Sabarmati.
Sabarmati River is about 371 km in length. In Gujarat, the river extends to a length of about 323 km, while in Rajasthan the river has a length of about 48 km.
Tributaries of Sabarmati River
The main tributaries of the Sabarmati river are Wakal river and the Sei Nadi, which also rise in the Aravalli hill range west of Udaipur city and flow south-westwards in courses generally parallel to the Sabarmati river. Wakal River, the main tributary of Sabarmati River begins its journey from the hills near Ghora village in Gogunda tehsil of Udaipur District. The Wakal River flows about 112 km across the state of Rajasthan and crosses the boundary near the village of Gau Pipli and enters Gujarat. The Manas River is the main tributary of the Wakal River. The Sei River is the tributary of Sabaramati River and flows in the state of Gujarat.
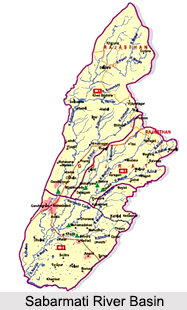
Sabarmati River Basin
 Sabarmati River Basin is situated in the mid-southern part of Rajasthan, between latitudes 23 degree 25` and 24 degree 55` and longitudes 73 degree 00` and 73 degree 48`. The Sabarmati River originates from the ranges of Arravalli in the Udaipur district of Rajasthan, Western India. The river is about 371 km in length. In its initial course, the river is also called as Wakal. The river empties into the Gulf of Cambay of Arabian Sea. The river traverses a stretch of about 400 Km. To the east of the river lies the Banas and Mahi Basins, to its north the Luni Basin and to its west the West Banas Basin. The southern boundary of the river is the border with Gujarat State. The total area of the Basin is 4,164 km square.
Sabarmati River Basin is situated in the mid-southern part of Rajasthan, between latitudes 23 degree 25` and 24 degree 55` and longitudes 73 degree 00` and 73 degree 48`. The Sabarmati River originates from the ranges of Arravalli in the Udaipur district of Rajasthan, Western India. The river is about 371 km in length. In its initial course, the river is also called as Wakal. The river empties into the Gulf of Cambay of Arabian Sea. The river traverses a stretch of about 400 Km. To the east of the river lies the Banas and Mahi Basins, to its north the Luni Basin and to its west the West Banas Basin. The southern boundary of the river is the border with Gujarat State. The total area of the Basin is 4,164 km square.
Sabarmati River Basin covers the mid-southern part of Rajasthan. The basin lies between latitudes 23 25` and 24 55` and longitudes 73 00` and 73 48`. The Banas and Mahi Basins lie to the east of Sabarmati basin, while the Luni Basin is in the north and to its west is the West Banas Basin. The southern boundary of the basin is the border with Gujarat State.
The total catchment area of the Basin is documented to be 4,164 km2 according to the 1:250,000 scale topographical maps published by the Survey of India. Sabarmati River Basin extends in the regions of Udaipur, Sirohi, Pali and Dungarpur Districts. The western part of the Basin is surrounded by hilly topography belonging to the Aravali chain. East of the hills lies a narrow alluvial plain with an undulating eastward slope.
Drainage in Sabarmati River
 The Sabarmati River and its tributaries define the drainage pattern of this River Basin. This basin drains down the slopes of the Aravalli hills in Udaipur District, and the Vatrak River, which rises in Dungarpur District.
The Sabarmati River and its tributaries define the drainage pattern of this River Basin. This basin drains down the slopes of the Aravalli hills in Udaipur District, and the Vatrak River, which rises in Dungarpur District.
Sabarmati River starting in the Aravali hills roughly marks the western limits of Udaipur District, i.e. Mount Abu area and also flows in a southwesterly direction. The main tributaries of the Sabarmati River are Wakal River and the Sei Nadi. The tributaries also rise in the Aravali hill range west of Udaipur city and flow southwestwards in courses generally parallel to the Sabarmati river, until it merges with the main river in Gujarat. The annual mean rainfall over the Sabarmati Basin was recorded as 575 mm, of which about 96% is experienced during the four Monsoon months, starting from June to September.
Course of Sabarmati River
 Sabarmati River originates in Aravalli Mountain Range in Udaipur district of the northern Indian state of Rajasthan. The river is also called Wakal in its initial course. The river flows in a south-westerly direction across Rajasthan and Gujarat. It finally empties into the Gulf of Cambay of the Arabian Sea.
Sabarmati River originates in Aravalli Mountain Range in Udaipur district of the northern Indian state of Rajasthan. The river is also called Wakal in its initial course. The river flows in a south-westerly direction across Rajasthan and Gujarat. It finally empties into the Gulf of Cambay of the Arabian Sea.
Banks of Sabarmati Rive
 Banks of Sabarmati River has Indian cities like Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar. There is a legend related to what inspired Sultan Ahmed Shah to establish Ahmedabad. It is believed that while the Sultan was resting on the bank of Sabarmati River, the courage of a rabbit to chase a bully dog inspired him to create the city. On the banks of the river Sabarmati, Mahatma Gandhi had established the Sabarmati Ashram, during Indian freedom struggle. The banks of Sabarmati River has been converted into a walkway by Narendra Modi, the then Chief Minister of Gujarat. The walkway has been provided with rides and water activities. The development of Sabaramati Riverfront along the river banks in Ahmedabad has been based on the grounds of improvement of environment, urban development, sustainable development, etc.
Banks of Sabarmati River has Indian cities like Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar. There is a legend related to what inspired Sultan Ahmed Shah to establish Ahmedabad. It is believed that while the Sultan was resting on the bank of Sabarmati River, the courage of a rabbit to chase a bully dog inspired him to create the city. On the banks of the river Sabarmati, Mahatma Gandhi had established the Sabarmati Ashram, during Indian freedom struggle. The banks of Sabarmati River has been converted into a walkway by Narendra Modi, the then Chief Minister of Gujarat. The walkway has been provided with rides and water activities. The development of Sabaramati Riverfront along the river banks in Ahmedabad has been based on the grounds of improvement of environment, urban development, sustainable development, etc.
Surface Water Projects of Sabarmati River
Surface Water Projects of Sabarmati River are several. The existing surface water projects in Sabarmati River have facilitated irrigation to a great strength. There are only 47 minor irrigation projects in the Sabarmati River basin, along with some small irrigation systems, covering less than 20 hectares, which are constructed and operated by Panchayat Samities.
Threat to Sabarmati River
Owing to the construction of the Dharoi Dam, Sabarmati River carries only dry weather flow or wastewater flow and starts stinking. Major storm water outlets discharge sewage and waste waters from industries in the river.



















