Introduction
 The Central Provinces and Berar was a former province under the rule of the British Empire in India. The province contained British occupations from the Mughal Empire and Maratha Empire in central India. It also covered several parts of the present state of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh states. Nagpur was the capital of the province in British India. The Central Provinces was created in the year 1861 by the merger of the Nagpur Province and the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories. The Marathi speaking region of Berar of the princely state of Hyderabad was annexed to the Central Provinces for administration in 1903. After 1936, the Legislative Assembly of Central Provinces and Berar was formed and the territory became the new province of Central Provinces and Berar on 24th October 1936.
The Central Provinces and Berar was a former province under the rule of the British Empire in India. The province contained British occupations from the Mughal Empire and Maratha Empire in central India. It also covered several parts of the present state of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh states. Nagpur was the capital of the province in British India. The Central Provinces was created in the year 1861 by the merger of the Nagpur Province and the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories. The Marathi speaking region of Berar of the princely state of Hyderabad was annexed to the Central Provinces for administration in 1903. After 1936, the Legislative Assembly of Central Provinces and Berar was formed and the territory became the new province of Central Provinces and Berar on 24th October 1936.
History of Central Provinces and Berar
 The History of Central Provinces and Berar can be traced back to the early 19th century. The Central Provinces and Berar, which existed under the rule of the British Empire in India, was located in the centre of the Indian peninsula. After the Third Anglo Maratha War, the Marathas were defeated and the regions of the Satpura Mountain Range were ceded by the Maratha Peshwa in the year 1817. It was later ceded by Appa Sahib in 1818. Later in the year 1820, the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were formed under the Governor General. In 1835 the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were incorporated in the newly created North Western Provinces. In the year 1842, the territories were again put under the jurisdiction of a Political Agent, also known as Resident of British India to the Governor General. The Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were restored to the North Western Province in the year 1853.
The History of Central Provinces and Berar can be traced back to the early 19th century. The Central Provinces and Berar, which existed under the rule of the British Empire in India, was located in the centre of the Indian peninsula. After the Third Anglo Maratha War, the Marathas were defeated and the regions of the Satpura Mountain Range were ceded by the Maratha Peshwa in the year 1817. It was later ceded by Appa Sahib in 1818. Later in the year 1820, the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were formed under the Governor General. In 1835 the Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were incorporated in the newly created North Western Provinces. In the year 1842, the territories were again put under the jurisdiction of a Political Agent, also known as Resident of British India to the Governor General. The Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were restored to the North Western Province in the year 1853.
The Maratha Bhonsle Maharajas of Nagpur accepted the sovereignty of the British administration in 1818. After the death of Raghoji III in 1853, the region of Nagpur was annexed by the British East India Company under the Doctrine of Lapse, as the native ruler had no heirs. The Nagpur Province, which consisted of the Nagpur division, Chhattisgarh and Chhindwara, was managed by a Commissioner under the Central Government till the creation of the Central Provinces in the year 1861.
The Saugor and Nerbudda Territories were merged with the British province of Nagpur to form the new Central Provinces in the year 1861. Later on 1st October 1903, Berar was put under the authority and administration of the Commissioner of the Central Provinces as well. In 1905, almost all of Sambalpur and the native states of Kalahandi, Patna state, Sonpur, Rairakhol and Bamra were reassigned to Bengal from the Central Provinces and Berar. The Hindi speaking princely states of Chota Nagpur, namely Jashpur, Udaipur, Surguja, Koriya (Korea) and Chang Bhakar were transferred to the Central Provinces and Berar from Bengal.
After the Government of India Act 1935 was passed by the British Parliament, the princely states were separated from the administration and control of the provinces and came under the authority of several new agencies, which were directly accountable to the Governor General of India. After elections were conducted in 1937, N. B. Khare was appointed as the first prime minister of the Central Provinces in the same year. In the next year, the Governor took charge of the province after Khare resigned. Later Ravi Shankar Shukla was appointed as the prime minister of the province after the elections of 1946.
After the country achieved independence from the dominion of the British on 15th August 1947, the Central Provinces and Berar became a province of the newly formed Union of India. The princely states which were part of the Central Provinces before 1936 were merged back into the province, and structured into new districts. When the Constitution of India went into effect in 1950, the Central Provinces and Berar became the new state of Madhya Pradesh. Indian princely states, which were part of the Central Provinces before 1936, were merged with the province and structured into new districts. After the Constitution of India went into effect in the year 1950, the Central Provinces and Berar formed the new Madhya Pradesh state.
In 1956, some of the regions of Madhya Pradesh, which included the Berar and Nagpur divisions, were incorporated as a part of the Bombay state.
Location of Central Provinces and Berar
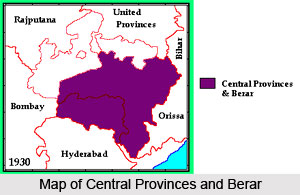
As it is suggested by the name, the Central Provinces and Berar province was located in the centre of the Indian peninsula. The region constituted vast segments of the extensive belt of hill and plateau that divided the plains of the Ganges and the Deccan plateau. The Central Provinces and Berar were bordered by the Central India Agency including the Bagelkhand agency and Bundelkhand agency on the north and northeast; by the United Provinces along the northern edge of Sagar district; by the states of Indore, Bhopal and district of Kandesh of Bombay Presidency; by the princely state of Hyderabad and the zamindari estates of the Madras Presidency in the south; and by the tributary states of Bengal in the east.
Administration of Central Provinces and Berar
The Central Provinces and Berar was formed of 22 districts, which were segmented into 5 divisions. These are mentioned below-
* The Jabalpur (Jubbulpore) Division was scattered over a total area of 18,950 sq miles and included the districts Mandla, Seoni, Damoh, Saugor (Sagar) and Jubbulpore.
* The Narmada (Nerbudda) Division covered a total area of 18,382 sq miles and comprised of the districts of Chhindwara, Betul, Nimar, Hoshangabad and Narsinghpur.
* The Nagpur Division included the districts of Balaghat, Wardha, Chanda, Bhandara and Nagpur and covered a total area of 23,521 sq miles.
* The Chhattisgarh Division covered an area of 21,240 sq miles and had the districts of Durg, Raipur and Bilaspur.
* The Berar Division included the districts of Wun, Basim, Buldhana, Ellichpur, Akola and Amravati (Amraoti).
The Central Provinces and Berar had jurisdiction over 15 princely states of India as well. These native state were the princely state of Bastar, the princely state of Kairagarh, the princely state of Udaipur, Makrai state, the princely state of Kanker, Korea state, princely state of Chang Bhakar, the princely state of Chhuikhadan, Kawardha state, the princely state of Nandgaon, princely state of Sirguja, Jashpur state, Sakti state, the princely state of Raigarh and Sarangarh state. The states of Sarangarh and Raigarh were under the control and administration of the Chhattisgarh Division.
Central Provinces and Berar after Independence
After the withdrawal of the British Government of India and the independence of the country on 15th August 1947, many erstwhile princely states of India were merged with the Central Provinces and Berar province. After the new Constitution of India went into effect in the year 1950, the previous Central Provinces formed the new Indian state of Madhya Pradesh, which comprised of Nagpur as its capital. In 1956, some of the regions of Madhya Pradesh, which included the Berar and Nagpur divisions, were included as a part of Bombay state.
In 1960, the Bombay state was reorganized, with the Gujarati speaking regions becoming Gujarat state and the Marathi speaking regions forming the state of Maharashtra. Later in the year 2000, the eastern part of the state of Madhya Pradesh was segregated in order to from the new Indian state of Chhattisgarh.
Governors of the Central Provinces and Berar
The chronology of the Governors of the Central Provinces and Berar are mentioned below-
Chief Commissioners of Nagpur Province and Saugor Nerbudda Territories
Edward King Elliot (1861- 1862)
Chief Commissioners of the Central Provinces
Edward King Elliot (1862- 1864)
Sir Richard Temple (1864- 1867)
Sir John Henry Morris (1867- 1883)
William Bence Jones (1883- 1884)
Sir Charles Haukes Todd (1884- 1885)
Dennis Fitzpatrick (1885- 1887)
Alexander Mackenzie (1887- 1889)
Sir Antony Patrick Macdonnell (1889- 1893)
Sir John Woodburn (1893- 1895)
Sir Charles James Lyall (1895- 1898)
Sir Denzil Charles Jelf Ibbetson (1898- 1899)
Sir Andrew Henderson Leith Fraser (1899- 1902)
John Prescott Hewett (1902- 1904)
Frederic Styles Philpin Ley (1904- 1905)
John Ontario Miller (1905- 1906)
Reginald Henry Craddock (1907- 1912)
Sir Benjamin Robertson (1912- 1920)
Sir Frank George Sly (1920)
Governors of the Central Provinces
Sir Frank George Sly (1920- 1925)
Sir Montagu Sherard Dawes Butler (1925- 1932)
Sir Hyde Balwant Sharma (1932- 1936)
Governors of the Central Provinces and Berar
Sir Hyde Clarendon Gowan (1936- 1938)
Hugh Bomford (1938)
Sir Francis Verner Wylie (1938- 1940)
Sir Henry Joseph Twynam (1940- 1946)
Sir Frederick Chalmers Bourne (1946- 1947)



















