Introduction
 History of India is believed to be amongst the grandest epics of the world history which dates back to ancient periods, nearly above 75, 000 years ago, which has witnessed the existence of Homo sapiens or the human race, as per historical evidence. The oldest human civilization in the country is the Indus Valley Civilization which thrived during 3300 and continued till 1300 BCE. The civilization was concentrated in the north-western portions of Indian subcontinent. The civilization with its main cities Mohenjadaro and Harappa flourished for over eight centuries. It is often said that `he who controls his past can control his future`. Hence knowledge of history is crucial for an individual`s growth.
History of India is believed to be amongst the grandest epics of the world history which dates back to ancient periods, nearly above 75, 000 years ago, which has witnessed the existence of Homo sapiens or the human race, as per historical evidence. The oldest human civilization in the country is the Indus Valley Civilization which thrived during 3300 and continued till 1300 BCE. The civilization was concentrated in the north-western portions of Indian subcontinent. The civilization with its main cities Mohenjadaro and Harappa flourished for over eight centuries. It is often said that `he who controls his past can control his future`. Hence knowledge of history is crucial for an individual`s growth.
The history of India is integrally related to the identity of the Indian diaspora and can be categorised into ancient, medieval and modern. While the ancient history deals with the gradual evolution of the civilisation, the medieval history narrates the tales of the rise of the native rulers, their administration, the rising fame of India and finally the Muslim and other foreign invasions. The history of the country is depicted in every religious texts and Hinduism relates about Indian civilisation.
Pre-Historic Period of India
The pre-historic era of the nation which existed around 7500 BC bore testimony to the Stone Age and also the Bronze Age. Over 5, 00, 000 to 2, 00, 000 years ago commenced the Stone Age. Various tools designed by humans during that time have been discovered at Tamil Nadu and north-western part of India. The Soan River Valley is the most ancient palaeolithic Site in India, followed by Mesolithic and Neolithic period which witnessed extensive human settlements 12, 000 years ago. Humans resided in Bhimbetka rock shelters, Madhya Pradesh 9, 000 years ago. Findings at Haryana (7500 BC), Mehrgarh (7000 BCE onwards which constitutes modern-day Pakistan) have revealed instances of Stone Age.
 It was a Bronze Age civilization which collapsed at the beginning of the second millennium BCE and was followed by the Iron Age Vedic period. The civilisation extended over the Indo Gangetic Plains and witnessed the rise of major kingdoms such as the `Mahajanapadas`. Sources of history of India such as coins and coinage, manuscripts and ancient texts narrate the story of creation of the country. Lead, copper, bronze and tin handicrafts were produced during this time.
It was a Bronze Age civilization which collapsed at the beginning of the second millennium BCE and was followed by the Iron Age Vedic period. The civilisation extended over the Indo Gangetic Plains and witnessed the rise of major kingdoms such as the `Mahajanapadas`. Sources of history of India such as coins and coinage, manuscripts and ancient texts narrate the story of creation of the country. Lead, copper, bronze and tin handicrafts were produced during this time.
Early Historic Period of India
During the period from 1500 to 500 BCE, the Vedic Period existed which introduced the `Indo-Aryan` culture to India that comprised Vedic texts, composed in Sanskrit language. The Vedas are probably the oldest Indian texts which contain the basic tenets of Hinduism and other faiths. Major portions of the Gangetic Plain and northern India were nerve-centres of Vedic civilization. The concept of `Mahajanapadas` developed around 600 to 300 BCE, which implies a collection of many tiny kingdoms or `city states` which grew throughout India. Kamboja, Matsya, Kosala, Magadha, Assaka, Gandhara, Panchala, Avanti, Vatsa, Vajji or Vriji, Surasena, Kuru, Anga, Chedi, Malla and Kasi were the 16 Mahajanapadas which were born by 500 BCE. The period about 520 BCE and 320 BCE saw some Persian and Greek conquests, especially when King Porus occupied a large portion of Punjab and Alexander conquered the `Achaemenid Empire`. Chandragupta Maurya established the Maurya Dynasty which lasted from 322 to 185 BCE and attained greater heights during the rule of Ashoka.
This period also consists of the `Golden Age of India`, the regime of the mighty Gupta Empire which dates from 320 to 550 CE. The country excelled in spheres of religion, philosophy, mathematics, literature, arts, astronomy, science and technology and Hindu culture. The idea of `zero` and decimal system were invented at this time and the renowned rulers were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and so on. Kalidasa, Aryabhata, Varahamihira and Vatsayana are amongst the noted scholars of the Gupta Age.
 Medieval History of India
Medieval History of India
The Delhi Sultanate rose in power during the 12th and 13th centuries, wherein the former Slave Dynasty, Delhi captured enormous areas of land in northern India and Khilji Dynasty conquered large tracts of central India. Indian literature, architecture, music, costumes, religion, etc. achieved new dimensions with the unique Indo-Islamic fusion, which brought in a cultural renaissance. In 1526, Babur firmly installed the Mughal Dynasty in India which was highly prosperous till the death of Aurangzeb in 1707. Humayun, Akbar, Jahangir, Shah Jahan and Aurangzeb were considered to be the jewels of the Mughal Empire. They fought many battles among themselves to establish power and supremacy. The lion`s share of India was controlled by the Mughals which finally crumbled in 1857.
Post-Mughal History of India
India, during the post-Mughal period was ruled by the Marathas who rose to power quickly after the Mughals by 18th century, thanks to Shivaji, the legendary Maratha ruler of the Bhonsles. From 1720 to 1760, Marathas dominated and Prime Ministers called `Peshwas` controlled the reigns of the Maratha Empire. However, 1820 saw the decline of the Marathas as they were defeated by the British in three Anglo-Maratha Wars. North-western portions of the nation were reigned by the Sikhs who belonged to Khalsa faith, led by Maharaja Ranjit Singh. The Punjabi Kingdom thrived from 1799 till 1849, extending from Khybar Pass, Kashmir in the north till Sindh in south, and Himachal to the east. Their downfall followed after the first and second Anglo-Sikh War.
Modern History of India
 Indo-European trade commenced in India following the discovery a sea route to the nation by Vasco da Gama in 1498. Portuguese, British and Dutch arrived and the Jahangir permitted British East India Company to carry out commercial activities here. Modern History of India is all about the British rule which lasted till 1947 from 1848, particularly after the Sepoy Mutiny in 1857. They tyrannized the entire country with their supremacy. Various thinkers, poet and reformists appeared at the moment to introduce a mass awakening programme against oppression by the British.
Indo-European trade commenced in India following the discovery a sea route to the nation by Vasco da Gama in 1498. Portuguese, British and Dutch arrived and the Jahangir permitted British East India Company to carry out commercial activities here. Modern History of India is all about the British rule which lasted till 1947 from 1848, particularly after the Sepoy Mutiny in 1857. They tyrannized the entire country with their supremacy. Various thinkers, poet and reformists appeared at the moment to introduce a mass awakening programme against oppression by the British.
A saga of political, social and cultural upheavals led to the Indian independence movement. The history of India is steeped in courageous tales of Indian freedom fighters. Personalities like Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, Mangal Pandey, Jatindranath Mukherjee, Subash Chandra Bose, Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Mahatma Gandhi and several others sacrificed everything to unchain their motherland from the barriers of colonisation. This long battle finally came to a halt with India achieving its independence on 15th August, 1947. However the independence left its indelible marks with the partition of India and the assassination of Mahatma Gandhi. Yet India moved on to establish itself as one of the most successful democracies in the world where an assortment of religions, cultures amalgamate, thus epitomizing unity in diversity.
Sources of History of India
 Sources of history of India are significant tools for tracing the lifestyle and culture of India since ages. India has a rich and colourful history and it is a treasure trove of earliest chronicle. Different parts of the subcontinent have different histories and legends. Historians discover the historical aspects of various regions of the country through diverse sources. Indian history has a past of over thousands of years. The history of India is evident in several forms. Sources of history of India are the evidences that relate the origin of earliest civilisations, their culture and their beliefs. Sources are important to trace the ancient records. These are vital for the historians as they get their information about what happened in the past. The sources belong to two types, both written and non-written and throw light to the relevance of the historical facts. These sources comprise of coins and coinages, manuscripts, texts and the archaeological survey.
Sources of history of India are significant tools for tracing the lifestyle and culture of India since ages. India has a rich and colourful history and it is a treasure trove of earliest chronicle. Different parts of the subcontinent have different histories and legends. Historians discover the historical aspects of various regions of the country through diverse sources. Indian history has a past of over thousands of years. The history of India is evident in several forms. Sources of history of India are the evidences that relate the origin of earliest civilisations, their culture and their beliefs. Sources are important to trace the ancient records. These are vital for the historians as they get their information about what happened in the past. The sources belong to two types, both written and non-written and throw light to the relevance of the historical facts. These sources comprise of coins and coinages, manuscripts, texts and the archaeological survey.
Indian Coins and Coinage
Indian coins and coinage is the one of the best sources of history of India. Coins provide information on the condition of country. Several coins are available that confirm the origin of earliest civilisation, kings and kingdoms. The coins of ancient times are made of gold, silver and copper and speak of the economic situation of that place in the period. Coins are essential that provide chronological information. These coins and coinage are the only source to provide idea of the Bactarian, Indo-Greeks and Indo-Parthian dynasty and the relation of the Roman Empire with the Indians. In addition to that coins also provide information on the coin artistry of India, various portraits and figures engraved on them and about the Hellenistic art. Dates, royal portraits and names of kings were usually engraved on the coins which help in understanding the era of different rulers and illuminate the hidden corners of Indian history. Dates and intrinsic value of coins narrate the evolution of the country`s economy. Religious and cultural condition of different eras can be deciphered by the type and shape of coins. Coins of Gupta dynasty have been discovered in large number and many of them were made of gold which showcases the Roman influence on India. During the period of Chandragupta II, Chaitya coins were the evidence of the relation with Sakas.
Indian Manuscripts
Among the copious sources of history of India, Indian manuscripts play a vital role and help in locating the earliest history of a place. The manuscripts are rich sources of written evidences. A manuscript is a document that is written by hand and offers information that is hand-recorded in other ways than writing. These constitute a variety of themes including textures and aesthetics, languages, scripts, calligraphies, illuminations and illustrations. These are written on metal, bark, palm leaf, cloth etc. Majority of these were written in Sanskrit language which forms the most versatile and rich source of history of India.

Ancient Texts of India
Ancient texts also provide abundant information about the ancient rulers, their supremacy and their reign. They also provide an idea about the lifestyle of ancient era. The four Vedas- Rig Veda, Sama Veda, Yajur Veda and Atharva Veda belong to the ancient Indian texts. Other ancient texts comprise of the Brahmanas, the Aryankas, the Upanishads, the Epics Ramayana and Mahabharata, the Brahmashastras and the Puranas.
Archaeology of India
Archaeology of India is the scientific study of the remains of the past. This study is considered to be essential among the sources of history of India. It is the study of buildings, monuments and other material relics. Excavations are conducted at various sites in the country to collect facts about the past details of the country. For instance the archaeological survey at Taxila gives an idea about the Kushanas. The rock cut temples of Ajanta and Ellora and its sculptures and paintings are archaeological sources. The Archaeological Survey of India is the premier organization for the archaeological researches and protection of the cultural heritage of the nation. It forms one of the significant sources of history of India. The survey looks after the maintenance of ancient monuments and archaeological sites and remains of the country. The organization has a large work force of trained archaeologists, conservators, epigraphist, architects and scientists for conducting archaeological research projects throughout the country.
Foreign Accounts
Foreign travellers have also contributed a lot in forming important sources of history of India. Various information have been recorded by classical and Greek writers, right from the 6th Century when the Persians invaded the country. Persian domination of north western India has been recorded by Ctesias and Herodotus. Records of historians such as Onesicritus and Nearchus throw light on the Alexander`s invasion of north western India. `Indika` is a renowned book written by Megasthenes that narrates the social and political scenario of the country during the era of Chandragupta Maurya. Other well known works includes the book "Geography" written by Ptolemy and "Natural History" written by Pliny. An account of ports and harbours of ancient India can be found in "Periplus of the Erythraean Sea". With the spread of Buddhism in China, amicable relations developed between India and China. Many Chinese pilgrims and travellers have also left invaluable historical records which depicts the history of India. In 8th century, a number of Arabian scholars also visited India who have left several accounts on India.
Medieval History of India
 Medieval history of India comprises of reigns and influences of a number of dynasties which ruled over the country in ancient past. Various kingdoms in India have left a deep impact on different aspects of the country including art, literature, architecture, administration and many more. The country was ruled by several empires at a time and medieval history of India also narrates the numerous battles that were fought between different dynasties for the expansion of their own kingdom.
Medieval history of India comprises of reigns and influences of a number of dynasties which ruled over the country in ancient past. Various kingdoms in India have left a deep impact on different aspects of the country including art, literature, architecture, administration and many more. The country was ruled by several empires at a time and medieval history of India also narrates the numerous battles that were fought between different dynasties for the expansion of their own kingdom.
Chola Dynasty
Chola dynasty ruled over India for a long period of time. The origin of this dynasty in India can be traced back to 3rd century BC and it continued to 13th century AD. Their major concentration was found in the valley of Kaveri River, but their kingdom gradually spread over larger areas. The dynasty left a deep impact on the evolution and development of Tamil literature. During this era, the whole of south India was under a single administration. Art, culture and foreign trade were highly developed during this period.
Hoysala Empire
After Chola dynasty, Hoysala Empire gained prominence during the period of 10th to 14th century. The rulers of this dynasty mainly belonged to Malnad, Karnataka. They took advantage of the war between Western Chalukyas and Kalachuri kingdoms and captured some of the areas of Kaveri river delta and greater parts of present day Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh. Religion, art and architecture flourished greatly during this period and temple architecture of this era are still greatly praised.

Kakatiya Dynasty
Kakatiya dynasty is another prominent dynasty which ruled between the periods of 1083 CE to 1323 CE. The rulers of this empire were originally Jains but later emerged as Shaivite Hindu. The reign of this empire lasted for a long time up to the advent of Delhi Sultanate. The notable rulers of this dynasty were Rudrama Devi and Prataparudra. Their empire spanned up to the western India. Numerous administrative reforms were introduced during this period. The decline of Kakatiya dynasty occurred with the conquest of south India by Alauddin Khilji in 1296 CE.
Rajput Kingdoms
Rajputs dominated the northern parts of India from 9th to 11th centuries. They became the primary hindrance to the Mughals in their conquest of India. Rajputs maintained their power in the regions of Rajasthan and central India even after their northern territory was captured by the Muslim invaders.
Delhi Sultanate
The golden period of medieval history began with the Turkish conquests led by Mahmud of Ghazni. Following his footsteps, Muhammad Ghori carried on the invasions in the soils of Indian Territory. At the battle of Tarain, he overpowered Prithviraj Chauhan, the Tomar ruler of Delhi, in the year 1192. After victory in the war, he left India and his deputy, Qutub-ud-din Aibak, reigned from 1206 A.D to 1210 AD. As he belonged to a family of slaves, the dynasty that he built is popular as the Slave dynasty. It was him who built the towering Qutub Minar in Delhi. His successor Iltutmish carried forward the legacy during his rule starting from 1210 to 1236 AD.

The lineage of Indian kings after Razziya, namely, Khiljis, Tughlaqs, Sayyids and Lodhis valiantly adopted the footsteps of the Slave rulers. This period is known as the Delhi Sultanate. They were popular in the medieval history for their valour and statesmanship. Allauddin Khilji ruled from 1296 to 1316. Another eminent ruler of medieval history of India was Muhammad bin Tughlaq. His tenure began from 1324 and ended on 1351. He was a visionary and was endowed with a keen intellect, proficient in various branches of learning like logic, philosophy and mathematics. Feroz Shah Tughlaq too was an important ruler of the medieval history.
Sayyid Dynasty
The next Indian dynasty that illuminated the medieval history of India is the rulers of Sayyid dynasty. Khizr Khan founded the Saiyyid Empire. The Sayyids reigned from about 1414 AD to 1450 AD. In 1412 AD, they conquered Gujarat, Gwalior and Jaunpur. In 1416, he defeated Bayana and in 1421AD he attacked Mewat. After his death few rulers reigned for quite some time. The empire came to an end in 1451 AD with the death of the last ruler Muhammad-bin-Farid.
Lodhi Dynasty
Behlol Lodhi founded the Lodhi dynasty and thus started a new era of the medieval history of India. After coming to the throne in 1451 AD he appeased the rebelling nobles and Jagirdars. He gave jagirs to the Afghan nobles to win their cooperation and brought Mewar, Sambal and Gwalior under his rule. Bahlul Lodhi nominated his son Nizam Khan as his successor. But the nobles placed Barbak Shah on the throne. Barbak Shah was appointed as the governor of Jaunpur. He brought Gwalior and Bihar under his rule. Though he was a religious fanatic yet he brought changes in some of the practices of the Muslims. He encouraged education and trade. His military skill helped him in bringing the Afghan nobles under his control.
Sikandar Lodi defeated Barbak Shah who in co-operation with Hussain Shah of Jaunpur fought against him. Ibrahim Lodi who is said to have been the last great ruler of the Lodhi dynasty succeeded Sikandar Lodi. He came to the power in 1517 AD. His relations with the Afghan nobles became worse and this led to several conflicts with him. The discontented Afghan chiefs sent Daulal Khan Lodhi to invite Babur the king of Kabul to India. In the year 1525 and1526 Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi in the battle of Panipat. With this defeat, Delhi Sultanate was laid to rest.

Mughal Dynasty
Medieval history of India got a new shape and dynamism with the coming of Babur. This was the beginning of the new era of Mughal rulers. Babur who reigned from 1526-30 was the founder of the Mughal Empire in India. There was a brief interruption to Mughal rule when Babur`s son Humayun (reign - 1530-40) was ousted from Delhi, by Sher Shah, an Afghan chieftain. The credit goes to the grandson of Babur for extending the Mughal rule by leaps and bounds. In medieval history of India he was the most significant ruler for his achievements as well as his good administration.
Jahangir (reign - 1605-27) who succeeded Akbar was a pleasure loving man of refined taste. Shah Jahan (1628-58), his son, ascended the throne next. Shah Jahan`s fame rests on the majestic buildings he has left behind viz. the Taj Mahal, the Red Fort and the Jama Masjid. His successor, Aurangzeb (reign - 1658-1707) was a brave general and an able administrator. However his staunch policies of expanding the empire brought about the fall of the Mughal Empire.
Ahom Kingdom
Ahom kingdom was another kingdom of medieval India which ruled over the Brahmaputra valley in Assam for about 600 years and resisted the invasion of Mughals in the north east India. It was established in 1228 by Chao Lung Siu-Ka-Pha, the first Ahom King. The expansion of the kingdom was quite rapid and influences of numerous regions led to a multi ethnic kingdom. Repeated Mughal attacks could not weaken the kingdom, instead the battles resulted in expanding their boundaries up to the Manas River in the west. When the kingdom went over to its last kings, the Tungkhungia kings, social conflicts became prominent in the kingdom. Repeated Burmese attacks further weakened the kingdom and finally they surrendered themselves to the British India.
Reddy Dynasty
Reddy dynasty ruled over southern India since 1325 to 1448 CE. The origin of this clan dates back to Kakatiya period when the Reddy chiefs were appointed as soldiers. This clan fought hard against the invasion of Delhi Sultanate and after the decline of Kakatiya kingdom, established their independent kingdom. Telugu literature blossomed during this period. Important rulers of this kingdom were Anavota Reddy, Anavema Reddy, Kumaragiri Reddy, Kataya Vema Reddy, Pedakomati Vemareddy, Racha Vema Reddy, Gondesi Reddy and Veerabhadra Reddy. Their reign continued up to the middle of 15th century till it came under the rule of Vijayanagar Empire.
Vijayanagar Empire
Vijayanagar Empire also dominated south India. It emerged at the end of 13th century and lasted till 1646 AD. The rich cultural legacy of the kingdom can be witnessed in the plethora of monuments spread all over the country as the testaments of brilliant architecture. Hinduism was greatly promoted during this era. The decline of this empire was brought about by the Deccan Sultanates.
Gajapati Empire
Gajapatis spanned their kingdom over the Kalinga, which is the present day Orissa, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar and Madhya Pradesh during the period of 1434-1541AD. Purushottama Deva, Prataparudra Deva and Kakharua Deva were some of the significant rulers of the dynasty. Literature and architecture during Gajapati Kingdom attained great heights.
Sikh Empire
Sikh Empire gained power in India under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, around Punjab. It established from 1799, the time when the decline of Mughal Empire began. The downfall of Sikh Empire occurred after their defeat in Anglo-Sikh wars by 1849.
Medieval history of India is marked by the heritage of efficient rulers, thereby contributing to the country`s richness of heritage and ethnicity. This can still be witnessed in the monuments, ancient texts and different art forms that are still existent in the country.
Geological History of India
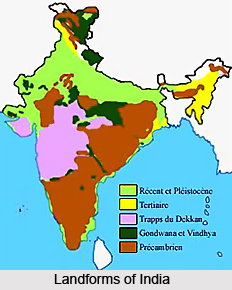 Geological history of India started with the geological evolution of rest of the Earth i.e. 4.57 billion years ago. India has a diverse geology. Different regions in India feature rocks of all types belonging to different geologic periods.
Geological history of India started with the geological evolution of rest of the Earth i.e. 4.57 billion years ago. India has a diverse geology. Different regions in India feature rocks of all types belonging to different geologic periods.
Some of the rocks in India that are quite significant geologically are deformed and transmuted while others are recently deposited alluvium that have yet to undergo diagnosis. Mineral deposits of high variety are found in the subcontinent in huge quantity. Even the fossil records are impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India`s geographical land area is classified into Deccan Trap, Gondwana and Vindhyan.
Deccan Trap is one of the most vital geological patches of India. Firstly, the Deccan Trap covers almost all of Maharashtra, a part of Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh marginally. It is believed that the Deccan Trap was formed as result of sub-aerial volcanic activity associated with the continental deviation in this part of the Earth during the Mesozoic era. That is why the rocks found in this region are generally igneous type. During the northward movements of the geological blocks after breaking off from the rest of Gondwana, the Indian Plate passed over a geologic hotspot, the Réunion hotspot, which caused widespread melting below the Indian craton. The melting broke through the surface of the craton in a massive flood basalt event, creating what is known as the Deccan Traps. It is also thought that the Reunion hotspot has resulted in the separation of Madagascar and India.

The Gondwana and Vindhyan region include within its fold parts of the present states like Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttaranchal. The Gondwana Supergroup forms a unique sequence of fluviatile rocks deposited in Permo-Carboniferous time. Damodar and Son river valley and Rajmahal hills in the eastern India is depository of the Gondwana rocks. The geological society of India has immense research works on the geological history of India. This society was established on 28th May, 1958, to promote the cause of advanced studies and research in all branches of Earth Systems Science. The Journal of the society is the flagship publication, which publishes peer-reviewed articles under the category of Review Papers, Research Papers, Notes, Short Communications, Corporate News, Correspondence and book reviews. The Society also brings out Memoirs, Articles, Field-Guides and other important publications that are important documentation associated with Indian geology.



















