About Western Chalukya Dynasty
The Western Chalukya Empire lined most of the western deccan, South India, amid the 10th and 12th centuries. This empire is occasionally referred to as the Kalyani Chalukya subsequent to its imperial capital at Kalyani, presently known Basavakalyan in Karnataka and alternatively the Later Chalukya cropping from its hypothetical association to the sixth century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called Western Chalukyas in order to distinguish from the contemporary Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty.
Preceding the rise of the Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta empire of Manyakheta proscribed majority of deccan and central India for over two centuries. In 973, observing the perplexity in the Rashtrakuta territory following a triumphant incursion of their capital by the Paramara of Malwa, Tailapa II a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta ruling from Bijapur region overpowered his overlords and made Manyakheta his capital. The dynasty speedily rose to power and grew into an empire under Somesvara I who moved the capital to Kalyani.
For over a century, the two empires of southern India, the Western Chalukyas and the Chola dynasty of Tanjore fought many fierce wars to control the fertile region of Vengi. During these conflicts, the Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, distant cousins of the Western Chalukyas but related to the Cholas by marraige took sides with the Cholas further complicating the situation. Its was only during the rule of Vikramaditya VI in the late eleventh century that the Western Chalukya empire convincingly eclipsed the Cholas and reached its peak with territories fanning out to majority of the deccan. Immense areas amid the Narmada River in the north and Kaveri River in the south came under Chalukya control. During this period the other major ruling families of the Deccan, the Hoysalas, the Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri, the Kakatiya dynasty and the Southern Kalachuri, were subordinates of the Western Chalukyas and gained their independence only when the power of the Chalukya waned during the later half of the twelfth century.
The Western Chalukyas developed an architectural style presently known as a intermediary style, an architectural link between the style of the early Chalukya dynasty and that of the later Hoysala Empire. Most of its monuments are in the districts bordering the Tungabhadra River in central Karnataka. Eminent instances are the Kasi Vishveshvara Temple at Lakkundi, the Mallikarjuna Temple at Kuruvatii, the Kalleshwara Temple at Bagali and the Mahadeva Temple at Itagi. This was an important period in the development of fine arts in Southern India, especially in literature as the Western Chalukya kings encouraged writers in the native language of Kannada and Sanskrit.
History of Western Chalukya Dynasty
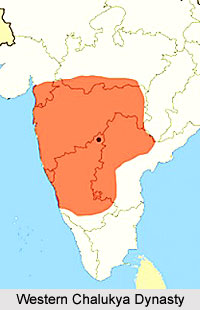 Comprehension of the Western Chalukyas history has approached through assessment of the abundant excavated Kannada language inscriptions left by the kings and from the study of important contemporary literary documents in Western Chalukya literature such as Gada Yuddha (982) in Kannada by Ranna and Vikramankadeva Charitam (1120) in Sanskrit by Bilhana. The initial writing is dated 957, during the rule of Tailapa II when the Western Chalukyas were still a feudatory of the Rashtrakutas and Tailapa II governed from Tardavadi in present day Bijapur district, Karnataka. The descent of the kings of the realm is still disputed.
Comprehension of the Western Chalukyas history has approached through assessment of the abundant excavated Kannada language inscriptions left by the kings and from the study of important contemporary literary documents in Western Chalukya literature such as Gada Yuddha (982) in Kannada by Ranna and Vikramankadeva Charitam (1120) in Sanskrit by Bilhana. The initial writing is dated 957, during the rule of Tailapa II when the Western Chalukyas were still a feudatory of the Rashtrakutas and Tailapa II governed from Tardavadi in present day Bijapur district, Karnataka. The descent of the kings of the realm is still disputed.
One theory, based on contemporary literary and inscriptional substantiation as well as the discovery that the Western Chalukyas employed titles and names commonly used by the early Chalukyas, suggests that the Western Chalukya kings belonged to the same family line as the well-known Badami Chalukya dynasty of sixth century while other Western Chalukya inscriptional evidence indicates they were a distinct line unrelated to the early Chalukyas.
Tailapa II re-established Chalukya rule and overpowered the Rashtrakutas during the supremacy of Karka II by timing his insurgence to correspond with the bewilderment rooted in the Rashtrakuta capital of Manyakheta by the invading Paramaras of Central India in 973. After overpowering the Rashtrakutas, Tailapa II moved his capital to Manyakheta and consolidated the Chalukya Empire in the western deccan by subjugating the Paramara and other aggressive rivals and extending his control over the land between the Narmada River and Tungabhadra River.
The severe competition among the kingdoms of the western deccan and those of the Tamil kingdoms came to the fore in the eleventh century over the acutely contested fertile river valleys in the doab region of the Krishna and Godavari River called Vengi (coastal Andhra Pradesh). The Western Chalukyas and the Chola Dynasty fought many bitter wars over control of this strategic resource. The imperial Cholas gained power during the time of the famous king Rajaraja Chola I and the crown prince Rajendra Chola I.
The Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi were cousins of the Western Chalukyas but were increasingly predisposed by the Cholas through their marital ties with the Tamil kingdom. As this was in opposition to the interests of the Western Chalukyas, they wasted no time in involving themselves politically and militarily in Vengi. When King Satyasraya succeeded Tailapa II to the throne, he was able to protect his kingdom from Chola aggression as well as his northern territories in Konkan and Gujarat although his control over Vengi was shaky. His descendant, Jayasimha II, fought several battles with the Cholas in the south while both powerful kingdoms struggled to choose the Vengi king. Concurrently, Jayasimha II restrained the Paramara of central India.
Jayasimha`s son, Somesvara I, moved the Chalukya capital to Kalyani in 1042 as hostilities with the Cholas continued and while both sides won and lost battles, neither lost significant territory during the enduring politics of installing a puppet on the Vengi throne. In 1068 Somesvara I, anguish from a fatal illness, drowned himself in the Tungabhadra River (Paramayoga). Regardless of countless divergences with the Cholas, Somesvara I managed to maintain control over the northern territories in Konkan, Gujarat, Malwa and Kalinga during his rule. His successor, his eldest son Somesvara II, feuded with his younger brother, Vikramaditya VI, an ambitious warrior the initial governor of Gangavadi in the southern deccan when Somesvara II was the king. Married to a Chola princess (a daughter of Virarajendra Chola), Vikramaditya VI maintained a friendly alliance with them.
After the death of the Chola king in 1070, Vikramaditya VI invaded the Tamil kingdom and installed his brother-in-law, Adhirajendra, on the throne creating conflict with Kulothunga Chola I, the powerful ruler of Vengi who sought the Chola throne for himself. At the same time Vikramaditya VI undermined his brother, Somesvara II, by winning the loyalty of the Chalukya feudatories: the Hoysala, the Seuna and the Kadambas of Hanagal. Anticipating a civil war, Somesvara II sought help from Vikramaditya VI`s enemies, Kulothunga Chola I and the Kadambas of Goa. In the ensuing conflict of 1076, Vikramaditya VI emerged triumphant and proclaimed himself king of the Chalukya empire.
The fifty-year reign of Vikramaditya VI, the most successful of the later Chalukya rulers, was an important period in Karnataka`s history and is referred to by historians as the "Chalukya Vikrama era".
Not only was he successful in controlling his powerful feudatories in the north and south, he successfully dealt with the imperial Cholas whom he defeated in the battle of Vengi in 1093 and again in 1118. He preserved this province for several years regardless of enduring skirmishes with the Cholas. This victory in Vengi reduced the Chola influence in the eastern deccan and made him emperor of territories stretching from the Kaveri River in the south to the Narmada River in the north, earning him the titles Permadideva and Tribhuvanamalla (lord of three worlds). The scholars of his time paid him shimmering tributes for his military leadership, interest in fine arts and religious tolerance. Literature proliferated and scholars in Kannada and Sanskrit adorned his court. Poet Bilhana, who immigrated from far away Kashmir, eulogized the king in his eminent work Vikramankadeva Charitam.
Vikramaditya VI was not only an able warrior but also a devout king as indicated by his numerous inscriptions that record grants made to scholars and centers of religion. The frequent militaristic with the Cholas fatigued both empires, offering their subsidiaries the prospect to insurgent. In the decades after Vikramaditya VI`s death in 1126, the empire steadily decreased in size as their powerful feudatories expanded in autonomy and territorial command. The time period between 1150 and 1200 saw many hard fought battles between the Chalukyas and their feudatories who were also at war with each other. By the time of Jagadhekamalla II, the Chalukyas had lost control of Vengi and his heir, Tailapa III, was overpowered by Kakatiya Prola in 1149. Tailapa III was taken captive and later unconstrained pulling down the stature of the Western Chalukyas.
Seeing decadence and uncertainty seeping into Chalukya rule, the Hoysalas and Seunas also impinged upon the empire. Hoysala Narasimha I defeated and killed Tailapa III but was unable to overcome the Kalachuris who were vying for control of the same region. In 1157 the Kalachuris under Bijjala II captured Kalyani and occupied it for the next twenty years, coercing the Chalukyas to shift their capital to Annigeri in the present day Dharwad district.
The Kalachuris were initially immigrants into the southern deccan from central India and called themselves Kalanjarapuravaradhisavaras. Bijjala II and his ancestors had governed as Chalukya commanders (Mahamandaleshwar) over the Karhad-4000 and Tardavadi-1000 provinces (overlapping region in present day Karnataka and Maharashtra) with Mangalavada as their capital. Bijjala II`s Chikkalagi record of 1157 calls him Mahabhujabala Chakravarti (emperor with powerful shoulders and arms) indicating he no longer was a subordinate of the Chalukyas. Nevertheless the heirs of Bijjala II were incapable of holding on to Kalyani and their decree ended in 1183 when the last Chalukya shoot, Somesvara IVmade a final bid to recuperate the realm by recapturing Kalyani.
Chalukya general Narasimha in this conflict killed Kalachuri King Sankama. During this time, Hoysala Veera Ballala II was mounting ruthless and clashed on numerous occasions with the Chalukyas and the other claimants over their empire. He defeated Chalukya Somesvara IV and Seuna Bhillama V fetching huge sections in the Krishna River valley under the Hoysala domains, but was ineffective against Kalachuris. The Seunas under Bhillama V were on an imperialistic expansion too when the Chalukyas regained Kalyani. Their ambitions were temporarily stemmed by their defeat against Chalukya general Barma in 1183 but they later had their vengeance in 1189.
The in general endeavor by Somesvara IV to rebuild the Chalukya Empire failed and the Seuna rulers who drove Somesvara IV into exile in 1189 ended the dynasty. After the fall of the Chalukyas, the Seunas and Hoysalas continued warring over the Krishna River region, each inflicting a defeat on the other at various points in time. This period saw the fall of two great empires, the Chalukyas of the western Deccan and the Cholas of Tamilakam. On the ruins of these two empires were built the Kingdoms of their feudatories whose communal antagonisms crammed the annals of Deccan history for over a hundred years, the Pandyas taking control over some regions of the erstwhile Chola Empire.
Society in Western Chalukya Dynasty
The ascend of Veerashaivaism was revolutionary and challenged the prevailing Hindu caste system which retained imperial support. The social role of women principally depended on their monetary status and level of education in this comparatively liberal period. Records depict the involvement of women in the fine arts, such as Chalukya queen Chandala Devi`s and Kalachuri queen Sovala Devi`s skill in dance and music. The compositions of thirty Vachana women poets included the work of the 12th century Virashaiva mystic Akka Mahadevi whose devotion to the bhakti movement is well known.
Contemporary records signify certain majestic women were involved in administrative and martial affairs such as princess Akkadevi, (sister of King Jayasimha II) who fought and defeated rebellious feudals. Inscriptions emphasise public acceptance of widowhood indicating that Sati (a custom in which a dead man`s widow used to immolate herself on her husband`s funeral pyre) though present was on a voluntary basis. Ritual deaths to attain salvation were seen among the Jains who preferred to fast to death (Sallekhana), while people of some other communities chose to jump on spikes (Shoolabrahma) or walking into fire on an eclipse.
In a Hindu caste system that was conspicuously present, These Brahmins were normally involved in careers that revolved around religion and learning with the exception of a few who achieved success in martial affairs. They were patronised by kings, nobles and wealthy aristocrats who persuaded learned Brahmins to settle in specific towns and villages by making them grants of land and houses. The relocation of Brahmin scholars was calculated to be in the interest of the kingdom as they were viewed as persons detached from wealth and power and their knowledge was a functional instrument in order to edify and tutor moral conduct and discipline in local communities. Brahmins were also actively involved in solving local problems by functioning as neutral arbiters (Panchayat).
Regarding eating habits, Brahmins, Jains, Buddhists and Shaivas were strictly vegetarian while the partaking of different kinds of meat was popular among other communities. Marketplace vendors sold meat from domesticated animals such as goats, sheep, pigs and fowl as well as exotic meat including partridge, hare, wild fowl and boar. People found indoor amusement by attending wrestling matches (Kusti) or watching animals fight such as cockfights and ram fights or by gambling. Horse racing was a popular outdoors past time. In addition to these leisurely activities, festivals and fairs were frequent and entertainment by traveling troupes of acrobats, dancers, dramatists and musicians was often provided.
Schools and hospitals are mentioned in records and these were constructed in the vicinity of temples. Marketplaces served as al fresco town halls where people gathered to discuss and ponder local issues. Choirs, whose main function was to sing devotional hymns, were maintained at temple expense. Young men were trained to sing in choirs in schools attached to monasteries such as Hindu Matha, Jain Palli and Buddhist Vihara. These institutions provided advanced education in religion and ethics and were well equipped with libraries (Saraswati Bhandara). Learning was imparted in the local language and in Sanskrit. Schools of higher learning were called Brahmapuri (or Ghatika or Agrahara). Teaching Sanskrit was a near monopoly of Brahmins who received royal endowments for their cause. Inscriptions record that the number of subjects taught varied from four to eighteen.
The four most popular subjects with royal students were Economics (Vartta), Political Science (Dandaniti), Veda (trayi) and Philosophy (Anvikshiki), subjects that are mentioned as early as Kautilyas Arthasastra. Additional subjects (Vidya) were the four Vedas, and six auxiliary subjects (Angas) namely Phonetics, Prosody, Grammar, Etymology, Astronomy and Ritual (Purana), Logic (Tarka), Exegesis (Mimamsa) and Law (Dharmasastra). To this were added Medicine (Ayurveda), Archery (Dhanurveda), Music (Gandharvaveda) and Politics (Arthasastra) to complete what seems to be a comprehensive list of subjects. Well known centers of learning (from a present day geographical perspective) were at Bagevadi, Kadalevad and Manigavalli in Bijapur district, Nargund and Hottur in Dharwad district, Balligavi in Shimoga district, and Nagayi in Gulbarga district.
Religion in Western Chalukya Dynasty
The fall of the Rashtrakuta Empire to the Western Chalukyas in the tenth century, corresponding with the overpower of the Western Ganga Dynasty by the Cholas in Gangavadi, was a retard to Jainism. The growth of Virashaivism in the Chalukya territory and Vaishnava Hinduism in the Hoysala region paralleled a general decreased interest in Jainism, although the succeeding kingdoms continued to be religiously tolerant. Two locations of Jain worship in the Hoysala territory continued to be patronaged, Shravanabelagola and Kambadahalli. The decline of Buddhism in South India had begun in the 8th century with the spread of Adi Shankara`s Advaita philosophy. The solitary places of Buddhist worship that remained during the Western Chalukya rule were at Dambal and Balligavi. There is no mention of religious conflict in the writings and inscriptions of the time, which propose the religious evolution was smooth.
Although the foundation of the Virashaiva conviction has been debated, the movement developed through its alliance with Basavanna in the twelfth century. Basavanna and other Virashaiva saints preached a faith without a caste system. In his Vachanas (a form of poetry), Basavanna appealed to the masses in simple Kannada and wrote, "work is worship" (Kayakave Kailasa). Also known as the Lingayats (worshipers of the Linga, the universal symbol of Shiva), these Virashaivas questioned several of the recognized norms of civilization such as the belief in rituals and the theory of rebirth and supported the remarriage of widows and the marriage of unwed older women. This gave more social freedom to women but they were not accepted into the priesthood.
Ramanujacharya, the head of the Vaishnava monastery in Srirangam, traveled to the Hoysala territory and preached the way of devotion (bhakti marga). Later he inscribed Sribhashya, a commentary on Badarayana Brahmasutra, a critique on the Advaita attitude of Adi Shankara. Ramanujacharya`s stay in Melkote resulted in the Hoysala King Vishnuvardhana converting to Vaishnavism, a faith that his successors also followed.
The impact of these religious developments on the culture, literature, and architecture in South India was profound. Significant works of metaphysics and poetry based on the teachings of these philosophers were written over the next centuries. Akka Mahadevi, Allama Prabhu, and a host of Basavanna`s followers, including Chenna Basava, Prabhudeva, Siddharama, and Kondaguli Kesiraja wrote hundreds of poems called Vachanas in praise of Lord Shiva.
The esteemed scholars in the Hoysala court, Harihara and Raghavanka, were Virashaivas. This tradition continued into the Vijayanagar Empire with such eminent scholars as Singiraja, Mallanarya, Lakkana Dandesa and other prolific writers of Virashaiva literature. The Saluva, Tuluva and Aravidu dynasties of the Vijayanagar Empire were followers of Vaishnavism and a Vaishnava temple with an image of Ramanujacharya exists today in the Vitthalapura area of Vijayanagara. Scholars in the succeeding Mysore Kingdom wrote Vaishnavite works supporting the teachings of Ramanujacharya. King Vishnuvardhana constructed several shrines following his conversion from Jainism to Vaishnavism including the famous Chennakesava Temple at Belur.
Language in Western Chalukya Dynasty
Amongst the three reigning Chalukya dynasties in India, the Western Chalukya Dynasty was also named as `Chalukyas of Kalyani` (after its majestic capital at Kalyani, present-day Basavakalyan in Karnataka) or `Later Chalukyas` (from its conjectural relationship to the sixth century Chalukya dynasty of Badami). The Western Chalukya Empire had ruled most of the western Deccan, South India within the 10th and 12th centuries. The dynasty is denominated as the Western Chalukyas to severalise from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Known to have served as patronages to literary figures and boosted evolvement of literature and language, language in western Chalukya dynasty was exceedingly rich and prosperous.
The Western Chalukyan epoch was a time of considerable literary activity in Kannada and Sanskrit. The exercise of these local languages like Kannada and Sanskrit were all-pervasive in the Western Chalukya administration. Further inscriptions in Kannada are accredited to Vikramaditya VI than any other king prior to the twelfth century, many of which have been deciphered and translated by historians of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). Inscriptions were commonly embossed on either stone (Shilashasana) or copper plates (Tamarashasana). This phase witnessed the inexhaustible growth of the provincial language into a literary and poetic medium, a tendency encouraged by former empires: the Kadambas, Chalukyas of Badami and Rashtrakutas. Language in western Chalukya dynasty had just begun to spread its wing to fly high into the domain of literary excellence and wonder.
During the most prolific age of Kannada literature, Jain scholars had penned about the life of Tirthankaras and Virashaiva poets, who articulated their intimacy with God through succinct and concise poems called Vachanas. More than two hundred contemporary Vachanakaras (Vachana poets), including thirty women poets have been registered. Language during western Chalukya dynasty with the aid of Kannada writers demonstrated literature at its most sublime, assimilating even epic performances. Early works by Brahmin writers were based upon the epics Ramayana, Mahabharata, Bhagavata, Puranas and Vedas. In the sphere of secular literature, subjects such as romance, erotics, medicine, lexicon, astrology, encyclopedia etc., were being penned for the first time in India. Most noteworthy among Kannada scholars were Ranna, grammarian Nagavarma II and Virashaiva saint Basavanna. Ranna who was patronised by king Tailapa II and Satyasraya from the western Chalukyas, is considered one amongst the "three gems of Kannada literature". He was bequeathed with the title "Emperor among poets" (Kavi Chakravathi) by King Tailapa II and possesses five major works to his acknowledgment. Of these, Saahasabheema Vijayam (or Gada yuddha) of 982 in Champu flair, is a panegyric of his patron King Satyasraya. The king is compared to Bhima in valiancy and achievements, with Ranna narrating the duel between Bhima and Duryodhana utilising clubs on the eighteenth day of the Mahabharata war. Ranna also had scripted Ajitha purana in 993, delineating the life of the second Tirthankara, Ajitanatha.
Language during Western Chalukyan dynasty was incessantly climbing lofty positions with Kannada literature spreading across seven seas. Nagavarma II, poet laureate (Katakacharya) of King Jagadhekamalla II, made contributions to Kannada literature in various subjects during the western Chalukyas. His works in poetry, prosody, grammar and vocabulary are regarded as standard authorities and their magnitude to the study of Kannada language is well acknowledged to this date. Nagavarma II`s comprehensive contributions to ancient language include Kavyavalokana in poetics, Karnataka-Bhashabhushana on grammar and Vastukosa a lexicon (with Kannada equivalents for Sanskrit words). A unique and native form of poetic literature in Kannada called Vachanas had developed during the time of the rise of language during Western Chalukyan dynasty. They were amazingly written by mystics, who expressed their reverence to God in uncomplicated poems that could charm the masses. Basavanna, Akka Mahadevi and Allama Prabhu are the best known amongst these mystic writers.
Sanskrit was another language that had highly-developed during Western Chalukya Dynasty, besides the rise of kannada. In Sanskrit, a well known poem called Mahakavya in 18 cantos, also called Vikramankadeva Charita by Kashmiri poet Bilhana, vividly recounts in epic style the life and achievements of his patron king Vikramaditya VI. The work recites the episode of Vikramaditya VI`s accession to the Chalukyan throne after overriding his elder brother Somesvara II. Manasollasa or Abhilashitartha Chintamani by king Somesvara III (1129) is a Sanskrit work designated for all classes of society.
The last work mentioned, is an example of an early encyclopaedia in Sanskrit, encompassing various subjects including medicine, magic, veterinary science, valuing of precious stones and pearls, fortifications, painting, music, games, amusements etc. While the book does not recount any of dealt topics, especially hierarchy of importance, it suffices as a landmark in understanding the state of knowledge in those subjects during Chalukyan times.
A Sanskrit scholar, Vijnaneshwara had turned legendary in the field of legal literature for his work Mitakshara in the court of Vikramaditya VI. Language in western Chalukya dynasty was not only centred on everything poetic, but also on things related with the administration of state. Perhaps the most recognised work in that field, Mitakshara is a treatise on law (commentary on Yajnavalkya), based on earlier writings and has found acceptance in most parts of modern-day India. Some significant literary works of the western Chalukyan times related to music and musical instruments were Sangita Chudamani, Sangita Samayasara and Sangita Ratnakara.
At an administrative level, the regional language in western Chalukyan dynasty was used to trace locations and rights associated with land grants. Sanskrit was the common language. Kannada was used in circumstances like: terms of the grants, as well as information on the land, its boundaries and the participation of local authorities, rights and obligations of the grantee, taxes and dues and witnesses. This guaranteed that the content was clearly understood and grasped by the local people without any uncertainty. During the western Chalukyan period, early chronicles called Vamshavalis, which were used to present historical particulars of dynasties, in addition to the inscriptions, came into being.
Language and literature during Western Chalukya dynasty included writings in Sanskrit, which successfully incorporated poetry, grammar, lexicon, manuals, rhetoric and commentaries on older works, prose fiction and drama. In Kannada literature, several primary works on secular subjects such as Chandombudhi in prosody and Karnataka Kadambari in romance by Nagavarma I, Rannakanda in lexicons (993), Karnataka-Kalyanakaraka in medicine, Jatakatilaka in astrology (1049), Madanakatilaka in erotics, and Lokaparaka in encyclopedia (1025) were inscribed.
Literature in Western Chalukya Dynasty
The Western Chalukya era was a time of significant legendary activity in Kannada and Sanskrit. In a golden age of Kannada literature, Jain scholars wrote about the life of Tirthankaras and Virashaiva poets expressed their closeness to God through pithy poems called Vachanas. More than two hundred contemporary Vachanakaras (Vachana poets) including thirty women poets have been recorded. Early works by Brahmin writers were on the epics, Ramayana, Mahabharata, Bhagavata, Puranas and Vedas. In the field of secular literature, subjects such as romance, mathematics, medicine, lexicon, astrology, encyclopedia etc. were written for the first time.
Ranna who was patronised by king Tailapa II and Satyasraya is one among the "three gems of Kannada literature".He was bestowed the title "Emperor among poets" (Kavi Chakravathi) by King Tailapa II and has five major works to his credit. Of these, Saahasabheema Vijayam (or Gada yuddha) of 982 in Champu style is a eulogy of his patron King Satyasraya whom he compares to Bhima in valour and achievements and narrates the duel between Bhima and Duryodhana using clubs on the eighteenth day of the Mahabharata war. He wrote Ajitanatha Purana Tilakam in 993 recitating the life of the second Tirthankara, Ajitanatha.
Nagavarma II, poet laureate (Katakacharya) of King Jagadhekamalla II made contributions to Kannada literature in various subjects. His works in poetry, prosody, grammar and vocabulary are standard authorities and their significance to the study of Kannada language is well accredited. Kavyavalokana in poetics, Karnataka-Bhashabhushana on grammar and Vastukosa a lexicon (with Kannada equivalents for Sanskrit words) are some of his comprehensive contributions. A unique and native form of poetic literature in Kannada called Vachanas developed during this time. Mystics, who expressed their devotion to God in simple poems that could appeal to the masses, wrote them. Basavanna, Akka Mahadevi, Allama Prabhu are the best known among them. Inscriptions mention a Bahurupi Chaudayya, a Vachanakara (Vachana poet) who was well known for his histrionic talent while reciting his poems and a Mokari Baramayya who is described as a "Brahma" (creator) of all arts with knowledge and talent in singing, dancing and playing musical instruments.
In Sanskrit, a renowned poem (Mahakavya) in 18 cantos called Vikramankadeva Charitha by Kashmiri poet Bilhana recounts in epic style the life and achievements of his patron king Vikramaditya VI. The work narrates the episode of Vikramaditya VI`s accession to the Chalukya throne after overthrowing his elder brother Somesvara II.
Manasollasa or Abhilashitartha Chintamani by king Somesvara III (1129) was a Sanskrit work proposed for all sections of society. This is an instance of an early encyclopedia in Sanskrit covering many subjects including medicine, magic, veterinary science, valuing of precious stones and pearls, fortifications, painting, music, games, amusements etc. While the book does not provide any dealt topics particular hierarchy of importance, it serves as a landmark in understanding the state of knowledge in those subjects at that time. The first song ever written in Marathi is in praise of Buddha avatar, in the Sanskrit work Manasollasa.
A Sanskrit scholar Vijnaneshwara famed in the field of legal literature for his Mitakshara, in the court of Vikramaditya VI. Perhaps the most accredited work in that field, Mitakshara is a treatise on law (commentary on Yajnavalkya) based on earlier writings and has originated approval in most parts of modern India. An Englishman Colebrooke later translated into English the section on inheritance giving it currency in the British Indian court system. Some important literary works of the time related to music and musical instruments were Sangita Chudamani, Sangita Samayasara and Sangitha Ratnakara.
Architecture in Western Chalukya Dynasty
 The architectureoin Western Chalukya Dynasty was designed during this time served as a conceptual link between the Badami Chalukya Architecture of the eighth century and the Hoysala architecture popularized in the thirteenth century. The art of the Western Chalukyas is sometimes called the "Gadag style" after the number of metaphorical temples they built in the Tungabhadra River-Krishna River doab province of present day Gadag district in Karnataka.
The architectureoin Western Chalukya Dynasty was designed during this time served as a conceptual link between the Badami Chalukya Architecture of the eighth century and the Hoysala architecture popularized in the thirteenth century. The art of the Western Chalukyas is sometimes called the "Gadag style" after the number of metaphorical temples they built in the Tungabhadra River-Krishna River doab province of present day Gadag district in Karnataka.
The dynasty`s shrine construction reached its peak and culmination in the 12th century with over a hundred temples built across the Deccan, more then half of them in present day Karnataka. Apart from shrines, the dynasty`s architecture is well known for the elaborate stepped wells (Pushkarni), which served as ritual bathing places, many of which are well preserved in Lakkundi. The Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara Empire later incorporated these stepped well designs in the coming centuries.
The Kasi Vishveshvara Temple at Lakkundi, Mallikarjuna Temple at Kuruvatii, Kalleshwara Temple at Bagali and Mahadeva Temple at Itagi are the finest examples produced by the later Chalukya architects. The twelveth century Mahadeva Temple with its well-executed sculptures is an exquisite example of decorative detail. The intricate, finely crafted carvings on walls, pillars and towers speak volumes about Chalukya taste and culture. An inscription outside the temple calls it "Emperor of Temples" and relates that Mahadeva built a  commander in the army of king Vikramaditya VI it. The Kedareswara Temple (1060) at Balligavi is an example of an early transitional Chalukya-Hoysala style. The Western Chalukyas built temples in Badami and Aihole during its second phase of temple building activity such as Mallikarjuna Temple and Yellamma Temple and Bhutanatha group of Temples.
commander in the army of king Vikramaditya VI it. The Kedareswara Temple (1060) at Balligavi is an example of an early transitional Chalukya-Hoysala style. The Western Chalukyas built temples in Badami and Aihole during its second phase of temple building activity such as Mallikarjuna Temple and Yellamma Temple and Bhutanatha group of Temples.
The Vimana of their temples (tower over the shrine) is a compromise in detail between the plain stepped style of the early Chalukyas and the decorative finish of the Hoysalas. To the credit of the Western Chalukya architects is the development of the lathe turned (tuned) pillars and use of Soapstone (Chloritic Schist) as basic building and sculptural material, a very popular idiom in later Hoysala temples. They popularised the use of decorative Kirthimukha (demon faces) in their sculptures. Many of the famous architects in the Hoysala kingdom were Chalukya architects native to places such as Balligavi. The artistic wall decor and the general sculptural idiom was dravidian architecture. This method is occasionally termed Karnata Dravida, one of the richest traditions in Indian architecture.
Administration of Western Chalukya Dynasty
The administration was highly decentralized and feudatory clans such as the Alupas, the Hoysalas, the Kakatiya, the Seuna, the southern Kalachuri and others were permitted to rule their self-directed provinces, paying a yearly honor to the Chalukya monarch. Excavated inscriptions record titles such as Mahapradhana (Chief minister), Sandhivigrahika, and Dharmadhikari (chief justice). Some positions such as Tadeyadandanayaka (commander of reserve army) were specialised in function while all ministerial positions included the role of Dandanayaka (commander), showing that cabinet members were trained as army commanders as well as in general administrative skills.
The kingdom was alienated into provinces such as Banavasi - 12000, Nolambavadi - 32000, Gangavadi - 96000, and each name counting the number of villages under its jurisdiction. The large provinces were divided into smaller provinces containing a lesser number of villages, as in Belavola-300. The big provinces were called Mandala and under them were Nadu further divided into Kampanas (groups of villages) and finally a Bada (village). A Mandala was under a member of the royal family, a trusted feudatory or a senior official. Tailapa II himself was in charge of Tardavadi province during the Rashtrakuta rule. Chiefs of Mandalas were transferable based on political developments. For example, an official named Bammanayya administered Banavasi-12000 under King Somesvara III but was later transferred to Halasige-12000. Women from the royal family also administered Nadus and Kampanas. Army commanders were titled Mahamandaleshwaras and those who headed a Nadu were entitled Nadugouvnda.
The Western Chalukyas minted punch-marked gold pagodas with Kannada and Nagari legends, which were large, thin gold coins with numerous varying punch marks on the obverse side. They usually carried multiple punches of symbols such as a stylised lion, Sri in Kannada, a spearhead, the king`s title, a lotus and others. Jayasimha II used the legend Sri Jaya, Somesvara I issued coins with Sri Tre lo ka malla, Somesvara II used Bhuvaneka malla, Lakshmideva`s coin carried Sri Lasha, and Jagadhekamalla II coinage had the legend Sri Jagade. The Alupas, a feudatory, minted coins with the Kannada and Nagari legend Sri Pandya Dhanamjaya. Lakkundi in Gadag district and Sudi in Dharwad district were the main mints (Tankhashaley). Their heaviest gold coin was Gadyanaka weighting 96 grains, Dramma weighted 65 grains, Kalanju 48 grains, Kasu 15 grains, Manjadi 2.5 grains, Akkam 1.25 grains and Pana 9.6 grain.
Economy of Western Chalukya Dynasty
The majority of the people lived in villages and worked farming the staple crops of rice, pulses, and cotton in the dry areas and sugarcane in areas having sufficient rainfall, with areca and betel being the chief cash crops. The living conditions of the laborers who farmed the land were bearable as no records of revolts by the landless against wealthy landlords were discovered. If peasants were dissatisfied the common practice was to migrate in great numbers away from the authority of the ruler who mistreated them, thereby depriving him of revenue from their labor.
Taxes were levied on mining and forest products, and supplementary income was raised through tolls for the exercise of transportation facilities. The state also collected fees from customs, professional licenses, and judicial fines. Records exhibit that horses and salt were taxed as well as commodities (gold, textiles, perfumes) and agricultural produce (black pepper, paddy, spices, betel leaves, palm leaves, coconuts and sugar). Land tax evaluation was based on recurrent surveys evaluating the eminence of land and the type of produce. Chalukya records specifically mention black soil and red soil lands in addition to wetland, dry land and wasteland in determining taxation rates.
Key figures mentioned in inscriptions from rural areas were the Gavundas (officials) or Goudas. The Gavundas belonged to two levels of economic strata, the Praja Gavunda (people`s Gavunda) and the Prabhu Gavunda (lord of Gavundas). They served the dual purpose of representing the people before the rulers as well as functioning as state appointees for tax collection and the raising of militias. They are mentioned in inscriptions related to land transactions, irrigation maintenance, village tax collection and village council duties.
The association of commercial enterprises was common in the 11th century. Almost all arts and crafts were prearranged into guilds and work was completed on a corporate basis; records do not reveal individual artists, sculptors and craftsman. Merchants structured themselves into influential guilds transcending political divisions, allowing their maneuvers to be largely unaltered by wars and revolutions. Their only threat was the prospect of theft from brigands when their ships and caravans traveled to distant lands. Powerful South Indian merchant guilds included the Manigramam, the Nagarattar and the Anjuvannam. Local guilds were called nagaram, while the Nanadesis were traders from neighbouring kingdoms who perhaps mixed business with pleasure.
The wealthiest and most dominant and renowned amongst South Indian merchant guilds was the self styled Ainnurruvar, also known as the 500 Svamis of Ayyavolepura (Brahmins and Mahajanas of present day Aihole), who conducted extensive land and sea trade and thereby contrbuted significantly to the total foreign trade of the empire. It severely confined its trade obligations (Vira Bananjudharma or law of the noble merchants) while its members frequently recorded their achievements in inscriptions called Prasasti. Five hundred such excavated Prasasti inscriptions, with their individual flag and the bull as their emblem, record their pride in their business.
Rich traders contributed significantly to the king`s treasury through paying import and export taxes. The edicts of the Aihole Svamis mention trade ties with foreign kingdoms such as Chera, Pandya, Maleya (Malayasia), Magadh, Kaushal, Saurashtra, Kurumba, Kambhoja (Cambodia), Lata (Gujarat), Parasa (Persia) and Nepal. Travelling both land and sea routes, these merchants traded mostly in precious stones, spices and perfumes, and other specialty items such as camphor. Business flourished in precious stones such as diamonds, lapis lazuli, onyx, topaz, carbuncles and emeralds. Commonly traded spices were cardamom, saffron, and cloves, while perfumes included the by-products of sandalwood, bdellium, musk, civet and rose. These items were sold either in bulk or hawked on streets by local merchants in towns. The Western Chalukyas proscribed most of South India`s west coast and by the 10th century they had established extensive trade ties with the Tang Empire of China, the empires of Southeast Asia and the Abbasid Caliphate in Bhagdad, and by the 12th century Chinese fleets were frequenting Indian ports.
Exports to China included textiles, spices, medicinal plants, jewels, ivory, rhino horn, ebony and camphor. The same products also reached ports in the west such as Dhofar and Aden. The final destinations for those trading with the west were Persia, Arabia and Egypt. The prosperous trade center of Siraf, a port on the eastern coast of the Persian Gulf, served an international clientele of merchants including those from the Chalukya Empire who were feasted by wealthy local merchants during business visits.
An indicator of the Indian merchants` importance in Siraf comes from records describing dining plates reserved for them. In addition to this, Siraf received aloe wood, perfumes, sandalwood and condiments. The most expensive import to South India was Arabian horse shipments, this trade being dominated by Arabs and local Brahmin merchants. Thirteenth century traveler Marco Polo recorded that the breeding of horses never succeeded in India due to differing climatic, soil and grassland conditions.



















