Introduction
Mahanadi is a river which is located in the Indian states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha. It is considered to be one of the most active silt-depositing streams in India. Presently, agriculture is thriving in the Mahanadi valley, which has fertile soil. The popular pilgrimage destination in eastern India namely, Puri is located in the coastal delta of Mahanadi on the shores of Bay of Bengal.
Etymology of Mahanadi
The term "Mahanadi" means "Great River". From the meaning of its name it can be comprehended that Mahanadi is one of the largest rivers in southeast India and the sixth largest river in India.
Geography of Mahanadi
Geography of Mahanadi relates to the features of the river. Mahanadi flows for about 533 miles (858 kilometers) and the drainage area of the river is estimated to be 51,000 square miles (132,100 square kilometers).
Course of Mahanadi
Course of Mahanadi relates to the journey of the river. For the first 80 km of its course, Mahanadi flows in the northerly direction. The river drains from the Raipur district and touches the eastern portions of Raipur city. At this stage, Mahanadi is a narrow river and the total width of its valley does not exceed 500 to 600 meters. After being joined by the Seonath River, Mahanadi flows in an easterly direction through the remaining part of its journey. It is joined by the Jonk and Hasdeo rivers before entering Odisha, after covering about half of its total length. The river skirts the boundaries of Baudh district and moves through a tortuous way between ridges and ledges in a series of rapids until it reaches Dholpur in Odisha. The rapids end and the river rolls towards the Eastern Ghats, forcing its way through it via a 64 km long Satkosia Gorge. The Satkosia Gorge ends at Badamul in Nayagarh. The river cuts a ravine in the Eastern Ghats. Before joining the Bay of Bengal at False Point through several channels, the river enters the plains of Odisha at Naraj, about 11 km from Cuttack, where it pours down between two hills that are a mile apart. The river then forms a delta. This delta is one of the largest mangrove forests in peninsular India and also a rice producing area.
Tributaries of Mahanadi
The main tributaries of Mahanadi are Seonath River, Jonk River, Hasdeo River, Mand River, Ib River, Ong River and Telen River.
Mahanadi Floods
Mahanadi is known for devastating floods. However, the construction of Hirakud Dam has greatly altered the situation. Today a network of canals, barrages and check dams keep the river well in control, but heavy rain can still cause large scale flooding.
Hirakud Dam on Mahanadi
The world`s largest earthen dam namely, Hirakud Dam has been built across Mahanadi, about 15 km from Sambalpur in Odisha. Before the construction of the Hirakud Dam in 1953, Mahanadi was about a mile wide at Sambalpur and carried massive amounts of silt, especially during the monsoon. But the dam now controls the flow of Mahanadi and produces hydroelectricity. It also supplies water to several irrigation canals near Cuttack.
History of Mahanadi River
 The Mahanadi rises in the highlands of Chhatisgarh. It flows across the Indian state of Orissa to reach the Bay of Bengal. The length of the river is around 860 km. Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa share its drainage basin. The Mahanadi River is a river of eastern India. The river is one of the longest rivers in India and drains a considerable part of peninsular India.
The Mahanadi rises in the highlands of Chhatisgarh. It flows across the Indian state of Orissa to reach the Bay of Bengal. The length of the river is around 860 km. Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa share its drainage basin. The Mahanadi River is a river of eastern India. The river is one of the longest rivers in India and drains a considerable part of peninsular India.
The world`s largest earth dam - the Hirakud Dam is built on the river and stands near the city of Sambalpur. It has a high tower, Gandhi Minar for check up of the dam; on other side of the dam another tower Ashok minar is constructed there.
The Mahanadi rises in Dhamtari District of Chhatisgarh. The productive plains of the Mahanadi valley are home to intensive rice cultivation. The Mahanadi and Brahmani rivers together form a large delta where they meet the Bay of Bengal. The city of Cuttack lies at the head of this delta. This delta features one of the largest mangrove forests in Indian peninsular, and is a main rice producing area of the eastern coast of India. The Mahanadi River irrigates a fruitful valley where crops of oilseed, rice, and sugarcane are cultivated.
Origin of Mahanadi River
Mahanadi River starts from Sihawa mountain of Chhatisgarh province and debouches into the Bay of Bengal near Paradeep Sea Port in Orissa province. The Mahanadi takes its starting point near Sihawa in the Amarkantaka hills of Chhatisgarh. Important tributaries like Hadso, Jonk, Mand, Sone, Ib, Ong and Tel feed the river. The river flows along the boundary of Athamallik Sub-Division and Boudh District at about 8 Kms, which lies west of Boudh and Kiakata.
The river however changes it`s course from southeast to south near Boudh town but after passing a few kilometer it again takes a southeastern course on rocky, solid and irregular bed. After that the river moves eastward in winding course and lies few kilometers west of Tikarpara into Barmul canyon, which is locally known as Satakosia Gonda. The Gorge is 22 Kms. long and here the river meanders round wooded hills, 457 to 915 meter in height, crags and peaks of rare beauty are found along the river`s course on both sides. Total length of Mahanadi since the origin is 832 Kms. of which only 77 Kms. crosses on southwest periphery of this district.
Geology of Mahanadi River
The alluvial valley of the Mahanadi River is poorly defined and the channel is predominantly meandering in nature as according to extensive reports found. The average annual discharge of Mahanadi river basin is 1,895 m3/sec, with a maximum of 6,352 m3/sec during the summer monsoon. Minimum discharge is 759 m3/sec that usually occurs during the months; from October to June.
The river is one of the most active silt-depositing streams in the entire Indian subcontinent. The area of the delta is around 10,589 sq km. The delta is tremendously complex with numerous deserted delta lobes. The presently active delta area lies to the south of the Mahanadi river and at least two other abandoned delta regions are located to the north. The older delta lobe lying in the north is presently subjugated by tidal influence and numerous tidal channels are found in this region.
Mangrove is the most common type of vegetation seen along the sea facing edges of the delta plain. The delta plain is one of the prime rice-growing regions in India and population density is extremely high. Numerous lakes and bays are present on the delta Plain of Mahanadi River. However, many of them are the remnants of former river courses. Wave energy is quite high along the delta front and well-developed beaches and barrier islands are widely present along the coast.
Geography of Mahanadi River
Mahanadi River Delta encompasses an area of 0.1 km, which counts nearly 4.3% of the total geographical area of the country. The basin lies in the Indian states of Chhattisgarh (covering 75,136 km²), Orissa (covering 65,580 km²), Bihar (covering 635 km²) and Maharashtra (238 km²) for a total of 141589-km² area. The main tributaries of the Mahanadi River are Seonth, the Hasdeo, the Mand, the Jonk, the Ib, the Ong, and the Tel. The geography of Mahanadi River is credited for irrigating a fertile valley where crops of rice, oilseed, and sugarcane are grown.
Geographically, the delta of River Mahanadi can be divided into four zones, namely, the Northern Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the Erosional Plains of Central Table Land. The first two zones are the hilly regions, while the coastal plain is the central interior region of the delta, which is traversed by the river and its tributaries. The main soil types found in the basin are red and yellow soils, mixed red and black soils, laterite soils and deltaic soils.
India is setting up a third Antarctic base in Larsemann Hills that, 120 million years ago, was contiguous with India`s eastern coast. One of the main aims of this base is to investigate how India broke away from Antarctica and Larsmann Hills could reveal vestiges of the Mahanadi River, which flowed there about 130 million years ago when the continent was included in the Gondwanaland.
An average annual surface water potential of 66.9 km³ has been recorded in the Mahanadi river basin. Out of this, 50.0 km³ is utilizable water and cultivable area in the basin is around 80,000 km², which is 4% of the total cultivable area of the country.
Present use of Mahanadi River`s surface water in the basin is 17.0 km³. Actual storage capacity in the basin has increased considerably since independence. From just about 0.8 km³ in the pre-plan period, the total live storage capacity of the completed projects has increased to about 8.5 km³. In addition, a significant storage quantity of more than 5.4 km³ would be created on conclusion of projects that are still under construction. Thereafter, additional storage of more than 11.0 km³ would be available on implementation of projects under planning. The hydropower prospective of the basin has been planned as 627 MW at 60% capacity factor.
Course of River Mahanadi
 Mahanadi River is about 885 km long that flows in central India. The river rises in Chhatisgarh State and flows eastwards through the Eastern Ghats Mountains before entering the Bay of Bengal through a delta near Cuttack, in the eastern state of Orissa. The Tel and Hasdo rivers are the major tributaries of River Mahanadi. The Hirakud Dam was constructed in1956 and it is the only large earthen structure at Sambalpur that regulates the flow of the Mahanadi and thus produces hydroelectricity.
Mahanadi River is about 885 km long that flows in central India. The river rises in Chhatisgarh State and flows eastwards through the Eastern Ghats Mountains before entering the Bay of Bengal through a delta near Cuttack, in the eastern state of Orissa. The Tel and Hasdo rivers are the major tributaries of River Mahanadi. The Hirakud Dam was constructed in1956 and it is the only large earthen structure at Sambalpur that regulates the flow of the Mahanadi and thus produces hydroelectricity.
The flow of Mahanadi River is augmented by the drainage of hills to the north and south. At Sambalpur the Hirakud Dam on the river has constructed a man-made lake, which is 55 km long; the dam has several hydroelectric plants. Below the dam the Mahanadi river turns southwards along a meandering course, across the Eastern Ghats through a forest-covered gorge. Twisting in the eastward direction, the river enters the Orissa plains near Cuttack and thus enters the Bay of Bengal at False Point by a number of channels.
The Mahanadi is also called the "Great River" because of its vast course of 560 miles (900 km). The river has an estimated drainage area of 51,000 square miles and it is one of the most active silt-depositing streams in the Indian subcontinent. The river supplies a number of irrigation canals, particularly near Cuttack and Puri, at one of its mouths, which is a famous pilgrimage site.
This central Indian River rises in the hills of southeastern Madhya Pradesh state. Its upper course runs north as an insignificant stream, draining the eastern Chhatt?sgarh Plain. After the confluence with the Seon?th River, below Baloda B?z?r, the river turns east and enters Orissa state and thus its flow is improved by the drainage of hills to the north and southwards.
At Sambalpur the H?r?kud Dam on the river has formed a man-made lake that is 35 miles long; the dam features several hydroelectric plants. Below the dam the Mah?nadi turns southwards along a meandering course, making its way though the Eastern Gh?ts through a deep, forested gorge. Bending towards the east, Mahanadi enters the Orissa plains near Cuttack and finally empties into the Bay of Bengal at False Point by several channels.
Mahanadi River Basin
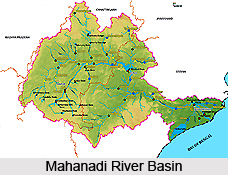 Mahanadi River Basin extends over an area of 141589 sq km which is nearly 4.3 % of total geographical area of the country. The basin lies in the states of Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar and Maharashtra. Mahanadi River rises from Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and flows for about 851 km before its outfall into the Bay of Bengal. Its main tributaries are Seonath, Jonk, Hasdeo, Mand, Ib, Ong, and Tel. Physiographically the basin can be divided into four regions namely the Northern Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the Erosional Plains. The first two are hilly regions. The coastal plain is the central interior region of the basin traversed by the river and its tributaries.
Mahanadi River Basin extends over an area of 141589 sq km which is nearly 4.3 % of total geographical area of the country. The basin lies in the states of Chhattisgarh, Orissa, Bihar and Maharashtra. Mahanadi River rises from Raipur district of Chhattisgarh and flows for about 851 km before its outfall into the Bay of Bengal. Its main tributaries are Seonath, Jonk, Hasdeo, Mand, Ib, Ong, and Tel. Physiographically the basin can be divided into four regions namely the Northern Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the Erosional Plains. The first two are hilly regions. The coastal plain is the central interior region of the basin traversed by the river and its tributaries.
The Mahanadi River marks the southern boundary of the Chhattisgarh district clearly. River Brahmani enters the district through Rengali reservoir passes through Talcher sub- division. Both these great rivers have too many tributaries, both large and small. Pallahara and Talcher Sub-Divisions and a major portion of Angul Sub-division form a part of Brahmani basin, which is also a part of Mahanadi River Basin. The Basin of Mahanadi River is spread over Athamallik Sub-division and some regions of Angul Sub-division.
There are some significant rivers in the Mahanadi River Basin some of them are as follows -
The Mahanadi River rises in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and then flows in the eastward direction, cutting a ravine in the Eastern Ghat. Before joining the Bay of Bengal at False Point through several channels, the river enters the plains of Orissa near Cuttack and forms a delta.
The Brahmani River originates in the vicinity of the Nagri village in the Dhenkanal district of Orissa at the confluence of the Sankh and the South Koel Rivers at an elevation of about 600 m. The river, with a total length of 480 km, winds around the south and southeast past Bonaigarh and Talcher and then turns towards the east to unite with the northern branches of the Mahanadi River.
Sankha River has its origin at the Chotanagpur region of Jharkhand and joins with the Koel River at Panposh near Rourkela of Sundargarh District. River Brahmani enters into Angul District through the Rengali Reservoir.
Drainage Density of Mahanadi River Basin
The river flows for 560 miles (900 km) and the drainage area of the river is estimated to be 51,000 square miles (132,100 sq km). The drainage density of the Mahanadi River Basin upto Manibhadra dam site works out to be 0.022, which is within the range of low drainage density value. It depicts that the basin has a high resistance with permeable soil under dense vegetative cover and low relief.
Tributaries of River Mahanadi
The major tributaries of River Mahanadi are Hadso and Tel rivers. However, most of the Mahanadi tributaries flow across the Bargarh district. Jira and Jhaun rivers flow through the Bargarh district and join the river Mahanadi in the extreme south of the district. The Jira has main tributary, the Danta that joins it a few miles north of its convergence with the Mahanadi near the village Gandturum in Bheden.
The other river that flows across the district is Ong (Ang) that rises in the Nawapara district and enters Borasambar (Padampur) at the extreme south-west corner of the district. The river flows through in a wide-semi-circle from west to east and leaves the district a few miles to the east of Gaisilat eventually joining the Mahanadi in the Subarnapur district.
The Tel River flows in Sonpur District of Orissa. Tel is the second largest river of Orissa and flows just 8 km away from the town of Titilagarh. This river is a significant tributary of the Mahanadi River. The convergence of the two rivers offers a remarkable view against a colorful landscape. The Hadso river is an important tributary of Mahanadi River, flowing in Madhya Pradesh.
Mahanadi River Delta
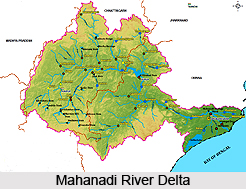 Mahanadi River Delta is a large depositional basin of about 9000 sqkm, created by both sea and river, situated in the state of Orissa, India. Mahanadi River Delta is a basin of deposit that washes away a large landmass of the Indian subcontinent into the Bay of Bengal. The alluvial valley is quite wide and relatively flat with a twisting river channel that alters its course. This coastal tract between Eastern Ghats in the west and Bay of Bengal in the east created fertile land and ecosystem with rich biodiversity. The main River Mahanadi branches into many distributory channels, which have been depositing sediment and forming broad, flat alluvial plain. This is a perfect delta with a fan angle of about 140 degrees between two outermost distributaries i.e. River Birupa in north and River Devi in south. The Hirakud Dam has a 55-km long lake or reservoir alongside. The famous city of Puri is located at one of the distributory mouths.
Mahanadi River Delta is a large depositional basin of about 9000 sqkm, created by both sea and river, situated in the state of Orissa, India. Mahanadi River Delta is a basin of deposit that washes away a large landmass of the Indian subcontinent into the Bay of Bengal. The alluvial valley is quite wide and relatively flat with a twisting river channel that alters its course. This coastal tract between Eastern Ghats in the west and Bay of Bengal in the east created fertile land and ecosystem with rich biodiversity. The main River Mahanadi branches into many distributory channels, which have been depositing sediment and forming broad, flat alluvial plain. This is a perfect delta with a fan angle of about 140 degrees between two outermost distributaries i.e. River Birupa in north and River Devi in south. The Hirakud Dam has a 55-km long lake or reservoir alongside. The famous city of Puri is located at one of the distributory mouths.
Mahanadi River
The Mahanadi River begins in south-eastern Madhya Pradesh as a small stream draining the eastern part of the Chhattisgarh Plain, later it enters Orissa state below Baloda Bazaar and crosses the Eastern Ghats to enter the Plains of Orissa near Cuttack and finally empty into the Bay of Bengal through a series of channels after travelling almost 900 km. The Mahanadi River has an estimated drainage area of 141,464 sqkm. The river deposits more silt than almost any other river in the Indian subcontinent. Drainage density is extremely dense in this area. The interior coastal plain has a relatively low height. The average altitude of the drainage basin is 426 m, with a maximum of 877 m and a minimum of 193 m.
Population density in Mahanadi River Delta
The area is situated within 60 km from the coast line and holds the highest density of population in the state. The upper part of the Mahanadi River Delta plain is heavily populated. The population density exceeds 36 people per sqkm, although moving towards the coast the population density falls.
Climate around Mahanadi River Delta
Mahanadi River Delta falls under tropical climate. Rainfall comes principally from the summer monsoon, during the months from June to September. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1,463 mm. Rainfall is recorded to be exceptionally low during the rest of the year, rarely exceeding 30 mm per month.
Nature of Mahanadi River Delta
The Mahanadi River Delta has always provided favourable condition for human habitation because of its rich productive soil and extensive water resources. The soil is rich comprising mostly coarse and fine loamy soils and coarse sandy soils and supports rich agriculture including paddy as the dominant crop, besides jute, pulses and grams.
Mahanadi River System
The Mahanadi River System rises in the Indian state of Chhatisgarh and then flows in the eastward direction, cutting a ravine in the Eastern Ghat. Before joining the Bay of Bengal at False Point through several channels, the river enters the plains of Orissa near Cuttack and forms a delta. This delta is one of the largest mangrove forests in peninsular India, and also a rice producing area. The term `Mahanadi` means Great River and it is truly one of the largest rivers in southeast India and the sixth largest in India. The Tel and the Hadso are the main tributaries of the Mahanadi. Maharashtra, Chhatisgarh, Jharkhand and Orissa share are drained by the Mahanadi.
 The river flows for 560 miles (900 kilometers) and the drainage area of the river is estimated to be 51,000 square miles (132,100 square kilometers). The world`s largest earthen dam Hirakud Dam is built across this river in Sambalpur. The dam controls the flow of Mahanadi and produces hydroelectricity. The Mahanadi River is one of the most active silt-depositing streams in India. It also supplies several irrigation canals, near Cuttack. The popular pilgrimage destination, Puri is located at one of its mouth.
The river flows for 560 miles (900 kilometers) and the drainage area of the river is estimated to be 51,000 square miles (132,100 square kilometers). The world`s largest earthen dam Hirakud Dam is built across this river in Sambalpur. The dam controls the flow of Mahanadi and produces hydroelectricity. The Mahanadi River is one of the most active silt-depositing streams in India. It also supplies several irrigation canals, near Cuttack. The popular pilgrimage destination, Puri is located at one of its mouth.
The river Mahanadi marks the southern boundary of the Chhatisgarh district clearly. River Brahmani enters the district through Rengali reservoir, passes through Talcher sub- division. Both these great rivers have too many tributaries, both large and small. Pallahara and Talcher Sub-Divisions and a major portion of Angul Sub-division form a part of Brahmani basin, which is also a part of Mahanadi river basin. The basin of Mahanadi is spread over Athamallik Sub-division and some regions of Angul Sub-division.
Mahanadi and its tributary the Brahmani River are perennial rivers. A multi purpose dam has been build over the Brahmani at Rengali. 250 MW of electricity is usually generated at Rengali hydropower station. A barrage has been constructed at 35 Kms. down stream at a place called Samal. This irrigation project is designed to irrigate around 3,36,400 hectares of land in Angul, Cuttack, Dhenkanal, Jajpur and Keonjhar districts. Other rivers of Angul are mountain streams, which during the monsoon months and in the summer contain little or no water. Their banks in the most part are highlands. Their beds are rocky and they are not accustomed for the purpose of navigation.
Religious Importance of Mahanadi River
 Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India and flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha. Like all other rivers, the Mahanadi too is revered one. It plays a major role in the life of people and is part of all the major religious functions and festivals. The water of Mahanadi is considered to be propitious for any occasion. It is believed that the water of Mahanadi has the power of converting bad into good.
Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India and flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha. Like all other rivers, the Mahanadi too is revered one. It plays a major role in the life of people and is part of all the major religious functions and festivals. The water of Mahanadi is considered to be propitious for any occasion. It is believed that the water of Mahanadi has the power of converting bad into good.
The river Mahanadi has a religious significance as there are lots of temples nestled either on its bank or are situated in the nearby area. The maximum number of its devotees is from Cuttack. Pilgrims from other parts of India too visit the various temples on the banks of this river. Some of the religious spots are as follows-
Laxman Temple
Laxman Temple nestled at Sirpur along the bank of Mahanadi River contributes to the religious significance of the river. Sirpur is an interesting site, at a one-hour distance from east of Raipur. Sited on the banks of the holy Mahanadi River, and known as `Shripur` in primitive times, it was the capital of South Kosala. The Laxman Temple here is believed to have been built in the 7th century and is one of the finest brick temples in India. The temple is still in good condition. It is characterized by beautiful carvings and precise construction.
 Gandheswar Temple
Gandheswar Temple
Gandheswar Temple is another must see spot situated on the bank of the Mahanadi River. This artistic temple mesmerizes the tourists with an amazing collection of rare statues like statue of Buddha touching the earth, Natraj, Garud Narayan and Mahishasur Mardini.
Leaning Temple of Huma
The Leaning Temple of Huma situated on the bank of the Mahanadi in Odisha is also a well known religious spot. Dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva, it is the only leaning temple in the world. It is nestled on the rocky cradle just on the bank of the river. Its leaning design attracts tourists from various parts of the country.
Rajim Temple
Rajim is another religious spot located close to Raipur, on the bank of the Mahanadi River. There are fine groups of temples, of which the main one is Rajivalochana Temple, which is dedicated to Lord Vishnu.
Other Temples
Other temples like Vatayan, Chitya Gawaksha, Bharwahakgana, Aja, Kirtimukh and Karna Amalak are situated close to Mahanadi River. Archaeological Survey of India has founded a museum in the temple premise, which houses a collection of rare statues and other relics significant to the Shaiva, Vaishnava, Buddhist and Jain faiths.



















