 Ministry of Labour is responsible for the formulation and implementation of labour policies and monitoring industrial relations. As regards its functions it is responsible for labour policy and legislation; safety, health and welfare of labour; social security of labour; policy relating to special target groups such as women and child labour; workers` education; labour and employment statistics; emigration of labour for employment abroad; employment services and vocational training; administration of central labour and employment services; international co-operation in labour and employment matters. Maintenance of industrial relations and the resolution of any disputes arising therein also comprise an important part of the responsibilities of the Ministry of Labour. The Ministry has to see to the enforcement of labour laws in the Central sphere as well as the adjudication of industrial disputes through Central Government Industrial tribunals cum Labour Courts and National Industrial Tribunals.
Ministry of Labour is responsible for the formulation and implementation of labour policies and monitoring industrial relations. As regards its functions it is responsible for labour policy and legislation; safety, health and welfare of labour; social security of labour; policy relating to special target groups such as women and child labour; workers` education; labour and employment statistics; emigration of labour for employment abroad; employment services and vocational training; administration of central labour and employment services; international co-operation in labour and employment matters. Maintenance of industrial relations and the resolution of any disputes arising therein also comprise an important part of the responsibilities of the Ministry of Labour. The Ministry has to see to the enforcement of labour laws in the Central sphere as well as the adjudication of industrial disputes through Central Government Industrial tribunals cum Labour Courts and National Industrial Tribunals.
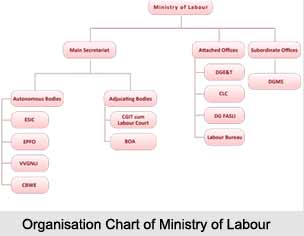
Organisation of Ministry of Labour
The Main Secretariat of the Ministry of Labour deals with a number of subjects. Items falling within its purview include the Social Security Division, Industrial Relations, Child and Women Labour, Economic and Statistics Division, International Labour Affairs and Labour Conference. The Attached Offices comprise the Office of the Chief Labour Commissioner (Central), New Delhi, the Directorate General, Employment and Training, New Delhi, the Labour Bureau at Shimla and the Directorate General, Factory Advice Service and Labour Institutes at Mumbai. The sub-ordinate offices include the Directorate General, Mines Safety, Dhanbad and the Office of the Welfare Commissioner, Allahabad, Bengaluru, Bhubaneshwar, Kolkata, Hyderabad, Jabalpur, Karma (Bihar) and Nagpur. The Adjudicating Bodies are the Central Government Industrial Tribunal-cum-Labour Court No.1 Dhanbad (Bihar) and Mumbai and at Asansol, Kolkata, Jabalpur, New Delhi, Chandigarh, Kanpur and Bengaluru and the Board of Arbitration (JCM) is at New Delhi. Among the autonomous organisations falling within the Ministry are the Employees` State Insurance Corporation, New Delhi; the Employees` Provident Fund Organisation, New Delhi; the V.V.Giri National Labour Institute, Noida, (Uttar Pradesh) and the Central Board for Workers` Education, Nagpur. The divisions within the Ministry are the following- Child Labour; Women Labour; Labour Welfare; Internal Work Study Unit; Labour Conference (LC); International Labour Affairs; Wage Board; Wage Cell; Planning; Industrial Relations; Chief Labour Commissioner; Economic and Statistical Analysis; Principal Accounts Office Statement of Expenditure and Receipts; Grant in Aid to States; Detailed Demand for Grants and Outcome Budget and Social Security.




















