 Maski village is a significant archaeological site in Lingasugur taluk of Raichur District, Karnataka, on the banks of Maski River, which is said to be a tributary of Tungabhadra River. The term `Maski` is a derivation from `Masangi` or `Mahasangha`, and this Indian town attained prominence after the discovery of a beautiful Ashokan rock edict during 1915. It is said that this was the first edict constructed during the time of emperor Ashoka which boasted of the name `Ashoka` embedded on it. This particular rock edict suggested that several other Ashokan edicts were noticed in various parts of India, termed as `Devanampiye piyadasi`. Upon a rock-face of `Durgada-gudda` is embedded the rock edict. The rulers of Chola Dynasty had reigned over Maski, which was close to Raichur Doab. This region is historically important since this was the very place where Jayasimha II, the Western Chalukya king lost to Rajendra Chola I in the battle which had occurred during 1019 to 1020 A.D.
Maski village is a significant archaeological site in Lingasugur taluk of Raichur District, Karnataka, on the banks of Maski River, which is said to be a tributary of Tungabhadra River. The term `Maski` is a derivation from `Masangi` or `Mahasangha`, and this Indian town attained prominence after the discovery of a beautiful Ashokan rock edict during 1915. It is said that this was the first edict constructed during the time of emperor Ashoka which boasted of the name `Ashoka` embedded on it. This particular rock edict suggested that several other Ashokan edicts were noticed in various parts of India, termed as `Devanampiye piyadasi`. Upon a rock-face of `Durgada-gudda` is embedded the rock edict. The rulers of Chola Dynasty had reigned over Maski, which was close to Raichur Doab. This region is historically important since this was the very place where Jayasimha II, the Western Chalukya king lost to Rajendra Chola I in the battle which had occurred during 1019 to 1020 A.D.
History of Excavations at Maski
Robert Bruce Foote commenced with some excavations which took place in the years 1870 and 1888. The Ashokan rock edict was unearthed by a mining engineer named C. Beadon during 1915. Maski was explored by the organisation of the Archaeological Department of Hyderabad during the period from 1935 to 1937 and also in the year 1954, when this area was excavated by Amalananda Ghosh on behalf of the Archaeological Survey of India or ASI.
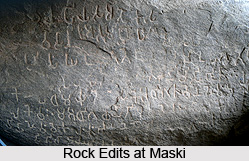 Archaeological Relics at Maski
Archaeological Relics at Maski
The excavations conducted at Maski has brought to light some facts which claim that this part of the country was inhabited across periods stretching from Neolithic to Chalcolithic Age (Period I), Megalithic Age (Period II), Early Historical Period (Period III) and Medieval Age (Period IV). Blades composed of carnelian, opal, chert and agate, as well as microliths have been found here, which can be traced back to Period I. Several ornate beads made of shells, corals and agate are also discovered at Maski village. Different kinds of pottery have also been discovered which include painted buff and dull-grey ware. Linear motifs adorn such paintings.
Animal remnants of goat, sheep, buffalo and cattle have also been excavated at Maski. Five types of burial practices and the beginning of usage of iron have been noticed from the archaeological relics found here. Colourful beads of terracotta and gold artefacts, daggers, lances, arrowheads and ferrule have been uncovered at Maski. Graffitti embellished megalithic red-and-black pottery ware, black-ware and red-slipped pottery ware belonging to Period II are amongst the historical remnants found from this spot. Russet-coated painted pottery-ware were unearthed from here which dates back to the Period III. A beautiful cylinder seal and earliest instances of Indian glass are also a few of the other items discovered. In the year 2012, remains of ancient skeletons have been unearthed at Maski.
Visiting Information
The closest railway station to Maski is based in the town of Raichur and one can approach Maski with the aide of KSRTC buses which ply from various cities and towns in Karnataka. Maksi is located on the Bangalore- Gulbarga Road and at a distance of about 430 km from Bangalore.



















