 History of Indian Astronomy dates back over four thousand years. It is said that Indian astronomy actually had a huge influence on the science of astronomy. The study of astronomy in the country shows that the early Indian astronomers are amongst the most powerful in their respective fields. Moreover, some of the earliest references of the history of Indian Astronomy can be found in the `Rigveda`, that is a collection of hymns dating back to almost 2000 B.C. The elaborate study of the history of astronomy in India states that astrology and Indian astronomy were very closely associated. According to the ancient Indians, it is the position of the different planets (particularly Saturn and Mars) that determined the fortunes of the people. And these were the beliefs that created the basis of horoscopes and modern astrology. Ancient Indian astronomy makes use of sidereal calculations, which are based on the stars. Moreover, sidereal period is also defined as the time that is taken by the object to make one full orbit around the Sun.
History of Indian Astronomy dates back over four thousand years. It is said that Indian astronomy actually had a huge influence on the science of astronomy. The study of astronomy in the country shows that the early Indian astronomers are amongst the most powerful in their respective fields. Moreover, some of the earliest references of the history of Indian Astronomy can be found in the `Rigveda`, that is a collection of hymns dating back to almost 2000 B.C. The elaborate study of the history of astronomy in India states that astrology and Indian astronomy were very closely associated. According to the ancient Indians, it is the position of the different planets (particularly Saturn and Mars) that determined the fortunes of the people. And these were the beliefs that created the basis of horoscopes and modern astrology. Ancient Indian astronomy makes use of sidereal calculations, which are based on the stars. Moreover, sidereal period is also defined as the time that is taken by the object to make one full orbit around the Sun.
The study of ancient Indian astrology clearly states that the sidereal astronomy is based upon the stars. The sidereal calculations can be traced to the final centuries BC. It can be attributed to the `Lagadha`, one of the circum-Vedic texts. This text describes rules for tracking the movements and motions of the moon and the Sun for ritual purposes. It was after the formation of the Indo-Greek kingdoms, astronomy in India was hugely influenced by Hellenistic astronomy and it adopting the zodiacal signs. Not only that, some identical arithmetical calculations for lunar cycles have also been found to be used in India. It was around 500 AD, Aryabhata I presented an arithmetical computation system, which took the Earth to revolve on its axis and he also considered the motions and movements of the planets with respect to the sun. Aryabhata also made a precise rough calculation of the Earth`s diameter and circumference. He also discovered how the solar eclipse and lunar eclipse happen and gave the radius of the terrestrial orbits in respect of the radius of the orbit of the Earth or the Sun (on the basis of their rotation periods around the Sun). He was also regarded as the earliest to find out that the courses of the different planets around the Sun are called as ellipses.
According to the history, Indian astronomy was developed during the Sunga Empire and most of the star catalogues were also produced during this time. Moreover, this period is also called as the `Golden age of astronomy in India`. Astronomy is considered as one such area that has attracted the mankind right from the beginning of the history. Initially, astronomy was intermingled with astrology and since the ancient times, in Indian the planets, which are called as the `Grahas`, have been closely involved with the determination of fortunes of the people. Brahmagupta was the chief of the astronomical observatory at Ujjain. During his term, he wrote an elaborate text on astronomy and associated sciences, the Brahmasphutasiddhanta (The Opening of the Universe) in the year 628. In fact, 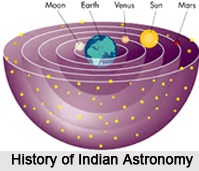 he was the earliest who used algebra for solving astronomical problems. Brahmagupta also developed several methods for calculations of the motions, movements and places of various planets, their conjunctions, rising and setting, and the estimation of eclipses. Next it was Bhaskara, who headed the astronomical observatory at Ujjain and continued the mathematical traditions started by Brahmagupta. He also wrote the Siddhantasiromani that includes two main parts and these are - Grahaganita (mathematics of the planets) and Goladhyaya (sphere). Moreover, he also observed and calculated the time taken by the Earth to complete its course around the sun to 9 decimal places. Mathematical as well as astronomical instruments were used for the general measurement of time at different periods of the day, computation of sunrise and sunset.
he was the earliest who used algebra for solving astronomical problems. Brahmagupta also developed several methods for calculations of the motions, movements and places of various planets, their conjunctions, rising and setting, and the estimation of eclipses. Next it was Bhaskara, who headed the astronomical observatory at Ujjain and continued the mathematical traditions started by Brahmagupta. He also wrote the Siddhantasiromani that includes two main parts and these are - Grahaganita (mathematics of the planets) and Goladhyaya (sphere). Moreover, he also observed and calculated the time taken by the Earth to complete its course around the sun to 9 decimal places. Mathematical as well as astronomical instruments were used for the general measurement of time at different periods of the day, computation of sunrise and sunset.
Early history of Indian astronomy also shows that this science just like other cultures was entwined with religion. In the country, the first documented mention of the several astronomical concepts comes from the Vedas (the religious Indian literature). Some of the significant chronological and astronomical references could be found in the Vedas. Like for instance, some Vedic notices mark the start of a year. In the book titled `Shatapatha Brahmana`, Yajnavalkya (1800 BC) defined the movements of the sun and the moon. Thus, the history of Indian astronomy proves that the whole concept of horoscopes developed out of complex astronomical observations and perceptions that are based on astronomical phenomenon.



















