History of Yamuna River
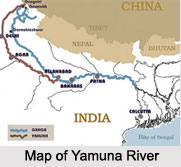 Yamuna River is one of the most prominent rivers of northern India. The river is also known as `Jamuna`. A number of ancient evidences states that Yamuna River in the past was a tributary of Ghaggar River but with the due course of time, this river changed its course. The river has great value in Indian mythology.
Yamuna River is one of the most prominent rivers of northern India. The river is also known as `Jamuna`. A number of ancient evidences states that Yamuna River in the past was a tributary of Ghaggar River but with the due course of time, this river changed its course. The river has great value in Indian mythology.
Significance of Yamuna River
Significance of Yamuna River has been increased by several canals, especially in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Vast tract of India has come under irrigation via these canals. Thus, Yamuna River has a vital role to play in agriculture in India Besides irrigation, Yamuna River has other utilities too. The cities which are located on its bank extort huge quantities of water for several uses such as industrial use.
History of Yamuna River
 Some ancient evidence indicated that River Yamuna was a tributary of the Ghaggar River in the past; with time it changed its course to east with a tectonic event in north India and became a tributary of the Ganges instead. The goddess of the Yamuna River, also known as Yami, is the sister of Yama, god of death, and the daughter of Surya, the Sun god, and his wife Samjn. The river Yamuna is also associated to the religious beliefs related to lord Krishna.
Some ancient evidence indicated that River Yamuna was a tributary of the Ghaggar River in the past; with time it changed its course to east with a tectonic event in north India and became a tributary of the Ganges instead. The goddess of the Yamuna River, also known as Yami, is the sister of Yama, god of death, and the daughter of Surya, the Sun god, and his wife Samjn. The river Yamuna is also associated to the religious beliefs related to lord Krishna.
The Yamuna and the Ganges are considered the most sacred rivers in India. According to the legends, Yamuna was the daughter of Surya, the Sun God, and sister to Yama, the God of Death and thus the popular belief have come up that those who take a dip in its holy waters are not besieged by fears of death.
The river Yamuna is closely connected to Lord Krishna`s childhood days. The Lord Krishna consecrated the River Yamuna from the beginning of His transcendental pastimes in the world. While His father Vasudeva was crossing the Yamuna with baby Lord Krishna for a safe place at Gokul on the other bank of the river from Mathura, the Lord fell down in the river, and by the dust of His lotus feet the river immediately became sanctified.
Geology of Yamuna River
 The geology of Yamuna River is known from the silt deposits it have all through the riverbed. The sediments that are collected from Delhi and Agra urban centres were examined for concentration and distribution of nine heavy metals by means of atomic adsorption spectrometry.
The geology of Yamuna River is known from the silt deposits it have all through the riverbed. The sediments that are collected from Delhi and Agra urban centres were examined for concentration and distribution of nine heavy metals by means of atomic adsorption spectrometry.
Total metal contents are different in the geological composition of the riverbed.
The ranges of the varied metal composition found in the riverbed are as follows
• Cr (157-817 mg/kg )
• Mn (515-1015 mg/kg)
• Fe (28,700-45,300 mg/kg)
• Co(11.7-28.4 mg/kg)
• Ni (40-538 mg/kg)
• Cu (40-1204 mg/kg)
• Zn (107-1974 mg/kg)
• Pb (22-856 mg/kg)
• Cd (0.50-114.8 mg/kg)
The degree of metal enrichment was compared with the standard shale concentration and shows exceptionally high values for Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd in the urban centres. In the total heavy metal concentration, anthropogenic input contains 70% Cr, 74% Cu, 59% Zn, 46% Pb, 90% Cd in Delhi and 61% Cr, 23% Ni, 71% Cu, 72% Zn, 63% Pb, 94% Cd in Agra.
A noteworthy relationship was observed between rising Cr, Ni, Zn, and Cu concentrations with increasing total sediment carbon and total sediment sulfur content. The Müller`s geoaccumulation index mentioned that the quality of the river sediments could be regarded as being moderately polluted to very highly polluted with Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd in the particular urban centres like Delhi and Agra. The present sediment analysis, therefore, plays an important role in environmental actions for the Yamuna River and the planning of these city centres.
Geography of Yamuna River
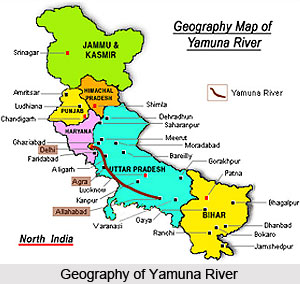 Yamuna or Jumna River is a river of northern India. River Yamuna is the longest tributary of the Ganges River, having a length of approximately 860 miles or 1,380 km. The source of the Yamuna happens to be in the western Himalayas. The river initially flows south and then southeast, thus running parallel to and just west of the Ganges. The river then passes by Delhi and Agra, and debouches into the Ganges at Allahabad. Hindus consider this point where the rivers meet to be sacred.
Yamuna or Jumna River is a river of northern India. River Yamuna is the longest tributary of the Ganges River, having a length of approximately 860 miles or 1,380 km. The source of the Yamuna happens to be in the western Himalayas. The river initially flows south and then southeast, thus running parallel to and just west of the Ganges. The river then passes by Delhi and Agra, and debouches into the Ganges at Allahabad. Hindus consider this point where the rivers meet to be sacred.
The Yamuna is navigable for small boats and barges. During the summer months the river dries down to a small stream, partly due to evaporation and partly because water is drawn away for the purpose of irrigation canals.
Origin of Yamuna River
 Known to be one of the largest tributary of the Ganga River in northern India, the Yamuna River has its origin in the Yamunotri Glacier of Uttarkashi in the state of Uttarakhand. The Yamunotri Glacier stands at an elevation of 6, 387 m on the south western slopes of Banderpooch massif of the Lower Himalayas.
Known to be one of the largest tributary of the Ganga River in northern India, the Yamuna River has its origin in the Yamunotri Glacier of Uttarkashi in the state of Uttarakhand. The Yamunotri Glacier stands at an elevation of 6, 387 m on the south western slopes of Banderpooch massif of the Lower Himalayas.
The river flows in a southwardly fashion through the Himalayan foothills and the Shivalik Hills, exiting Uttarakhand and flows onto the Indo- Gangetic Plain along the borders between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Haryana to the west. The river then passes through Delhi, where it feeds the Agra Canal. The Yamuna River flows through Mathura, Agra, Firozabad and Etawah, where it receives a number of southern tributaries, the largest of which are the Chambal, Sindh, Betwa and Ken rivers.
The Yamuna also flows through Allahabad for a course of about 1, 376 km and joins the Ganga River. The confluence of these 2 rivers is considered to be extremely sacred and is the site of annual festivals along with the Kumbh Mela, which is held every 12 years and is attended by millions of devotees.
The origin of Yamuna River- Yamunotri, is considered to be a sacred place because of the Yamunotri temple, dedicated to Goddess Yamuna which is one of the holiest shrines in Hinduism and part of the Chota Char Dham pilgrimage journey.
Course of Yamuna River
 After originating in Yamunotri, River Yamuna enters Himachal Pradesh at Khadar Majri in Sirmaur district. Yamuna River is the largest tributary of the Ganga. The Yamuna River has a mythical association to the Sun. The river rises from Yamunotri in Gharwal hills and thus forms the Eastern boundary with Uttar Pradesh. The Yamuna is the Eastern-most river of Himachal Pradesh. Its well-known tributaries are Tons, Pabbar and Giri or Giri Ganga. The Giri Ganga begins near Kupar peak just above Jubbal town in Shimla district, Tons from Yamunotri and Pabbar from Chandra Nahan Lake near the Chansal peak in Rohru tehsil of Shimla district. The total catchment area of River Yamuna in Himachal Pradesh is 2,320 km. The river leaves the state near Tajewala and enters into the Haryana state.
After originating in Yamunotri, River Yamuna enters Himachal Pradesh at Khadar Majri in Sirmaur district. Yamuna River is the largest tributary of the Ganga. The Yamuna River has a mythical association to the Sun. The river rises from Yamunotri in Gharwal hills and thus forms the Eastern boundary with Uttar Pradesh. The Yamuna is the Eastern-most river of Himachal Pradesh. Its well-known tributaries are Tons, Pabbar and Giri or Giri Ganga. The Giri Ganga begins near Kupar peak just above Jubbal town in Shimla district, Tons from Yamunotri and Pabbar from Chandra Nahan Lake near the Chansal peak in Rohru tehsil of Shimla district. The total catchment area of River Yamuna in Himachal Pradesh is 2,320 km. The river leaves the state near Tajewala and enters into the Haryana state.
The main geographic features of the Yamuna valley in the course of the river are interlocking spurs, gorges, steep rock benches and terraces. The river has formed these features over the past thousands of years. The area is thoroughly drained by the Yamuna system includes Giri-Satluj water divide in Himachal Pradesh to the Yamuna Bhilagana water divide in Gharwal.
The Southeastern slopes at the Shimla ridges are drained by the Yamuna river system too. The utilization of water of the river system is being done by the way of transportation of timber wood, irrigation and a hydel power generation. After Himachal Pradesh, the river passes the Indian states of Haryana, Delhi and Uttar Pradesh where it confluences with the Ganga river at Allahabad. The Yamuna River is almost 2,525 km. long.
Tributaries of River Yamuna
 The tributaries of Yamuna are the main source of water in Northern India. These rivers form an elaborate web of water channels all across North India. A detailed information about the tributaries of River Yamuna are as follows -
The tributaries of Yamuna are the main source of water in Northern India. These rivers form an elaborate web of water channels all across North India. A detailed information about the tributaries of River Yamuna are as follows -
Tons river is an important tributary of the Yamuna River. This river joins Yamuna at Kalsi in the North-Western part of Dehradun valley, which is approximately 48 km. away from Dehradun. The origin of Tons river is at the convergence of two feeder streams - the Supin river rises from in the Northern part of the Tons catchment near the Himachal Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh border and the Rupin river rises from a glacier at the head of the famous Har-Ki-Dun valley in the North-North Eastern part of the Tons catchment.
A principal tributary of the Yamuna River is the Chambal River (also known as Charmanwati, or Charmawati), which is an important river of the Malwa Plateau. It is a perennial river, which arises at Manpura, which is in the south of Mhow town near Indore. It is in the southern slope of the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh. Geographically, the river is situated between 22degree 27` North latitude and 73degree 20` East longitudes at a height of 354 metres.
The Bata river originates in the boulders below the Nahan ridge in the South-Western corner of Himachal Pradesh as the Jalmusa-Ka-Khala. It is mainly fed by the rain water that is cycled as underground water before finally coming up on the surface as a spring. The river flows below the surface for a part of its length in its upper reaches, thereafter the water flows on the surface. Ken River flows in northern part of India and is a tributary to the Jumna on its right bank, that flows across Bundelkhand.
 Jalal River is the small tributary of the Giri river in Himachal Pradesh. The river begins from Dharti ranges, adjacent to Pachhad and joins Yamuna at Dadahu from the right side. It also merges with the river Giriganga at Dadahu. Markanda is a small river of Nahan area of the Sirmaur district. It rises from the Southern face of the lower Himalayas on the Western ranges of the Kiarda dun or Paonta valley.
Jalal River is the small tributary of the Giri river in Himachal Pradesh. The river begins from Dharti ranges, adjacent to Pachhad and joins Yamuna at Dadahu from the right side. It also merges with the river Giriganga at Dadahu. Markanda is a small river of Nahan area of the Sirmaur district. It rises from the Southern face of the lower Himalayas on the Western ranges of the Kiarda dun or Paonta valley.
The Pabbar River is a tributary of the Tons River and finally drains into the river Yamuna. The river begins from the Dhauladhar range, which are the south facing slopes near the border of Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh and the extreme North-Eastern of Shimla district. Patsari River is a small spring fed tributary of the Pabbar River. This river starts its journey from the lower Himalayan hills near Kharapathar in Shimla district of Himachal Pradesh.
The Ashni River is a tributary of the Giri River and finally debouches into the Yamuna river. This river flows along a deep V shaped valley whose side slopes vary from very steep to abrupt ones. The river Giri is an important tributary of the Yamuna River. It is the main source of water in the South-Eastern Himachal Pradesh. The Giri River or Giriganga is famous in the Jubbal, Rohru hills that rises from Kupar peak just above Jubbal town after flowing across the heart of Shimla hills. Betwa River is a north Indian river and a tributary of the Yamuna originating in the Vindhya Range just north of Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh. In Sanskrit `Betwa` is called `Vetravati` which means containing reeds.
Wildlife and surroundings of River Yamuna
 The surroundings of River Yamuna are abundance in wildlife and ecological species. The boundary line of River Yamuna has the rare collection of Asian Elephant. There are no elephants to be found over 900 km of the western Himalayas and their foothills and also not in the west of the Yamuna. The forests of the lower Yamuna are thought to be ideal haven for elephant movement. The principal forests to be found here are exquisite collections of Sal, Khair (Acacia), and Sissoo (Rosewood) trees, and the Chir Pine forests of the Shivalik Hills.
The surroundings of River Yamuna are abundance in wildlife and ecological species. The boundary line of River Yamuna has the rare collection of Asian Elephant. There are no elephants to be found over 900 km of the western Himalayas and their foothills and also not in the west of the Yamuna. The forests of the lower Yamuna are thought to be ideal haven for elephant movement. The principal forests to be found here are exquisite collections of Sal, Khair (Acacia), and Sissoo (Rosewood) trees, and the Chir Pine forests of the Shivalik Hills.
Religious Importance of Yamuna River
 This River originates from the Champasar Glacier at an altitude of 4421 m in the state of Uttarakhand; the respected Yamuna is specially mentioned in the Hindu mythology as a mythological river. Some say the source of the river is the Saptarishi Kund, a glacial lake, where a sacred shrine of Yamunotri or Yamnotri is constructed. There is also a temple dedicated to the Goddess Yamuna, which remains closed from November to May. At Hanumanchatti, the Hanuman Ganga converges with Yamuna River. According to a legend, this remote hilly spot was the home of an ancient sage, the Asit Muni.
This River originates from the Champasar Glacier at an altitude of 4421 m in the state of Uttarakhand; the respected Yamuna is specially mentioned in the Hindu mythology as a mythological river. Some say the source of the river is the Saptarishi Kund, a glacial lake, where a sacred shrine of Yamunotri or Yamnotri is constructed. There is also a temple dedicated to the Goddess Yamuna, which remains closed from November to May. At Hanumanchatti, the Hanuman Ganga converges with Yamuna River. According to a legend, this remote hilly spot was the home of an ancient sage, the Asit Muni.
 The religious books say that, Yamuna is the companion of Lord Shri Krishna. Gokula, the divine dwelling of the Lord is the home of Yamuna. Source of Yamuna River at YamunotriIt is that, the river first went round Shri Krishna before descending down to earth according to the order of her Lord. RiverYamuna came to be called as "Kalindi" as she touched the peak of Kalind. Then she descended down the hills and reached the plains at Khandav Vana, which has been urbanized as Delhi city now.
The religious books say that, Yamuna is the companion of Lord Shri Krishna. Gokula, the divine dwelling of the Lord is the home of Yamuna. Source of Yamuna River at YamunotriIt is that, the river first went round Shri Krishna before descending down to earth according to the order of her Lord. RiverYamuna came to be called as "Kalindi" as she touched the peak of Kalind. Then she descended down the hills and reached the plains at Khandav Vana, which has been urbanized as Delhi city now.
According to tradition, Yamuna and Yama are believed to be the daughter of Sun God `Surya`. Hence she is considered pure and whoever takes a dip in her holy waters of the source stream of Yamuna may not have fear of death. The rivers Ganga and Yamuna along with the now dried Saraswati are the most revered rivers in India. Yamuna, according to the legends, is the daughter of the Sun God and the sister of Yama, the God of Death. This river is also closely associated to Mahabharata and Lord Krishna. His father Vasudeva crossed the Yamuna with baby Lord Krishna for a safer place. It is said that Lord Krishna played along with his cowherd friends on the banks of river Yamuna during his childhood.
Pollution and Protection of Yamuna River
 Pollution in Yamuna River has increased rapidly and the protection of this river includes
several governmental steps. Yamuna is unfortunately one of the most polluted rivers in
the world, especially in the banks near New Delhi, the capital of India. Almost 57% of
the citys waste is dumped into the river. Numerous attempts have been made to clean it;
however the efforts have brought few changes. In addition, the water in this river remains
torpid for almost 9 months in a year infuriating the situation.
Pollution in Yamuna River has increased rapidly and the protection of this river includes
several governmental steps. Yamuna is unfortunately one of the most polluted rivers in
the world, especially in the banks near New Delhi, the capital of India. Almost 57% of
the citys waste is dumped into the river. Numerous attempts have been made to clean it;
however the efforts have brought few changes. In addition, the water in this river remains
torpid for almost 9 months in a year infuriating the situation.
Pollution of Yamuna River
Yamunas water is distinguishable as "clear blue" as compared to silt-ridden yellow of
the Ganges. Due to high density population growth, rapid industrialization, today
Yamuna is terribly polluted. Delhi alone debouches around 3,296 MLD (million litres per
day) of dirt in the river. This makes harms to aquatic life and depletes oxygen level
resulting into bad odours and turbidity. The river water is suitable due to pollution, for
uses like drinking, outdoor bathing, propagation of aquatic life, irrigation and industrial
purposes.
Industrial pollution affects oxygen, temperature & pH etc. Large and medium industrial
units - 22 in Haryana, 42 in Delhi and 17 in Uttar Pradesh have been accused as
directly discharging and polluting the river Yamuna under the Action Plan area.
 Protection of Yamuna River
Protection of Yamuna River
The government of India has prepared elaborate plans to reconstruct and revamp the
sewage system and also the drainage system that empty into the river. In the context of
river pollution, certain actions of cleaning river have been strictly taken by the Ministry
of Environment and Forests (MoEF) of the Government of India (GOI) in 12 towns of
Haryana, 8 towns of Uttar Pradesh and Delhi under an action plan called the Yamuna
Action Plan (YAP), which is being implemented since 1993 by the National River
Conservation Directorate (NRCD) of the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
The Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC) also participates actively in the
Yamuna Action Plan in 15 of the above 21 towns, excepting the 6 towns of Haryana
included later on the direction of the honourable Supreme Court of India. In August
2009, he Delhi Jal Board (DJB) prompted its plan for resuscitating the Yamuna?s 22 km
stretch in Delhi by constructing interceptor sewers.



















