Introduction
 Krishna River is an Indian river which has been named upon a God of India, Lord Krishna. River Krishna is also called Krishnaveni, a mythological river of India. It means dark in Sanskrit and is the fourth biggest river in India in terms of water inflow and river basin area. A number of bridges and dams have been formed on the Krishna River and is known to be a polluted river.
Krishna River is an Indian river which has been named upon a God of India, Lord Krishna. River Krishna is also called Krishnaveni, a mythological river of India. It means dark in Sanskrit and is the fourth biggest river in India in terms of water inflow and river basin area. A number of bridges and dams have been formed on the Krishna River and is known to be a polluted river.
Krishna River Basin
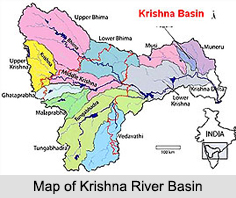 Krishna River Basin covers an area of 258,948 sqkm, which is nearly 8 percent of total geographical area of the country. The basin covers the states of Andhra Pradesh (113,271 sqkm), Maharashtra (69,425 sqkm) and Karnataka (76,252 sqkm).
Krishna River Basin covers an area of 258,948 sqkm, which is nearly 8 percent of total geographical area of the country. The basin covers the states of Andhra Pradesh (113,271 sqkm), Maharashtra (69,425 sqkm) and Karnataka (76,252 sqkm).
An average annual surface water potential of 78.1 cubic km has been detected in this basin. Out of this, 58.0 cubic km is utilizable water. Cultivable area in the basin is about 203,000 sqkm, which is 10.4 percent of the total cultivable area of the nation.
Most of the topography of this basin is rolling and undulating except the western border, which is formed by a regular line of ranges of the Western Ghats. The significant soil categories found in the basin are black soils, laterite, red soils and lateritic soils, alluvial, mixed soils, red and black soils and saline and alkaline soils.
 Course of Krishna River
Course of Krishna River
Krishna River begins in the Western Ghats at an elevation of about 1337 m just north of Mahabaleshwar, about 64 km from the Arabian Sea and flows for 1400 km and outfalls into the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaledevi. The principal tributaries of Krishna are the Ghataprabha, the Malaprabha, the Bhima, the Tungabhadra and the Musi. It flows through the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Krishna River Origin
 Krishna River is one of the longest rivers in India, which originates from Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar at an elevation of 1300 meters in Maharashtra. The river is around 1400 km in length. Krishna River originates from Mahabaleshwar near the Jor village of Satara District of Maharashtra. Then it flows towards the west to finally reach Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi in Andhra Pradesh. Krishna River causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon floods. It flows very fast after reaching the depths of over 75 feet.
Krishna River is one of the longest rivers in India, which originates from Western Ghats near Mahabaleshwar at an elevation of 1300 meters in Maharashtra. The river is around 1400 km in length. Krishna River originates from Mahabaleshwar near the Jor village of Satara District of Maharashtra. Then it flows towards the west to finally reach Bay of Bengal at Hamasaladeevi in Andhra Pradesh. Krishna River causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon floods. It flows very fast after reaching the depths of over 75 feet.
Religious Significance Of Krishna River
 All Hindus respect the Krishna River and a holy dip in the river is believed to purify the mortals. The river is personified as the Goddess Krishnaveni mata. Many pilgrim places including the Mallikarjuna temple (Srisailam), Amareshwara Swamy temple (Amaravati) and the Durga-Malleshwara temple (Vijayawada) flourish along the course of the river. These pilgrimages attract thousands of devotees all round the year. The Krishna Pushkaram fair is held on the banks of the river once in every twelve years.
All Hindus respect the Krishna River and a holy dip in the river is believed to purify the mortals. The river is personified as the Goddess Krishnaveni mata. Many pilgrim places including the Mallikarjuna temple (Srisailam), Amareshwara Swamy temple (Amaravati) and the Durga-Malleshwara temple (Vijayawada) flourish along the course of the river. These pilgrimages attract thousands of devotees all round the year. The Krishna Pushkaram fair is held on the banks of the river once in every twelve years.
Tributaries of River Krishna
 The River Krishna, meaning "dark" (feminine) in Sanskrit, is also called the Krishnaveni. It is about 1300 km in length. Krishna River originates in the Western Ghats at an altitude of about 1300m above sea level in Mahabaleshwar. It passes through Sangli and conjoins the sea in the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaledevi in Andhra Pradesh. It flows through the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
The River Krishna, meaning "dark" (feminine) in Sanskrit, is also called the Krishnaveni. It is about 1300 km in length. Krishna River originates in the Western Ghats at an altitude of about 1300m above sea level in Mahabaleshwar. It passes through Sangli and conjoins the sea in the Bay of Bengal at Hamasaledevi in Andhra Pradesh. It flows through the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Three tributaries meet Krishna River near Sangli. Warana River meets Krishna River near Sangli at Haripur. This place is also known as Sangameshwar. Panchaganga River meets Krishna River at Narsobawadi near Sangli. These places are thought to be one among the most sacred places in Hindu mythology. It is said that Lord Dattatraya had spent some of his days at Audumber on the banks of river Krishna. Tungabhadra River is the principal tributary of Krishna River, which is formed by the Tunga River and Bhadra River that start off in the Western Ghats. Other tributaries of Krishna river include the Koyna River, Bhima River (and its tributaries such as the Kundali River feeding into the Upper Bhima River Basin), Malaprabha River, Ghataprabha River, Yerla River, Warna River, Dindi River, Musi River and Dudhganga River.
 Tungabhadra River
Tungabhadra River
The Tungabhadra River which is the main tributary of Krishna, starts and flows through the state of Karnataka during maximum of its course, before flowing along the border between Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. It ultimately joins the Krishna River near Sangameswaram village in Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh. In the epic Ramayana, the Tungabhadra was known by the name of "Pampa".
Bhima River
Bhima River originates in Bhimashankar hills in Maharashtra and flows southeast for 861 km through Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh. It is a major tributary of the Krishna River. The bank of the river forms a fertile agricultural area. During its 861km course, many small rivers flow into it. Kundali River, Kumandala River, Ghod river, Bhama, Indrayani River, Mula River, Mutha River and Pavna River are the major tributaries of Bhima.
Malaprabha River
Malaprabha River: river flows in Karnataka. It rises at Kanakumbi in the Belgaum district and joins Krishna at Kudalasangama in Bagalkot. It also flows through Dharwar District. Hubli city gets its drinking water from this river. Bennihalla, Hirehalla and Tuparihalla are the major tributaries of Malaprabha.
 Ghataprabha River
Ghataprabha River
Ghataprabha is an important tributary of Krishna. It flows in Karnataka. The Ghataprabha Project at Hidkal is a hydroelectric and irrigational dam constructed across the river. Hiranyakeshi and Markandeya rivers are the tributaries of Ghataprabha.
Koyna River
The Koyna River is a tributary of the Krishna River which originates in Mahableshwar. Unlike most of the other rivers in Maharashtra which flow in the East-West direction, Koyna flows in North-South direction. The Koyna River is famous for the Koyna Hydroelectric Project. Today the project is the largest completed hydroelectric project in India. The reservoir is Shivasagar Lake. It is a huge lake, 50 ckm in length. Due to its electricity generating potential Koyna river is known as the Life Line of Maharashtra. The river meets the Krishna River at Pritisangam in Karad.
Dindi River
The Dindi River in Telengana, is an important tributary of the Krishna River. The river flows through Mahabubnagar and Nalgonda districts and finally converges with the Krishna River. The Dindi Reservoir is a medium water reservoir constructed across the river. It serves the areas: Nalgonda, Mahbubnagar and Khammam.
Musi River
Musi River is a tributary of the Krishna River flowing through Telangana. It lies in the Deccan Plateau. Hyderabad stands on the banks of Musi river. The river divides the historic old city and the new city. Himayat Sagar and Osman Sagar are dams constructed across Musi. The river was also known as Nerva during Qutub Shahi period. The Musi river was the cause of frequent floods in the Hyderabad city until the early decades of the 20th century.
Dudhganga River
This river is a right bank tributary of the Krishna in western India. It rises in Sindhudurg district of Maharashtra and flows eastward through Kolhapur and Belgaum in Karnataka before joining Krishna. During its course it forms a part of the boundary between Karnataka and Maharashtra. The Kalammawadi reservoir in the west of Kohlapur district is constructed by the Dudhganga river.
Kundali River
Kundali River is a significant tributary of Krishna River. It originates in the Kundali Hills of the Western Ghats in the state of Maharashtra and flows across the Upper Bhima River Basin.
Other tributaries of Krishna include the Venna River, Koyna River, Yerla River, Warna River, Dindi River, Paleru River, Musi River, Urmodi River, Tarli River and Dudhganga River. The rivers Venna, Koyna, Vasna, Panchganga, Dudhganga, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha and Tungabhadra join Krishna from the right bank; while the Yerla River, Musi River, Paleru and Bhima rivers join the Krishna from the left bank.
In 2009 October heavy floods occurred, isolating 350 villages and leaving millions homeless, which is believed to be first occurrence in 1000 years.
Ecological Significance of Krishna River
 Krishna River has an Indian forest called mangrove forest beside it, which is ecologically significant in different ways. It is a home of a large number of species like fishing cat, otter, estuarine crocodile, spotted deer, sambar, black buck and resident and migratory birds. This forest has been declared as Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary. This sanctuary has nurtured rich vegetation with plants like Rhizophora, Avicennia and Aegiceros.
Krishna River has an Indian forest called mangrove forest beside it, which is ecologically significant in different ways. It is a home of a large number of species like fishing cat, otter, estuarine crocodile, spotted deer, sambar, black buck and resident and migratory birds. This forest has been declared as Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary. This sanctuary has nurtured rich vegetation with plants like Rhizophora, Avicennia and Aegiceros.
Dams on Krishna River
There are two dams which have been constructed on the Krishna River, one at Srisailam called the Srisailam dam and other one at the Nagarjuna hill. There are many waterfalls found along its tributaries namely Ethipothal, Pedda Dukudu, Gundam and Chaleswaram.
Places of Interest on the Banks of Krishna River
Wai is the first Indian city on the banks of Krishna River in Satara district. Sangli is the largest city on the banks of Krishna River in Maharashtra, while Vijayawada is the largest city on the banks of Krishna River in Andhra Pradesh. Places like Audumber and Narsobawadi are situated on the banks of Krishna River near Sangli are famous pilgrimage spots. Srisailam, one of the twelve jyotirlingas which has a shrine in one of the shakti peethas in India on the Krishna River. There are three tributaries which meet Krishna River near Sangli. Warana River meets Krishna River near Sangli at Haripur. This spot is also known as Sangameshwar. These places are considered among the most sacred in Hindu mythology.
Drainage Basin Of Krishna River
The climate of the drainage basin in Krishna River is dominated by the southwest monsoon, which provides most of the precipitation for the entire region. High water level is found in the river during the month of August - November and low water is from April to May, especially at Vijayawada. Climatic feature ranges from per-humid through dry sub-humid in the west through semi-arid in the central and eastern parts of the basin. However, only in the very south central part of the basin is acutely dry.
The geology of the drainage basin is subjugated in the northwest by the Deccan Traps, in the central part is uncategorized crystalline and in the east by the Cuddapah Group. The Dharwars lies in the southwest central and the Vindhian lies in the east central. This formation is a significant part of the outcrops within the unclassified crystalline. The deltaic region itself is formed mainly of Pleistocene to Recent material.
The Krishna River is also known in mythology. The drainage basin originates near Mahabaleshwar [1438 m.] in Maharashtra State within the Western Ghats. In the terms of geology this is the Dharwar [Karnataka] Craton, which is a Granite-Gneiss-Greenbelt massif. The provenance consists of Deccan Traps and the Dharwar Archean rocks. From its source the river flows east-northeast to the town of Wai for about 1280 kilometers and then east-southeast for the last 80 kilometers, passed Sangli into Karnataka State and then Andhra Pradesh. It final empties into the Bay of Bengal. The total drainage length of Krishna River is 25,344 km with a total annual mean runoff of 55764 million cusecs and a maximum - minimum discharge of 33810 - 3 cusecs. The total length of the river is 968 km and it`s drainage basin shares a common border with that of the Godavari River, lying to the north. The river drains 305,300 sq km and the drainage density is quite high being 0.22 km stream length per 500 sq km.
About 75% of the basin is under a semi-arid climate, receiving monsoon rainfall. The rainfall of the Krishna delta is 910 mm with precipitation mainly in June all through October. The temperature of the drainage basin is around 22 - 27.5 - 34 C.
Krishna River is about 1300 km in length. The Krishna River Basin extends over an area of about 258,948 sq. km, which is nearly 8 percent of the total geographical area of the country. Regur soils, red soils, laterite and lateritic soils, alluvial soils, mixed soils and saline and alkaline soils are found in the Krishna River Basin. The River Krishna Delta is one of the most fertile regions in India. Krishna River flows past the Kodashi Dam Barrage in Maharashtra. Ecologically, Krishna River causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon. In the months of June and July, Krishna River takes the fertile soil from Maharashtra, Karnataka and western Andhra Pradesh towards the delta region.



















