 The coins of South India during the Muslim rule exhibited the impact of the Delhi Sultanate. When the invasion was taking place in the North India its impact was reflected in several parts of South India like Madura, Deccan, Ahmadnagar, Maharashtra, Bijapur, Golkonda, Warangal and in Hyderabad. The Sultans of Delhi like Alauddin Khilji and Muhammad Tughlaq had appointed their provincial governors there as they did in North. These governors gradually became the kings of the domain and started issuing coins of their own. Some of the coins also had their names and titles with legends.
The coins of South India during the Muslim rule exhibited the impact of the Delhi Sultanate. When the invasion was taking place in the North India its impact was reflected in several parts of South India like Madura, Deccan, Ahmadnagar, Maharashtra, Bijapur, Golkonda, Warangal and in Hyderabad. The Sultans of Delhi like Alauddin Khilji and Muhammad Tughlaq had appointed their provincial governors there as they did in North. These governors gradually became the kings of the domain and started issuing coins of their own. Some of the coins also had their names and titles with legends.
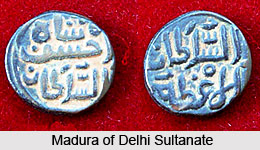
Madura, the capital of the ancient Pandya kingdom was situated in the southern part of the southernmost part of the country. The system of ruling the province through the governors continued upto the early years of Muhammad Tughlaq and appointed Jalaluddin Ahsan Shah. He took advantage of the weakness of the centre proclaimed himself as the ruler and rules nearly a century. The kingdom was absorbed in the Vijayanagar Empire and the successive eight rulers issued their coins in silver, billon, copper and probably in gold. Jalaluddin Ahsan Shah, the first ruler of this dynasty had issued coins in gold and the coins contained inscriptions. Some coins in other metals were divided into two types. In one division, the obverse side of the coin was decked with the Sultan`s name in a circle and the reverse side of the coin contained the date in Arabic numerals. The metrology of the coins was perhaps gained the influence by the metrology of the early South Indian coinage.
With the revolt of other provinces of Delhi Sultanate, the Province of the Deccan also revolted against Delhi. Ismail Mukh assumed royal authority over Deccan and took the title of Nasiruddin Ismail Shah and issued copper coins. These coins were of Delhi style that bore simple legend. The Bahmani dynasty also issued coins in gold, silver and copper. Among these coins the copper coins are found in abundance while the gold coins are rare. Among the seventeen rulers of the dynasty, gold coins are known of only nine rulers. The copper coins were issued in varying weight and almost all rulers issued copper coins. The copper coins were issued of a number of denominations. The earlier rulers followed the weight standard of 57 grains and issued coins of its multiple or sub multiples. Later, Firoz Shah ushered a new coinage in his reigning period. The early Bahmani rulers adopted the pattern of the Delhi coinage and the coins issued in the prime era of this dynasty closely resemble the Khilji and the Tughlaq coins. The first ruler of the Bahmnai dynasty adopted the Khilji legends word for word on both sides of his coins. Sometimes the name of the father or those of both father and grandfather were added on the coins along with the name of the issuer.
The later dynasty of Bahmnai dynasty was Imad Shahi dynasty. It was believed that the rulers of this dynasty did not issue any coin in their name. But some coins have now come to light that show that the first ruler of this dynasty had issued some copper coins. These coins bore the legend `Fathullah Imad` and the prayer `Khald Kibreya Allah` (let Allah perpetuate the greatness) on the obverse side of the coin. The reverse side of the coin bore the mint name `Dar-ul-saltanat Gawil`.
 The Nizam Shahi dynasty, the later rulers of Imad Shahi dynasty, also issued some coins during their ruling period. The coins issued were exclusively in copper which bore the name of the issuer and the mint name on one side and the date on the other side of the coin. As the rulers of this dynasty were called either Murtaza Shah or Burhan Shah, the coins contained their names as `Murtazi` or `Burhan`. Since there was more than one ruler of the same name, their coins were distinguished only by the date and the mint name.
The Nizam Shahi dynasty, the later rulers of Imad Shahi dynasty, also issued some coins during their ruling period. The coins issued were exclusively in copper which bore the name of the issuer and the mint name on one side and the date on the other side of the coin. As the rulers of this dynasty were called either Murtaza Shah or Burhan Shah, the coins contained their names as `Murtazi` or `Burhan`. Since there was more than one ruler of the same name, their coins were distinguished only by the date and the mint name.
During the Adil Shahi dynasty, the coins were issued in copper and were of three denominations. Though most of the coins were found in 60, 120 and 180 grains, some higher weight coins were also issued then. Some gold coins are rare though some are found and were issued by Muhammad Adil Shah bearing the same inscriptions as those on the copper coins. During this time, silver currency of a quite different and of a foreign pattern. The later coins of the Qutb Shahi dynasty were almost all issued in copper though the first ruler did not issue any coin in his name not struck any coin. He coins of this dynasty were of several denominations and of many weights. The rulers of this dynasty did not give proper attention to the detail of the inscriptions. The coins bore the name of the Sultan on the obverse and the name of the mint with or without date on the reverse side of the coin. Besides, the common type coins, Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah had issued some coins with the Persian couplet. Some of these coins did not bear the name of the king and had a distich on each side. On the other coins the couplet was etched on one side and an inscription with the mint`s name on the other side of the coin. Some extraordinary inscriptions were found during the reigning period of the successors of this dynasty. Later the issued coins testify that they were issued from Muhammadnagar and Hyderabad.
During the early period of the Barid Shahi dynasty, no proofs have been found that testify the issuing of coins. But in the later period, coins were issued with the name of the king. The fourth ruler of this dynasty, Ibrahim Barid retained the name of the Bahmani ruler Kalimullah on one side and inscribed his name with the date on the other side of the coin. Later he issued exclusively his own coins and his coins bore the inscription `Sultan Amir Barid Shah bani` on one side and a legend on the other side of the coin.
The coins of South India during the Muslim rule primarily followed the coin and coinage system of the Delhi sultanate. These south Indian dynasties also issued coins amalgamating their own exclusivity with subtle modification and sometimes they included legend in the coins.






































