Introduction about Bijapur Fort
 Bijapur Fort is a 16th century Indian fort that is situated in Bijapur city in the district of Bijapur, Karnataka. The fortress comprises of numerous historical structures that were erected during the reign of the Adil Shahi dynasty. It was constructed in 1566 by Yusuf Adil Shah. Bijapur Fort was mostly built with granite and lime mortar. Due to its architectural grandeur, Bijapur fort is called the Agra of South India.
Bijapur Fort is a 16th century Indian fort that is situated in Bijapur city in the district of Bijapur, Karnataka. The fortress comprises of numerous historical structures that were erected during the reign of the Adil Shahi dynasty. It was constructed in 1566 by Yusuf Adil Shah. Bijapur Fort was mostly built with granite and lime mortar. Due to its architectural grandeur, Bijapur fort is called the Agra of South India.
History of Bijapur Fort
The Adil Shahi dynasty was founded by Yusuf Adil Shah in 1489. He later constructed the fort and the Faroukh Mahal with skilled architects from Rome, Turkey and Persia. In 1510, he was succeeded by his son Ibrahim Adil Shah who became the ruler of Bijapur Sultanate. He made several additions to the fortress and also constructed the Jami Masjid in the vicinity of the fort. Ali Adil Shah I, the son of Ibrahim Adil Shah, also built a number of monuments in the fort and near the town. These include the Jami Masjid, a well named Chand Bawdi, his tomb Ali Rauza and the Gagan Mahal. His nephew Ibrahim II succeeded Ali Adil Shah I as the king of the region and served as an intellectual and liberal ruler. He established several Hindu temples in the precinct and also constructed the Gol Gumbaz, the mausoleum of Mohammed Ali Shah. The Mallik-E-Maidan was also established during his rule. He was succeeded by Ali Adil Shah II, his adopted son, in 1646.
His nephew Ibrahim II succeeded Ali Adil Shah I as the king of the region and served as an intellectual and liberal ruler. He established several Hindu temples in the precinct and also constructed the Gol Gumbaz, the mausoleum of Mohammed Ali Shah. The Mallik-E-Maidan was also established during his rule. He was succeeded by Ali Adil Shah II, his adopted son, in 1646.
After the fall of the Adil Shahi dynasty, the Bijapur sultanate was included into the Mughal Empire in 1686. Eventually in 1877, the British Empire in India took control of the fort. However most of the fort and palaces were in ruins by that period.
Structure of Bijapur Fort
The Bijapur Fort includes several historical structures, such as, fortifications, temples, tombs, mosques, palaces, gardens etc. There are also some ancient temples which predate the Adil Shahi dynasty. The most prominent buildings in the vicinity of the fort are the Arkilla (Citadel), Jumma mosque (Jamia Masjid), the Gagan Mahal palace, Taj Bawdi (also known as Chand Bavdi), Mehtar Mahal, Jal Mahal, Ibrahim Rauza, Barakaman, Malik-e-Maidan, Sat Manzili, Asar Mahal. Some of the structures have been discussed below:
Jamia Masjid: Jamia Masjid is located in the south east part of the city. It is the largest mosque of Bijapur, which was started in 1565, but not fully completed. It has an arcaded prayer hall with fine aisles supported on massive piers and has an impressive dome in the façade which has nine bays. The large courtyard has a water tank.
Gagan Mahal Palace: Gagan Mahal also called Heavenly Palace was built by Ali Adil Shah I in 1561 as a royal palace with a durbar hall in it. It has three impressive arches the central arch of which is the widest. The durbar hall was located in the ground floor while the first floor was built as the private residence of the royal family; both the floors are now in ruins. The outer portion of the main entrance of the palace has three arches; the central arch, which is the largest of the three, is 20 meters long and 17 meters in height.
Taj Bawdi: Taj Bawdi is a water reservoir that was built to commemorate the Taj Sultana, Ibrahim II "s first wife. The entrance arch of the reservoir has an impressive architectural grandeur. It has two octagonal towers; the east & west wings of the two towers were used as rest houses.
Mehtar Mahal: Mehtar Mahal, dated to 1620, is one of the most elegant structures in the fort. The entrance of the mahal has been built in Indo-Saracenic style; outer portion of the entrance has three arches. A gateway of the mahal leads to the Mehtar mosque, which is a three-storey building. Its carvings are in Hindu architectural style, in the form of brackets supporting the balconies and stone trellis work.
Visiting Information to Bijapur Fort
Belgaum airport is the nearest to this fort. Bijapur city is 530 km northeast of Bangalore, 650 km from Mysore and 550 km from Mumbai. Bijapur is a Broad gauge station on the South Western Railways; direct trains are available from Bangalore, Mumbai, Hubli, Solapur and Shirdi to the city of Bijapur.
Architecture of Bijapur Fort
The architecture of Bijapur Fort is influenced by the Turkish, Ottoman and Persian architectural style. The fort and the citadel were constructed in 1565 by Yusuf Adil Shah and were further developed during the reign of the Adil Shahi dynasty. The fort includes various buildings like, fortifications, tombs, mosques, temples, palaces, gardens etc. Some of the major structures in the fort are Jal Mahal, Dilkusha Mahal (Mahatar Mahal), Taj Bavdi (Chand Bavdi), Gagan Mahal palace, Malikah-e- Jahan Mosque, tomb of Ali Rauza, Jumma mosque (Jamia Masjid), Arkilla (Citadel) and others. The Dattatreya Temple, located towards the west of the fort, was built by Ibrahim II.
The Bijapur Fort and the citadel were constructed in 2 concentric circles. The fortress at the middle of the concentric circles has a circumference of 400 m and the east west axis of the fort is 3 km. The fortifications include 96 bastions which were built in different designs. The fort consists of 5 major entranceways which also have 10 more bastions. These main gateways are well decorated and arch shaped. There is also a 50 feet wide moat that surrounds the entire fort. It is around 50 feet high and the width from bastion to bastion is 25 feet. The walls are battlemented and are almost 10 ft in height.
The 5 main gateways in the Bijapur Fort are known as the Fateh gate (on the south east); the Allahpur gate (on the east); the Bahmani gate (on the north), the Shahapur gate (at the north-west corner); and the Makka gate (on the west).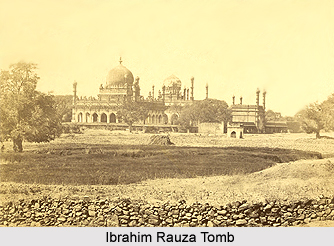 During the reign of the Adil Shahi dynasty on the Bijapur sultanate, the fortress was strongly fortified and around 1000 iron and brass canons were installed. There was also a palace inside the fort which was surrounded by 2 separate moats.
During the reign of the Adil Shahi dynasty on the Bijapur sultanate, the fortress was strongly fortified and around 1000 iron and brass canons were installed. There was also a palace inside the fort which was surrounded by 2 separate moats.
The following monuments are incorporated in the precincts of the Bijapur Fort-
Jamia Masjid
This is the largest mosque of Bijapur which is situated towards the south east of the city. It was founded in 1565 and is also known as Jumma Masjid or Jami masjid. The mosque has a prayer hall with aisles that are supported on huge piers. There is also a water reservoir in the vast courtyard. Jamia masjid covers a total area 10,810 sq m. It consists of an impressive dome which has a semi-circular shape. Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb further modified the mosque and built an eastern gate and galleries towards the north, the south and the east.
Ibrahim Rauza Tomb
This is a tomb that was constructed in 1627 and is also known as Ali Rauza. It contains Ibrahim Adil Shah II`s tomb as well as the grave of his queen Taj Sultana. The structure is square shaped and includes subtle carvings. The tomb is in a central chamber of 13 sq m. there are minarets on the corners of each building. It was built on a single block of rock. There was a basement that was utilized as a storehouse for food and ammunitions. The doors were built with teak wood with decorated metal strips. There are motifs on the outer walls of the tomb as well as above the doors and windows.
Mehtar Mahal
It is one of the most graceful structures inside Bijapur Fort. It was founded in 1620. One of the gateways in the building opens to the three-storeyed Mehtar mosque. The Mahal has a flat roof, whereas the minarets have rounded ceilings.
Barakaman
It is the mausoleum of Ali Roza which was erected in 1672. It is situated on a raised platform in the middle of a garden towards the north the Gagan Mahal and the citadel. The mausoleum was initially known as Ali Roza but was renamed as the Barakaman by Shah Nawab Khan as the structure had 12 arches.
Malik-i-Maidan Malik-i-Maidan, also known as Burj-E-Sherz, was built by Ibrahim Adil Shah II. It is situated on the western ramparts of the fort. The structure includes a large cannon with a length of 4.45 m and 1.5 m in diameter. The weight of the cannon is 55 tonnes.
Malik-i-Maidan, also known as Burj-E-Sherz, was built by Ibrahim Adil Shah II. It is situated on the western ramparts of the fort. The structure includes a large cannon with a length of 4.45 m and 1.5 m in diameter. The weight of the cannon is 55 tonnes.
Gagan MahaL
Gagan Mahal was constructed as a royal palace in 1561 by Ali Adil Shah I. It has a durbar hall in the ground floor and three arches. Presently the structure is in ruins.
Sat Manzili
Sat Manzili is a seven storeyed palace which was erected during the rule of Ibrahim II Adil Shah in 1583.
Asar Mahal
Asar Mahal was built by the Adil Shahi dynasty in 1646 and is situated towards the east side of the citadel. The structure is also called Dad Mahal as it was originally utilized as hall of justice. But later it was modified into a reliquary for storing religious relics. The ceiling and walls of the hall have paintings of landscape. Women are not allowed to enter Asar Mahal.
Taj Bavdi
It is a water tank which is also known as Chand Bavdi. The reservoir was built to commemorate the first wife of Ibrahim II named Taj Sultana. The entrance arch includes 2 octagonal towers. The west wing and the east wing of both the towers were utilized as rest houses.



















