Introduction
 Dehradun District is situated in the north-west corner of Uttarakhand. Dehradun is the district administrative headquarters. Nestled in the mountain ranges of the Himalaya, Dehradun is one of the oldest cities of India. Also known as the `Abode of Drona`, Dehradun has always been an important centre for Garhwal rulers, which was captured by the British government. Total area of the district is 3088 sq kms and its average altitude is 640 metres (2100 ft) above sea level. Main languages spoken in the district are Hindi Language, Sindhi Language, Punjabi Language, Garhwali Language and Urdu Language.
Dehradun District is situated in the north-west corner of Uttarakhand. Dehradun is the district administrative headquarters. Nestled in the mountain ranges of the Himalaya, Dehradun is one of the oldest cities of India. Also known as the `Abode of Drona`, Dehradun has always been an important centre for Garhwal rulers, which was captured by the British government. Total area of the district is 3088 sq kms and its average altitude is 640 metres (2100 ft) above sea level. Main languages spoken in the district are Hindi Language, Sindhi Language, Punjabi Language, Garhwali Language and Urdu Language.
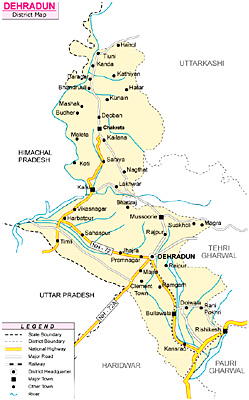
Location of Dehradun District
Dehradun District lies between 29 degrees 58 minutes and 31 degrees 2 minutes 30 seconds north latitudes and 77 degrees 34 minutes 45 seconds and 78 degrees 18 minutes 30 seconds east longitudes. Dehradun District is bounded on the north and to some distance in the north-west by the district of Uttarkashi, in the east by the districts of Tehri Garhwal and Pauri-Garhwal, in the south by Saharanpur District of Uttar Pradesh, and its southern tip touches the boundary of Haridwar District. The western boundary of Dehradun District adjoins the Sirmaur District of Himachal Pradesh with Tons River and Yamuna River separating the two.
History of Dehradun District
 History of Dehradun first finds its proud mention in the primordial Indian Puranas. In this place one can find the true essence of ancient, medieval and modern history of North India.
History of Dehradun first finds its proud mention in the primordial Indian Puranas. In this place one can find the true essence of ancient, medieval and modern history of North India.
Early History of Dehradun
In Skanda Purana, Dun is mentioned as a part of the region called `Kedar Khand`, the abode of Shiva. Another belief states that Dronacharya, the great teacher of Kauravas and Pandavas dwelled here, for a brief period; hence the name, "Drona-nagri". Dehradun during its historical era was part of the region of Kendarkhand, which was the abode of Lord Shiva who gave his name to the Shivalik Hills. Numerous lords and famous personalities have paid a visit to Dehradun, Uttarakhand for peace and atonement. Rama and Lakshmana gave themselves atonement for killing the Lanka King, Ravana. Dronacharya also had landed in Dehradun in quest of peace; the place was then named as Drona Ashram, the habitat of Drona. The five Pandavas also came on their way in Dehradun to the Himalayas to sacrifice themselves.
Medieval History of Dehradun
The recorded history of Dehradun can be traced later in the times subsequent to Christ. In 1469, reformer Guru Nanak, founder of the Sikh faith, sought shelter in the city of Dehradun. It was he who declared the names as Dehra-Camp, Doon-Valley etc. In 1757, Nazib-ud-Daula, Governor of Saharanpur, captured Dehradun; but after his death, the city lay prone to the attack of umpteen invaders. The last invaders were the Gurkhas from Nepal, who annexed it. With the decline of the colonial power in Delhi, the British defeated the forces of Siraj-ud-Daula, Mughal Viceroy, at the Battle of Plassey, with the help of rebellion led by unfaithful Mir Jafar. In 1764, Robert Clive, leading the British forces, defeated the reformed colonial army at Buxar. Under the leadership of Nadir Shah there were repeated invasions from the Afghans and Persians, which had left the Mughal Empire in complete darkness. This can be considered as a build-up of ancient history, leading to the final modern history of Dehradun. In 1761 the defeat of the battle of Panipat had left India in a position that of a high tide, angry and violent, but still divided and lacking in direction. In 1765, the British acquired from the Mughal Emperor, Shah Alam the Diwani Right (revenue collection rights) of the three provinces of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. The British East India Company was able to infiltrate into the core slowly, but progressively. The Company had brought into security the weak viceroyalties of the Mughals, endangered by the Marathas.
Modern History of Dehradun
The principal objective of the Company had been trade and commerce. Jeopardised with bankruptcy, East India Company appointed Warren Hastings as Governor in 1774. One of his first acts was to clear the dominions of the Nawab of Oudh of the Rohilla menace. Oudh was crucial as a defence state from the Marathas. The Rohilla ruler, Rehmat Khan was defeated in the battle of Miranpur Katra. As a result of treaty with the ruler of Oudh in 1801, the whole of Uttar Pradesh was in the hands of the British. After the defeat of the Marathas by Wellesley and General Lake in 1803, the rest of U.P. also came under their province. The final stage started with a war with the Gurkhas in Nepal from which both came forth with joint respect. The frontier war gained with the Treaty of Sugauli, in 1816 the districts of Garhwal, Nainital, Kumaon and Dehra Dun. Precisely from this starts the modern history of Dehradun. Till 1835, the whole area was included in the Bengal Presidency when it was divided and called the North West Frontier Province, under a Lt. Governor. Due to Dehradun`s charming natural loveliness, it is a favourite residential city and an important educational centre in Uttar Pradesh.
Geography of Dehradun District
 Geography of Dehradun District mainly includes highland areas having cooler temperatures and vast forests. Topographically, the region can be divided into two distinct tracts namely the montane tract and the sub-montane tract. The montane tract covers the entire Chakrata tehsil of the district and consists entirely of a succession of mountains and gorges and comprises Jaunsar-Bawar. The mountains are very rough with steep slopes. The most important features of the tract are the ridge which separates the drainage areas of Tons River on the west from that of Yamuna River on the east. Below the montane tract follows the sub-montane tract, which is the famous Dun valley bounded by Shivalik hills in the south and outer scarp of Himalaya Mountains in the north.
Geography of Dehradun District mainly includes highland areas having cooler temperatures and vast forests. Topographically, the region can be divided into two distinct tracts namely the montane tract and the sub-montane tract. The montane tract covers the entire Chakrata tehsil of the district and consists entirely of a succession of mountains and gorges and comprises Jaunsar-Bawar. The mountains are very rough with steep slopes. The most important features of the tract are the ridge which separates the drainage areas of Tons River on the west from that of Yamuna River on the east. Below the montane tract follows the sub-montane tract, which is the famous Dun valley bounded by Shivalik hills in the south and outer scarp of Himalaya Mountains in the north.
The climate of Dehradun District is generally temperate. It varies greatly from tropical to severe cold depending upon the altitude of the area. The district being hilly, temperature variations due to difference in elevation are considerable. In the hilly regions, the summer is pleasant, but in the summer season, the heat is often intense, although not to such degree as in the plains of the adjoining district. The temperature drops below freezing point during the winters, when the higher peaks are also under snow. The area receives an average annual rainfall of 2073.3 mm. Most of the annual rainfall in the district is received during the months from June to September, July and August being rainiest
 Geography of Dehradun District is distinguished from most of the other districts in the state by the existence of very large forests chiefly stocked with Sal. Forest products play an important role in the economy of the district. Besides, supplying fuel, fodder, bamboos and medicinal herbs, they also yield a variety of products like honey, gum, catechu, wax, horns and hides. The forest area of Dehradun District account for near about 1477 sq kms of area, around 43.70 percent of the total area of the district. Owing to the variation in altitudes and other aspects, the flora of the district varies from tropical to alpine species. Different types of forests and varying species of shrubs, climbing plants and grasses, depending upon the aspect, altitude and soil condition are found in Dehradun District. Sal forest and coniferous forests are predominant in the western part of the district. In the eastern part of Dehradun District, the forests may be divided into a number of Botanical divisions that are mainly Moist Shivalik Sal Forests (low quality of Sal is found in these forests), Moist Bhabar Doon Sal Forests, West Gangetic Moist Deciduous Forests, and Dry Shivalik Sal Forests (these forests are found on the higher slopes of Shivalik hills. In Chakrata tehsil they occur near the junction of the Tons and the Yamuna rivers. Sal is the predominant species found in these forests). Besides these, many other types of forests occur in small belts in the plain of the district.
Geography of Dehradun District is distinguished from most of the other districts in the state by the existence of very large forests chiefly stocked with Sal. Forest products play an important role in the economy of the district. Besides, supplying fuel, fodder, bamboos and medicinal herbs, they also yield a variety of products like honey, gum, catechu, wax, horns and hides. The forest area of Dehradun District account for near about 1477 sq kms of area, around 43.70 percent of the total area of the district. Owing to the variation in altitudes and other aspects, the flora of the district varies from tropical to alpine species. Different types of forests and varying species of shrubs, climbing plants and grasses, depending upon the aspect, altitude and soil condition are found in Dehradun District. Sal forest and coniferous forests are predominant in the western part of the district. In the eastern part of Dehradun District, the forests may be divided into a number of Botanical divisions that are mainly Moist Shivalik Sal Forests (low quality of Sal is found in these forests), Moist Bhabar Doon Sal Forests, West Gangetic Moist Deciduous Forests, and Dry Shivalik Sal Forests (these forests are found on the higher slopes of Shivalik hills. In Chakrata tehsil they occur near the junction of the Tons and the Yamuna rivers. Sal is the predominant species found in these forests). Besides these, many other types of forests occur in small belts in the plain of the district.
Geography of Dehradun District also includes several major rivers, canals and waterways. The Shivalik range (outer and lower ranges of Himalayas) lies at its feet, the outer scrap of the Himalayas bound it on the north and the scared Ganga River and the Yamuna skirt in on the east and the west respectively. Ganga enters Dehradun District in the eastern part and meandering south-west goes to Haridwar via Raiwala village near Rishikesh. Yamuna enters the district in Jaunsar and flows southwards for about 32 kms on the south-east border of the district. Besides, Ganga and Yamuna, the other rivers that flow through Dehradun District are Asan, Suswa, Tons, Rispana, Bindal and Amalava.
Administration of Dehradun District
Dehradun District, at present comprises six Tehsils, namely Dehradun, Chakrata, Vikasnagar, Kalsi, Tyuni and Rishikesh. There are six Community Development blocks in Dehradun District namely, Chakrata, Kalsi, Vikasnagar, Sahaspur, Raipur and Doiwala. Further, it has 17 towns and 764 villages (746 inhabited and 18 uninhabited).
Economy of Dehradun District
 Economy of Dehradun District is agrarian in character. Agriculture in Dun Valley is carried in the same way as in the plains, but in the hill areas, it requires hard labour and skill. The facilities for irrigation from canals and rivers are abundant in Dehradun District but there is a great deficiency of manure. Cultivation in the hill tract of Dehradun tehsil and throughout the Jaunsar Bawar area is of two descriptions, regular and intermittent. The hills, however, contain very little level ground and terraced cultivation is prominent in the region. Intermittent cultivation consists of small patches of hill sides cleared of shrubs and grass usually by fire. These patches are cultivated for a year or so and then left fallow both to recuperate and also to enable the coarse grass to grow.
Economy of Dehradun District is agrarian in character. Agriculture in Dun Valley is carried in the same way as in the plains, but in the hill areas, it requires hard labour and skill. The facilities for irrigation from canals and rivers are abundant in Dehradun District but there is a great deficiency of manure. Cultivation in the hill tract of Dehradun tehsil and throughout the Jaunsar Bawar area is of two descriptions, regular and intermittent. The hills, however, contain very little level ground and terraced cultivation is prominent in the region. Intermittent cultivation consists of small patches of hill sides cleared of shrubs and grass usually by fire. These patches are cultivated for a year or so and then left fallow both to recuperate and also to enable the coarse grass to grow.
In Dehradun District there are two harvests, the kharif sown in June or little earlier in the hills and reaped in September and October and the rabi sown in October-November and reaped in march in the plains and in April and May in the hills. Paddy is one of the most important kharif food crops cultivated in the district. Many kinds of Rice are sown in the area, both superior and interior. The district is famous for its basmati rice. Other important kharif crops are Maize, mandus, jhangora, sonk, kulath, arhar and Sugarcane. Wheat is principal crop of Rabi and is grown in almost all parts of the district. Barley and mustard are other important Rabi crops. Important fruits grown in Dehradun District are mango, guava, peach, grape, strawberry, pear, lemon and litchi. Dehradun is famous for its litchi. Among vegetables, potato is the most important crop. Potato cultivation in Mussoorie hills is an old and established industry. Besides, catering to the needs of the town of the district, a considerable portion of the production of potato is exported to other districts of the state.
Animal husbandry is another major sector of economy of Dehradun District. Livestock plays an important role in rural areas in raising the income of small scale farmers. Cows and buffaloes are the main sources of milk, sheep and goats are also reared in great numbers. Wool is of immense importance and is used for making home-spun woollen cloth and blankets. The production of milk however is very low. Action is being taken for the improvement of breed of the cattle. There is ample scope for poultry development in Dehradun District.
Economy of Dehradun District also includes several industries. Like for instance, tourist industry possesses tremendous possibilities of development. Many institutions of national importance like the Forest Research Institute; Oil and Natural Gas Commission; Indian Military Academy; Indian Institute of Petroleum and Survey of India etc. are located in Dehradun, which makes it a place of national importance attracting tourists in large numbers. Further, a variety of items are produced in small scale units of industries like dairy, canning and preservation, bakery, chocolate, teal, malt, textiles, card board boxes, printing, timber goods, steel furniture, liquor, Ayurvedic medicines, resin and turpentine, tubes, leather products, musical instruments, optical lenses, miniature bulbs, medical instruments, agricultural implements, utensils and hospital equipments, sewing machines and metal goods, etc. In the rural areas of Dehradun District there are several cottage and village industries like wool industry, handloom cloth, power loom, durries, tailoring, oil, rice, baskets, cots and mats, walking sticks, pottery, brick kilns and leather. Further, under the sericulture scheme, Government Control Silk Farm was established in the district.
Fairs of Dehradun District
 Fairs of Dehradun District reflect the rich culture and traditions of the region. Some of the fairs in this district of Uttarakhand are organized on some religious events. All the fairs of Dehradun District are organised with great enthusiasm and zeal. It can also be said that the fairs of the district hold religious significance. Few of the important fairs that are organised in different parts of this district are mentioned below.
Fairs of Dehradun District reflect the rich culture and traditions of the region. Some of the fairs in this district of Uttarakhand are organized on some religious events. All the fairs of Dehradun District are organised with great enthusiasm and zeal. It can also be said that the fairs of the district hold religious significance. Few of the important fairs that are organised in different parts of this district are mentioned below.
Jhanda Fair: Jhanda Fair is held every year at the historic Guru Ram Rai Darbar in Dehradun on the fifth day after the occasion of Holi in the sacred memory of the Guru. The fair begins with putting up a new Jhanda (Flag) in the compound of the historic complex. Besides local people, a large number of devotees turn up from adjoining areas of Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh, etc.
Tapkeshwar Mela: Tapkeshwar is a legendary place located on the eastern bank of the Tons River. The ancient Tapkeshwar temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva. In Skanda Purana, the place has been referred to as Deveshwara. It is believed that during Dwapara, this place was abode of Dronacharya who lived here with his family. Since then, the cave is known as Drona Gufa. It is also said that Ashwathama, was born here. A legend is associated with the origin of the name of the place. It says that when Ashwathama was very young, the poor father could not find any milk for him. The Guru was too poor to afford a cow. One day, when young Ashwathama was crying for milk, the helpless Guru advised him to pray and worship Lord Shiva, who would bless him with milk. Ashwathama did so. Pleased with the young boy`s tough penance, Lord Shiva appeared before him and enquired about his wish. Little Ashwathama asked for milk. Lord Shiva blessed him and said that milk would be made available here. Ashwathama had prayed to the Lord by the name of Tapkeshwar and hence the place was known by the same name. A big fair takes place here on the occasion of Shivaratri. Thousands of devotees congregate at this place on this sacred day to offer prayers. Tapkeshwar is easily approachable from Dehradun through roadways.
 Lakshman Siddha Fair: Lakshman Siddha is one of the four Siddha piths around Dehradun. It has immense religious importance. It is mainly a local religious fair held every Sunday, but last Sunday of April has a special significance, when people turn up in large numbers and offer obeisance to the Samadhi here. It is about 10 kms away on Dehradun-Rishikesh road and can be easily approached.
Lakshman Siddha Fair: Lakshman Siddha is one of the four Siddha piths around Dehradun. It has immense religious importance. It is mainly a local religious fair held every Sunday, but last Sunday of April has a special significance, when people turn up in large numbers and offer obeisance to the Samadhi here. It is about 10 kms away on Dehradun-Rishikesh road and can be easily approached.
Bissu Fair: This fair is held at the Jhanda ground in cantonment area of Chakrata block of Dehradun District. It is about 3 kms from Chakrata. The fair reflects cultural heritage and tradition of Jaunsari tribe. A large number of people turn up in this fair from nearby Tehri, Uttarkashi and Saharanpur district. The fair marks harvesting season in the area and reflects the happiness of the local people.
Mahasu Devta`s Fair: Mahasu Devta`s fair is held at Hanol. The fair takes place in the month of August every year, when Mahasu Devta is taken out in a procession. Musical prayers continue for three days and nights. This is a local fair of Jaunsari tribe. Thousands of participants throng the place on the occasion from the adjacent Tehri, Uttarkashi and Saharanpur district.
Saheed Veer Kesri Chandra Fair: This fair is held at Ramtal of Chakrata tehsil in Dehradun district. Ramtal is a beautiful natural tank of about 30 metres long and 30 metres wide, located on a hill. The venue of the fair is a big ground that is surrounding the lake. Every year, in the month of April this fair is held here. A temple and a memorial, dedicated to the freedom fighter Veer Kesri Chandra are located at this spot.
These prominent fairs of Dehradun District are attended by devotees from all parts of the country.
Tourism in Dehradun District
 Dehradun District is visited by a large number of tourists every year. Tourism in Dehradun District comprises several sightseeing options. On one hand, there are beautiful hill resorts, there are places like Sahasra Dhara, famous for its sulphur springs, religious and on the other hand there are ancient places like Rishikesh and Lakhamandal. The climate of the city is temperate and that along with the scenic beauty enhances the charm of travelling for the visitors. Even during summer, it is not so warm at Dehradun. There are several religious places in Dehradun District. The Gurudwara built by Guru Ram Raj during the reign of Aurangzeb is a religious place of eminence. The other places of importance are the Robber`s cave, situated at a distance of about 8 kms from Dehradun. The cave is a natural picnic spot surrounded by hills.
Dehradun District is visited by a large number of tourists every year. Tourism in Dehradun District comprises several sightseeing options. On one hand, there are beautiful hill resorts, there are places like Sahasra Dhara, famous for its sulphur springs, religious and on the other hand there are ancient places like Rishikesh and Lakhamandal. The climate of the city is temperate and that along with the scenic beauty enhances the charm of travelling for the visitors. Even during summer, it is not so warm at Dehradun. There are several religious places in Dehradun District. The Gurudwara built by Guru Ram Raj during the reign of Aurangzeb is a religious place of eminence. The other places of importance are the Robber`s cave, situated at a distance of about 8 kms from Dehradun. The cave is a natural picnic spot surrounded by hills.
Pilgrimage Tourism in Dehradun District
Tapkeshawar Temple: Tapkeshwar Temple is an ancient place of worship and is dedicated to Lord Shiva. There is a legend associated with the origin of its name. It is named Tapkeshwar as water droplets, originating from a rock, fall on the Shivling placed in the shrine. People in large numbers participate in the fair organized here on the occasion of Shivaratri and pay their obeisance to the deity.
 Laxman Siddh: 12 kms away from Dehradun it is a famous temple known as Laxman Siddh. Legend has it that a sage underwent penance over here. Due to easy accessibility the temple is visited by a large number of people from all parts of the country.
Laxman Siddh: 12 kms away from Dehradun it is a famous temple known as Laxman Siddh. Legend has it that a sage underwent penance over here. Due to easy accessibility the temple is visited by a large number of people from all parts of the country.
Sai Darbar: Situated 8 kms along, is the Sai Darbar Temple. This place holds a high cultural and spiritual value and is visited by tourists from across the country and foreigners as well.
Tibetan Temple: Situated on Rajpur Road near the Sai Darbar Temple, it is a huge and colourful temple dedicated to Lord Buddha.
Santala Devi Temple: This temple is located at around 15 kms from Dehradun. The temple stands as a symbol of faith people have in the temple and has a great cultural and religious significance. Legends says that Santla Devi, along with her brother, on realizing that they would not be able to face the Mughal Army, abandoned their weapons and began to pray. A light flickered and within moments they both were transformed into stone images. It is within the fort that the shrine was built.
Tapovan: Approximately, 5 kms from the City Bus Stand on the Dehradun-Rajpur road, this place is situated amidst beautiful surroundings. Legend has it that Guru Dronacharya had done penance in this area.
Nature Tourism in Dehradun District
Mussoorie: 38 kms from Dehradun is Mussoorie with its green hills and varied flora and fauna, is a fascinating hill station. It offers a wonderful view of the snow clad Himalaya Mountains. The mesmerizing view creates a serene atmosphere for the tourists. Mussoorie, the queen of hill stations, is famous for its scenic beauty, vibrant social life and entertainment. The excellent climate makes it an attractive holiday resort. Badrinath Peak, Kedarnath, Sri Kantha and Nanda Devi peaks can be seen from here.
 Sahasra Dhara: Sahasra Dhara, literally meaning, `thousand fold spring` is situated at a distance of around 11 kms from Dehradun. The place makes an ideal picnic spot and is of immense attraction to the visitors. There is also a sulphur spring in which visitors often take bath. Its water is said to cure skin infections and possess other medicinal properties.
Sahasra Dhara: Sahasra Dhara, literally meaning, `thousand fold spring` is situated at a distance of around 11 kms from Dehradun. The place makes an ideal picnic spot and is of immense attraction to the visitors. There is also a sulphur spring in which visitors often take bath. Its water is said to cure skin infections and possess other medicinal properties.
Malsi Deer Park: 10 kms from Dehradun, Malsi Deer Park is situated at the foot hills of the Shivalik hills. Malsi Deer Park is a mini-zoological park comprising of a children`s park enveloped by beautiful, natural surroundings. Along with the attractive environs the availability of refreshments makes the place an ideal sight-seeing cum picnic spot.
Chandrabani: It is a popular tourist spot of Dehradun. Situated 7 kms from Dehradun there is the famous temple of Chandrabani (Gautam Kund). According to the mythological beliefs, this spot was inhabited by Maharishi Gautama. Every year devotees, in large numbers, take a dip in this holy kund. 2 kms away from the main road, located in the midst of Shivalik hills, the place is a beautiful tourist spot.
Robber`s Cave: Robber`s Cave is a beautiful and easily accessible picnic spot.
 Lachhiwala: 3 kms from Doiwala and 22 kms from Dehradun, on the Hardwar- Rishikesh road is Lachhiwala. The serene and blissful is an ideal picnic spot.
Lachhiwala: 3 kms from Doiwala and 22 kms from Dehradun, on the Hardwar- Rishikesh road is Lachhiwala. The serene and blissful is an ideal picnic spot.
Bhagirathi Resort: Bhagirathi Resort at Selaqui, Dehradun lends a breath-taking spectacle of the Himalayan ranges. The resort lures the tourists with its tranquil swimming pool, water slides and fountains. Against the backdrop of the mountain ranges, the resort is an ideal tourist spot.
Asan Barrage Water Sports Resort: A water sports resort has been developed at the Asan Barrage by Garhwal Mandal Vikas Nigam in the year 1994. Asan Barrage was created in the year 1967 and it is popularly known as Dhalipur Lake. Situated 43 kms from Dehradun on Chandigarh-Shimla highway, the resort offers facilities like water skiing, boating, rowing, kayaking, canoeing, etc. Wildlife lovers have an added bonus during the winter season as migratory birds can be seen in the vicinity.
Dakpathar: 45 kms from Dehradun, Dakpathar is a beautiful tourist spot in the western Doon Valley, amidst the Shivalik range. Dakpathar has emerged as a wonderful tourist spot.
Dehradun is well linked by railways and roadways with Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Lucknow and Varanasi.
Pilgrimage Tourism in Dehradun
 Pilgrimage Tourism in Dehradun includes the temples dedicated to Hindu Gods and Goddesses, which are of thousands years origin. The idyllic, delightful, lush and relaxing hill station of Dehradun has been significantly circumvented by the Himalayan Mountains.
Pilgrimage Tourism in Dehradun includes the temples dedicated to Hindu Gods and Goddesses, which are of thousands years origin. The idyllic, delightful, lush and relaxing hill station of Dehradun has been significantly circumvented by the Himalayan Mountains.
The capital city of Uttarakhand, Dehradun is very much admired for its satisfying climate all round the year. This can be considered as the most defining and motivating a reason for pilgrimage to further heighten the city`s prestige and grandeur.
Indeed, pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun is a major source of income for hoteliers who provide ample information to the religious in terms of tour itinerary. This awe-inspiring picturesque hill haunt as such holds recognition and regard in terms of pilgrims` footfall for its places of religious interests. One can plan his/ her strategy accordingly, with the most revered of the pilgrim tours in Dehradun to choose from as far their convenience and accessibility is concerned.
Tapkeshwar Temple
Tapkeshwar Temple is a prehistoric place of worship dedicated to Lord Shiva and is situated on the banks of a rivulet, in the Garhi Cantonment Area of Dehradun, 5.5 km from the city bus stand; the Shiva temple, dedicated to Mahadeva is well linked by roadways. The temple is named so in an unusual manner as water droplets trickling from the rock ceiling above, falls upon the Shiva lingam (a phallic symbolic representation of Lord Shiva), which is enshrined here. Colossal number of pilgrims visit this place for a fair coordinated here on Shivratri, paying their homage to the mysterious deity. Tapkeshwar Temple is a much decisive temple included in the pilgrim tours in Dehradun.
Gautam Kund
At a distance of approximately 7 km from the proper city boundary on the Dehradun-Delhi road, there lies another sacred temple location, referred to as Chandrabani (Gautam Kund). According to mythological impressions, this spot was once inhabited by Maharishi Gautam, his wife and daughter Anjani, who are extensively worshipped by the people. It is believed that the daughter of heaven - Ganga had manifested Herself on this spot, which is presently prevalently identified as the Gautam Kund.
 Every year, devotees in huge numbers take a dip in this holy Kund. Two kilometres farther from the main road, located in the midst of Shivalik hills, the place truly heightens pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun to a considerable extent.
Every year, devotees in huge numbers take a dip in this holy Kund. Two kilometres farther from the main road, located in the midst of Shivalik hills, the place truly heightens pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun to a considerable extent.
Sai Darbar Temple
Placed 8 km along the Clock Tower on Rajpur Road is the Sai Darbar Temple, coming next in list in the prestigious line up of pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun. The temple has been known to upheld brilliant cultural and spiritual value for its all types of devotees. As such, Sai Darbar is visited not only by tourists from within India, but also thronged from the international scenario.
Tibetan Temple
There lies one more temple, very near to the Sai Darbar temple, venerated as the Tibetan Temple. Noted for its colourfulness and colossus in appearance, Tibetan temple is dedicated to Lord Buddha. This Buddhist pilgrim wonder in Dehradun is located on Rajpur Road near the Sai Darbar Temple.
Santala Devi Temple
Approximately 15 km from Dehradun to arrive at the legendary temple of Santala Devi, one can make use of bus facilities till Jaitunwala; from there, it is a 2 km drive to Punjabiwala by a jeep or any light vehicle and a further 2 km trek leading to the principal shrine. Santala Devi temple stands as an insignia of faith people bestow upon the temple and possesses immense cultural and religious significance. Truly, Santala Devi Temple upholds pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun perhaps to its fullest scope. Known from legends, Santala Devi, along with her brother, on realising that they would not be able to face the Mughal Army, had abandoned their weapons to pray for betterment. A light had then quivered and within a blink of an eye they both were metamorphosed into stone images. It is within a fortress that the shrine was erected and Saturdays mark the transformation of the Goddess into stone.
 Haridwar and Rishikesh
Haridwar and Rishikesh
Twelve kilometres away from Dehradun city, precisely towards the route of Haridwar/Rishikesh is a legendary temple acknowledged as the Laxman Siddh. Myth has it that a sage had undergone propitiation in this very spot. Legends also stand in difference that this sage indeed was Laxmana from Ramayana. Due to hassle free approachability, the temple is visited by a massive number of faithfuls, especially on Sundays. Pilgrimage tourism in Dehradun however brings up its curtain here, with loads of other wonders and still hidden religious spectacles perhaps in some corner of the Himalayan undulations.
Nature Tourism in Dehradun
 Nature Tourism in Dehradun serves the tourists with waterfalls, small hilly resorts and the thin forest in nearby ashramas. Dehradun serves as the capital city of the state of Uttarakhand (previously acknowledged as Utttaranchal) in India. It is magnificently and gorgeously placed within the Himalayas and Shivalik ranges in the north and south respectively and the Ganga River and Yamuna River on the east and west flowing in that serial order. Mother Nature perhaps had, during Her time of creation of the Universe, poured out all her brilliance of naturalism upon Dehradun, making nature tours in Dehradun, the most sought after travel guidebook, towards a path of discovery unto nothingness.
Nature Tourism in Dehradun serves the tourists with waterfalls, small hilly resorts and the thin forest in nearby ashramas. Dehradun serves as the capital city of the state of Uttarakhand (previously acknowledged as Utttaranchal) in India. It is magnificently and gorgeously placed within the Himalayas and Shivalik ranges in the north and south respectively and the Ganga River and Yamuna River on the east and west flowing in that serial order. Mother Nature perhaps had, during Her time of creation of the Universe, poured out all her brilliance of naturalism upon Dehradun, making nature tours in Dehradun, the most sought after travel guidebook, towards a path of discovery unto nothingness.
The gurgling waterfalls, snow topped mountains, impenetrable woodlands, the reverberation of the wild and pleasant climate, truly possess the capability to captivate thousands tourists to this gorgeous place. This city of Dehradun has much to offer and hence nature tours and trails in Dehradun becomes a very exciting experience, which can perhaps only come about once in one lifetime.
Tapowan
To begin with the very first trail towards natural tourism in Dehradun, one can verily be attracted to the legends abounding Tapowan. It is believed that Guru Dronacharya from the time of Mahabharata had performed his penance here.
 Rajaji National Park
Rajaji National Park
Rajaji National Park was established in 1966 and branches out over an area of 820 sq. km. The park with its superb ecosystem is nestled within the verdant valley of Shivalik range, with nature tours in Dehradun emoting out at its best from within this extended tract of green. Rajaji National Park represents the flora of several zones of the forest, riverine, broad leaf mixed forest, chir pine forest, scrubland and grassy pasturelands. There are 23 species of mammals and 315 of avian-fauna available here. The National Park had been named after Chakravarti Rajagopalachari, popularly identified as Rajaji. The best tourist season ranges between November to mid June.
Zoological Survey
Zoological Survey creates extraordinary attraction amongst tourists who tour Dehradun for natural beauty, with loads of enthusiasm. The foundation was laid in the year 1916. Zoological Survey of India was integrated as a department under the Ministry of Environment and Forests. It has its location almost five km away on Kaulagarh road. The Survey serves as an institute of excellence, fully dedicated for practicing research on varied fauna species of Indian subcontinent. To top it all, it conducts numerous surveys in all the important areas and collects relevant data. The institute maintains a detail list of all fauna species of the entire country.
Sahasra Dhara Water Fall
 Sahasra Dhara, literally standing for, the `thousand fold spring`, is situated at a distance of 11 km from Dehradun city. The place stands as a superlative picnic spot and attracts ample visitors throughout, thus unquestionably hankering one back to enjoying nature tours in Dehradun, as well as saturating one`s gastronomical pursuit. The Baldi River and the caves further render an overwhelming view. The water here cascades from an approximate height of 9 metres and leaves an incrustation of lime of all that it touches. Particles thus accumulating over centuries have established a protruding ledge and a kind of cave, from the roof of which falls an eternal shower. There is also a sulphur spring by Sahasra Dharam in which visitors often take a merry bath. The spring water is believed to cure skin infections and possess other medicinal properties.
Sahasra Dhara, literally standing for, the `thousand fold spring`, is situated at a distance of 11 km from Dehradun city. The place stands as a superlative picnic spot and attracts ample visitors throughout, thus unquestionably hankering one back to enjoying nature tours in Dehradun, as well as saturating one`s gastronomical pursuit. The Baldi River and the caves further render an overwhelming view. The water here cascades from an approximate height of 9 metres and leaves an incrustation of lime of all that it touches. Particles thus accumulating over centuries have established a protruding ledge and a kind of cave, from the roof of which falls an eternal shower. There is also a sulphur spring by Sahasra Dharam in which visitors often take a merry bath. The spring water is believed to cure skin infections and possess other medicinal properties.
Malsi Deer Park
Located 10 km away from Dehradun city, on the way to Mussoorie, is situated a brilliantly developed tourist spot lying at the foothills of the Shivalik Hills. Malsi Deer Park is a miniature zoological park, comprising a children`s park, encased within splendid, natural surroundings and building up Dehradun`s nature tourism to the utmost reachable position. Along with the striking surroundings, the availability of refreshments make the place a perfect sightseeing cum picnic spot.
Lachhiwala
 Three kilometres from Doiwala and 22 km from Dehradun, on the Haridwar to Rishikesh road is the Lachhiwala, considered Dehradun`s nature tourism at its best, the serene and delightful spot is notable for its organising of outings. Indeed, nature tours are so much present in Dehradun that each one vies for another, with the visitor spoilt for choice.
Three kilometres from Doiwala and 22 km from Dehradun, on the Haridwar to Rishikesh road is the Lachhiwala, considered Dehradun`s nature tourism at its best, the serene and delightful spot is notable for its organising of outings. Indeed, nature tours are so much present in Dehradun that each one vies for another, with the visitor spoilt for choice.
It may be just an understatement when stated that nature tours in Dehradun are a wonderful experience for am adventurer to go through. Tourists can have a panoramic view of every snow covered to the quietly flowing rivers, thereby making the trip more pleasant and memorable than everything else.



















