About Nagpur District
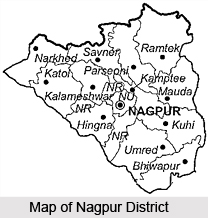 Nagpur district, located at the very centre of the Indian state, lies in the state of Maharashtra. Nagpur was the capital of the Central Provinces and Berar State till 1960. On 1st May 1960, it became the Second Capital of Maharashtra State. Located here is Nagpur city, popularly known, as the `Orange Capital of India`. The district covers a total area of 9890 Sq. kms. It contains of 13 Tahsil places and 1969 small villages. According to the 2001 census, the population of this region is 34, 36,765. The history of the district can be traced right back to the 1st Century AD, following which, the growth and development of the district is strongly connected to the rise and fall of the city of Nagpur. Further details about the district of Nagpur are given below.
Nagpur district, located at the very centre of the Indian state, lies in the state of Maharashtra. Nagpur was the capital of the Central Provinces and Berar State till 1960. On 1st May 1960, it became the Second Capital of Maharashtra State. Located here is Nagpur city, popularly known, as the `Orange Capital of India`. The district covers a total area of 9890 Sq. kms. It contains of 13 Tahsil places and 1969 small villages. According to the 2001 census, the population of this region is 34, 36,765. The history of the district can be traced right back to the 1st Century AD, following which, the growth and development of the district is strongly connected to the rise and fall of the city of Nagpur. Further details about the district of Nagpur are given below.
History of Nagpur District
 History of Nagpur district is closely connected to the rise and development of the city of Nagpur. Thus to trace the historical rise and fall of the district, the development of the city too has to be looked into since the district and the city are so closely linked. The earliest history of Nagpur district can be 1st century B.C. Evidences pointing towards the same are found in the hills and hillocks of Hidimba Tekadi, 40 kms from Nagpur near Mansar, where pieces of Terracotta belonging to the Vakataka dynasty, Maruya Empire and the Shung period have been obtained by archaeologists. The name of Nagpur appeared for the first time on record in the 10th century A.D. Nagpur was founded in the year 1702 AD by the Gond King Bakht Buland Shah of Devagad, on the banks of the Nag River. That is why the city was named as `Nagpur`. He founded the city by joining 12 small hamlets formerly known as `Rajapur Baraasa` or `Barasa`. In 1706, the eldest son of Bakht Buland Shah, Raja Chand Sultan ascended on the throne of Devagad in 1706 A.D. and he shifted his capital from Devagad to Nagpur. The contemporary Devagad was a small wooden fortress located 30 kms away in the Chhindwara district. The contemporary Devagad state included Nagpur, Bhandra, Seoni, Balaghat, Betul and Hoshangabad districts. Raja Chand Sultan initiated the construction of his fortress at Mahal. He constructed a 3 km long wall around this fortress and for the first time laid the foundation of a planned layout for Nagpur city. He continuously ruled over and made an all out development of Nagpur for 33 years.
History of Nagpur district is closely connected to the rise and development of the city of Nagpur. Thus to trace the historical rise and fall of the district, the development of the city too has to be looked into since the district and the city are so closely linked. The earliest history of Nagpur district can be 1st century B.C. Evidences pointing towards the same are found in the hills and hillocks of Hidimba Tekadi, 40 kms from Nagpur near Mansar, where pieces of Terracotta belonging to the Vakataka dynasty, Maruya Empire and the Shung period have been obtained by archaeologists. The name of Nagpur appeared for the first time on record in the 10th century A.D. Nagpur was founded in the year 1702 AD by the Gond King Bakht Buland Shah of Devagad, on the banks of the Nag River. That is why the city was named as `Nagpur`. He founded the city by joining 12 small hamlets formerly known as `Rajapur Baraasa` or `Barasa`. In 1706, the eldest son of Bakht Buland Shah, Raja Chand Sultan ascended on the throne of Devagad in 1706 A.D. and he shifted his capital from Devagad to Nagpur. The contemporary Devagad was a small wooden fortress located 30 kms away in the Chhindwara district. The contemporary Devagad state included Nagpur, Bhandra, Seoni, Balaghat, Betul and Hoshangabad districts. Raja Chand Sultan initiated the construction of his fortress at Mahal. He constructed a 3 km long wall around this fortress and for the first time laid the foundation of a planned layout for Nagpur city. He continuously ruled over and made an all out development of Nagpur for 33 years.
After the death of Raja Chand Sultan, Nagpur again went into obscurity and was gradually dominated by the Bhonsle dynasty of Deor. In 1742 A.D. the Bhonsle King Raghuji Bhonsle ascended the throne of Nagpur in place of the Gond king Raja Chand Sultan. Nagpur became the capital of Raghuji Bhonsle. Nagpur was burnt substantially in 1765 and again partially in 1811 by the marauding tribe of the Pindaris. However, the development of the city of Nagpur continued. Nawabpur, Old Mangalwari, Shukrawari Tank, Hansapuri, Jaripatka, Rajabaksha, Rambagh and Itwari areas were established and developed during the Bhonsle period.
 In the famous battle of Sitabuldi, the Marathas lost the fortress and the city to the Britishers. Britishers became the undisputed rules and monarch of the area. Nagpur was ultimately incorporated into British residency in 1853 A.D. In 1857, the effect of the first freedom struggle was felt at Nagpur too. This laid down the foundation of many non violent, non co-operation movements here. In 1861 Nagpur was declared the capital of the central provinces, and the Municipality of Nagpur was established in 1864. A number of developments and incidents took place in the years that followed right up till the country got its independence.
In the famous battle of Sitabuldi, the Marathas lost the fortress and the city to the Britishers. Britishers became the undisputed rules and monarch of the area. Nagpur was ultimately incorporated into British residency in 1853 A.D. In 1857, the effect of the first freedom struggle was felt at Nagpur too. This laid down the foundation of many non violent, non co-operation movements here. In 1861 Nagpur was declared the capital of the central provinces, and the Municipality of Nagpur was established in 1864. A number of developments and incidents took place in the years that followed right up till the country got its independence.
These are briefly listed below.
1867 A.D. - A new British train route between Nagpur to Mumbai, - `Great Indian Peninsula (G.I.P) `railway` was laid down which transformed the future of Nagpur for good. The first train steamed out of the city in 1867 A.D.
1891 A.D. - On 28th December 1891, the seventh All India Congress Session was organized at Lalbagh locality at Nagpur, in which the famous P. Anandacharlu presided.
1899 A.D. - The great plague strikes and takes a heavy toll in Nagpur.
1912 A.D. - Foundation Stone of Vidhan Sabha was laid.
1920 A.D. - 35th All India Congress session was held for the second time at Nagpur for which a new colony Congress nagar was laid down near Dhontoli park. In this session over 60 thousand Congress representative attended. The session was presided over by Shri. Jamnalal Bajaj. He openly supported Mahatma Gandhi as the undisputed leader of the union.
1923 A.D. - Nagpur University was founded. To mark the all India `Jhanda Satyagrah Aandolan` a protest rally was also organized at Nagpur in which Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru and Rajrishi Tondon participated.
1940 A.D. - Netaji Subash Chandra Bose`s All India Forward Bloc organized its second all India session at Nagpur.
1942 A.D. - Nagpur participated in `Bharat Chodo Aandolan` in which Maganlal Bagdi`s Lal Sena actively participated. He was imprisoned and the freedom fighter Shankar was hanged.
1947 A.D. - The country got its freedom from the British yoke and Nagpur also participated in this celebration. All India Radio Station was founded at Nagpur.
The Nagpur Municipality was converted to a Municipal Corporation in the year 1951. In the same year, the foundation of the `Bhartiya Jansangh` was also laid. Finally, in the year 1960 A.D., Nagpur city and district were transferred to Maharashtra State, as a part of state reorganization.
Geography of Nagpur District
Location of Nagpur District
Nagpur district lies between the north latitude of 21.07 and east longitude of 79.07. It is located at the very geographical centre of India. In fact the zero milestone of India is in the city of Nagpur. All major highways NH-7 (Varanasi - Kanyakumari) and NH-6 (Mumbai - Sambalpur - Kolkata) and major railways trunk route (Mumbai, Chennai, Howrah, Delhi) pass through the city.
Geography of Nagpur District
 Nagpur district lies practically at the very geographical centre of India. Nagpur is 837 kms from Mumbai, 1094 Kms south of Delhi, 1092 kms north of Chennai and 1140 kms west of Kolkata. It is located at the north latitude of 21.07 and east longitude of 79.07. It lies at a height of 312.42 metres above mean sea level. The town is dominated by the British fort built in 1818 on the twin hills of Sitabuldi in the centre of the city of Nagpur. It overlooks the civil lines on the west, the city proper on the east and north, and the suburb of Sitabuldi (Burdi) to the south. Northwest of the civil lines is the Gorewara reservoir with a dam 2,350 ft long. There are several fine old reservoirs (tanks) notably Shukrawari (Jumma) Talao, Ambazari and Telankhedi, and many parks in and around the city.
Nagpur district lies practically at the very geographical centre of India. Nagpur is 837 kms from Mumbai, 1094 Kms south of Delhi, 1092 kms north of Chennai and 1140 kms west of Kolkata. It is located at the north latitude of 21.07 and east longitude of 79.07. It lies at a height of 312.42 metres above mean sea level. The town is dominated by the British fort built in 1818 on the twin hills of Sitabuldi in the centre of the city of Nagpur. It overlooks the civil lines on the west, the city proper on the east and north, and the suburb of Sitabuldi (Burdi) to the south. Northwest of the civil lines is the Gorewara reservoir with a dam 2,350 ft long. There are several fine old reservoirs (tanks) notably Shukrawari (Jumma) Talao, Ambazari and Telankhedi, and many parks in and around the city.
The surrounding region is an undulating plateau rising northward to the Satpura mountain Range, from 889 to 2,142 feet (271 to 653 m) high. It is drained by the Kanhan River and Pench River in the centre, the Wardha River in the west, and the Wainganga River in the east. Both these rivers later merge as tributaries into the Godavari River. The soil is fertile black (cotton) in the west and the north and alluvial soil in the east. Forest Cover in the district is 28 percent, i.e., 2818 sq. Kms. The average annual rainfall is 45 inches, with more rain in the east than in the west. In the west, the hills are forested. In the northeast are the hills of Ramtek. Maximum, Average and Minimum Rain fall are 1993 mm, 1205 mm and 606 mm respectively.
The climate of Nagpur follows a typical seasonal monsoon weather pattern. The peak temperatures are usually reached in May/June and can be as high as 48 degree Celsius. The onset of monsoon is usually from July and the season extends up to September, with monsoon peaking during July and August. After monsoons, the average temperature varies between 27 degree Celsius and approximately 6 to 7 degree Celsius right through December and January. Wind blows with a maximum speed of 22 Km / Hrs or higher in the month of February and the onset of monsoon season i.e. in the end of May and first week of June. This is due to the generation of a low pressure area in this region. Rest of the time, the wind speed is below 5 to 7 Km/Hr and the humidity is usually between 70 and 20 percent.
Grain Riots In The Nagpur District
Grain riots in the city of Nagpur and in different parts of the district had begun at the end of September, 1869. There was famine in the north of the Province that is in the Jabalpur Division, as well as in the adjoining parts of the North-west Provinces. There was no famine in the Nagpur Division, but the prices of grain were very high. The reason of this was partly the demand for the export of grain from that part of the province to the famine-stricken parts, and partly the determination of the grain merchants to hold up their grain in hope of still higher prices when the famine elsewhere should have developed. There was some distress occasioned by these high prices. People with fixed incomes found it hard to purchase for themselves even the necessaries of life; and there was a great deal of ill-feeling in the community against the grain merchants.
The main causes of the disturbance were undoubtedly: (1) the discontented state of the Koshti population, whom the mills had deprived of a great part of the profits of their own peculiar calling, and who did not readily turn to any other ;(2) the rise in prices owing to the want of rain and the demand for food grains from the North-Western Provinces and parts of Bengal; (3) the export of grain which led the people to fear that there would soon be no grain at all in Nagpur; and (4) the efforts of the goons to fan the flame of resentment against the grain-sellers and rich merchants, so as to create for themselves an opportunity for robbery.
A number of inquiries found out that a number of these people of Nagpur had set themselves to foment this ill-feeling and to incite the people to rise against the grain-sellers and take their stock by force. Their object was to stir up a riot and incite an attack on the grain merchants` shops, in the hope that, while the rioters were possessing themselves of grain, they might take advantage of the disturbance of the peace to break into the treasuries and secure the bullion and valuables belonging to the merchants. A rumour had spread that that Government would not tolerate any prolonged disturbance, but was quite willing to have the grain dealers robbed of a certain amount of their grain, provided that the disturbance did not last more than two or three hours, by which time it would be possible to give them a sound lesson without too seriously injuring them. These extraordinary statements were received without doubt by a large number of ignorant persons; and riots in Nagpur city and in several towns in the District were the result.
It was later found out the prime arrests of the riots were all of bad characters, some of them having several previous convictions against them, and that one of the principal promoters of the disturbance was an ill-conditioned distant relative of the old Bhonsla family of Nagpur, who was well known for encouraging crime and reaping profit from it.
The rioters were mainly ill-disposed persons bent on plunder. But the prompt action of the military helped to turn down the riots in the city. Although the riot was promptly quelled in the city, however, the disturbance spread to surrounding villages.
The results of the riot were that the people were generally alarmed, and the ill-disposed were encouraged in lawlessness. The entire area of Nagpur was panic-stricken.
Monuments of Nagpur
 The monuments of Nagpur are contained in the temples, forts and provincial style buildings found herein. Located in the state of Maharashtra, the city derives its name from the Nag River flowing through it. Though the city is a modern route centre with no great architectural pretensions, the monuments of Nagpur form quite a picturesque sight.
The monuments of Nagpur are contained in the temples, forts and provincial style buildings found herein. Located in the state of Maharashtra, the city derives its name from the Nag River flowing through it. Though the city is a modern route centre with no great architectural pretensions, the monuments of Nagpur form quite a picturesque sight.
Though the origins of the city date back to the 18th century, ancient history of the district is shrouded in obscurity, with traces dating back to the 5th century. The current city of Nagpur was founded by The Gond King Bhakt Buland. In 1467 AD Muhammad Bahmani conquered the area, but in the following century the local Gonds underwent a resurgence of power, which lasted until 1740, when the Bhonslas conquered the country. On 26 and 27 November 1817 Maratha troops attacked the British Resident and his bodyguard. After a lengthy struggle the British prevailed and the Bhonsla`s army was disbanded. When the succession lapsed in 1853, the territory was annexed by the British and eight years later it was formed with Saugor and Narbada into the Central Provinces. In spite of a local uprising in 1857, the garrison remained loyal.
 On entering Nagpur city a fine view can be witnessed. The railway station has been rebuilt on a grand scale with an impressive facade. Outside there is a fine view of Sitabaldi Fort. The roads from here run in three directions: to Sitabaldi, Sadar and Hansapuri. Behind the railway station the road leads through the orange market towards the Jumma Talao, a large artificial lake with a beautiful garden in the centre. There are two other main tanks to the west of the city: the Ambazari Tank and the Telin Khedi. The former, built by the Bhonsla Rajas, was made into a reservoir in 1873. There is a pleasant garden area with romantic views across the lake.
On entering Nagpur city a fine view can be witnessed. The railway station has been rebuilt on a grand scale with an impressive facade. Outside there is a fine view of Sitabaldi Fort. The roads from here run in three directions: to Sitabaldi, Sadar and Hansapuri. Behind the railway station the road leads through the orange market towards the Jumma Talao, a large artificial lake with a beautiful garden in the centre. There are two other main tanks to the west of the city: the Ambazari Tank and the Telin Khedi. The former, built by the Bhonsla Rajas, was made into a reservoir in 1873. There is a pleasant garden area with romantic views across the lake.
Among the monuments of Nagpur, the prime attraction is the Sitabaldi Fort. Other architectural constructions of the years gone by can also be found, both historical and religious in nature.
Historical Monuments of Nagpur
Among the historical monuments of Nagpur, the Sitabaldi fort is the chief attraction. Apart from this some other structures of civic amenity can also be found standing tall here from the colonial times.
The Sitabaldi fort is the prime among the historical monuments of Nagpur. The Fort actually embraces two hills joined by a narrow saddle of land. There are two sets of defences, the larger embracing both hills and the smaller, much stronger set forming a central redoubt on the larger hill. The walls and ramparts are surrounded in places by sheer cliff faces and elsewhere by a moat. There are five bastions to the inner area and two to the outer defences, each with gun emplacements.
 Crowning the larger hill is a monument to those who fell in the Battle of Sitabaldi of 1817. Just before the tunnel entrance that leads to the inner fort on the right-hand side are a number of British graves. Facing the city to the east is another monument, marking the spot where King George V and Queen Mary gave an audience to the people of Nagpur in 1911.The fort now houses the offices of the territorial army.
Crowning the larger hill is a monument to those who fell in the Battle of Sitabaldi of 1817. Just before the tunnel entrance that leads to the inner fort on the right-hand side are a number of British graves. Facing the city to the east is another monument, marking the spot where King George V and Queen Mary gave an audience to the people of Nagpur in 1911.The fort now houses the offices of the territorial army.
The old civil station lies west of Sitabaldi Hill. The main European buildings are concentrated here.
There are two post-independence statues of note. The Statue of Maharani Lakshmi Bai of Jhansi, cast in bronze, was erected in 1962. The other statue is that of the Indian patriot Sankar.It was unveiled by Pundit Jawaharlal Nehru in February of the same year.
The Central Museum was constructed in 1863.The museum maintains collections which are mainly for Vidharba region. It has excellent collections divided into six separate sections: art and industry, archaeology, anthropology, geology, paintings and natural history. International film shows and lectures are also conducted here from time to time. A well stocked is also to be found here.
 One of the most distinguished buildings in the city is the Council Hall. It was built in 1912 by the British. The building is a two-storey affair in red brick with a distinctive central range and wings on each side. To the west of the Council Hall lies the Secratariat, a construction of the modified Renaissance style. The High Court designed by Henry Medd, is an impressive civic range in the distinctive style evolved by Lutyens at New Delhi and is very similar to Viceroy`s House.
One of the most distinguished buildings in the city is the Council Hall. It was built in 1912 by the British. The building is a two-storey affair in red brick with a distinctive central range and wings on each side. To the west of the Council Hall lies the Secratariat, a construction of the modified Renaissance style. The High Court designed by Henry Medd, is an impressive civic range in the distinctive style evolved by Lutyens at New Delhi and is very similar to Viceroy`s House.
North of Sadar Bazaar is another high hill, Takli, on which stands Government House or Raj Bhavan. Within are some interesting drawings depicting the battle of 1817 and other paintings of local British residents.
Religious Monuments of Nagpur
A number of temples and mosques figure among the historical monuments of Nagpur. One of the most revered shrines in Nagpur is the Badri Narayan temple. It is dedicated to Lord Badrinath who is the presiding deity here. The chief deity is flanked by Lord Kubera and Narnarayan on either side. A number of other deities are also worshipped here- Lord Ganesh, Lord Shiva, Lord Hanuman, and Goddess Lakshmi. The main festival celebrated here is Baisakhi which draws a number of devotees from far and wide.
The Poddareshwar Ram Mandir was built in 1923.It is a beautiful temple that has been constructed out of marble and sandstone. The temple is dedicated to Lord Rama, and along with him, Sita, Lakshman and Lord Shiva are also worshipped here. The major festivals celebrated here are the Ramnavami, Mahashivratri, Janmashtami, Vinayak Chaturthi and Hanuman Jayanti.
 In the south-east of the city in Sakkardara district is Tajabad Sharif, a square Muslim tomb with arches on all sides supported by four giant pillars crowned by minarets, over which rises a large round dome. It is the tomb of Baba Tajul Aulia, popularly known as Tajabad Sharif Baba Tajauddin.
In the south-east of the city in Sakkardara district is Tajabad Sharif, a square Muslim tomb with arches on all sides supported by four giant pillars crowned by minarets, over which rises a large round dome. It is the tomb of Baba Tajul Aulia, popularly known as Tajabad Sharif Baba Tajauddin.
Between the eastern fort walls and the barracks is the Nav Gaz Ali Baba, believed to be the grave of Nawab Kadar Ali, grandson of Tipu Sultan of Mysore, who was hanged with his associates by the British for their role in the rebellion of 1857.
The Anglican Cathedral of All Saints was designed in 1851 by Lieutenant-General Sir Richard Hieram Sankey and subsequently altered in 1879 by the gifted English architect G. F. Bodley. The later alterations involved lengthening the nave, deepening the transepts and adding a chancel, two vestries and an organ chamber. Nearby is the Roman Catholic Cathedral and school.
The Cenotaphs of th Bhonsla Rajas lie in the Shukrawari quarter, south of the old city.
Though Nagpur is now primarily a modern city with buildings and civic structures built in the latest architectural style, some remnants of a historic past can also be found here in the form of these various monuments.
Tourism in Nagpur District
 Tourism in Nagpur District is all about visiting the various places of varied interest that the district has to offer. There are many places of worship, historical interest as well as natural beauty that the district of Nagpur offers its various tourists. One of the most well known of the tourist spots in Nagpur is the Lotus temple. It is a beautiful Buddhist temple, well known for its construction. With its remarkable, the temple has already received an international award for its construction. Other well known tourist spots in the district include Ramtek, Adasa, Deekshabhoomi, Sitabuldi Fort, Jaadu Mahal, Vishwakarma Nagar etc. The various places of tourism in Nagpur district are discussed below.
Tourism in Nagpur District is all about visiting the various places of varied interest that the district has to offer. There are many places of worship, historical interest as well as natural beauty that the district of Nagpur offers its various tourists. One of the most well known of the tourist spots in Nagpur is the Lotus temple. It is a beautiful Buddhist temple, well known for its construction. With its remarkable, the temple has already received an international award for its construction. Other well known tourist spots in the district include Ramtek, Adasa, Deekshabhoomi, Sitabuldi Fort, Jaadu Mahal, Vishwakarma Nagar etc. The various places of tourism in Nagpur district are discussed below.
Pilgrimage Tourism in Nagpur District
Shri Balaji and Shri Kartikeya Temple Complex
The most popular of Indian deities, Shri Balaji, is the presiding deity in this temple situated in the serene and picturesque surroundings of, Nagpur`s famed Seminary Hills. This temple also houses the idols of Lord Kartikeya who is believed to be the commander of the army of Gods.
Ramtek Mandir
This place has been immortalised by the visit of Lord Rama, Sita and Lakshmana, hence the name Ramtek. The place is also famous as the place where the poet Kalidasa composed his epic `Meghaduta`. The main attractions here are the Ram temple which is more than 600 years old, as well as the Jain temple which has some beautiful carvings and sculptures. Besides the Shri Ram Temple and the Kalidas Memorial, Ramgiri hill and Ramsagar Lake are also located here. Ramtek is about 50 kms from Nagpur.
 Dhapewada
Dhapewada
Dhapewada is situated on the bank of the Chandrabhaga River. The town possesses a notable temple of Vithoba, overlooking the river. It was built by Umaji Aba, Diwan to Raja Baji Rao Bhonsle. Dhapewada is being known as Vidarbha`s Pandharpur.
Adasa
Adasa is a small village in the Nagpur District. The village contains some fine old temples. In the temple of Lord Ganesha, the image consists of a single stone set up so that worshippers may walk around it. On a hill near the village is a temple of Mahadeo with three lingam which are believed to have come out of the ground on their own.
Sri Poddareshwar Ram Mandir
In the year 1923, this beautiful temple was built with marble and sandstone carving work. The three principle characters of the Indian epic, the Ramayana, are the presiding deities.
The Dragon Palace Temple, Kamptee
The magnificent Dragon palace temple is located at Kamptee, satellite township of Nagpur. It is a unique Buddhist temple with attractive architecture and landscape. The temple sprawls on 10 acres of land, and has a serene and beautiful Buddhist prayer centre. A huge idol of Lord Buddha is installed on the first floor of the Meditation hall which is carved out of a single sandalwood block. The temple, with its beautiful architecture, has already received an international award for best concrete structure. The dazzling white walls of the temple signify peace, purity and divinity. Also called the `Lotus Temple`, it stands tall amidst sprawling lush green lawns, dotted with flowering plants and set in an attractive landscape pattern.
 Deekshabhoomi
Deekshabhoomi
Deekshabhoomi is regarded as a pilgrimage centre for the followers of Buddhism. The place started with the construction of a Bhikshu Niwas in 1968, followed by a Postgraduate degree college and finally a majestic towering monument consisting of replicas of the gate of Sanchi Stupa, constructed at a cost of Rs. 6 crores. 5000 Bhikshus can be accommodated in each storey. The diameter and height of the dome is 120 ft. Granite, Marble and Dholpur Sandstone have been used for the construction of this 4000 sq. ft. hall.
Leisure Tourism in Nagpur District
Sitabuldi Fort
A visit to Nagpur is not complete without a visit to this important landmark of the Sitabuldi Fort, nestled on the Twin Mountains. In the year 1857 a British officer, built this fort and since then it has been one of the most interesting destinations in Nagpur.
Nagardhan
Nagardhan is an old town and was formerly of considerable importance as it gave its name to the district. It was founded by a Suryavanshi King, though there are disputed claims of its being established by a King named Nandvardhan belonging to the Shail Dynasty. There is a fort here said to have been built by the Bhonslas with brick walls.
Jaadu Mahal
The Jaadu Mahal is situated at Vishwakarma nagar in Nagpur. The building, literally translating to magic palace, has been constructed by the famous magician on Nagpur, the Late Sunil Bhavsar. This is perhaps the only magic palace in the country with its unique construction. In the premises of the palaces, various magic tricks are demonstrated. The Jaadu Mahal remains open even on sundays. It is a real treat to visit this gem of Nagpur.
These are the various places of tourism located in the district of Nagpur.
Nature Tourism in Nagpur District
 Nature tourism in Nagpur District is a truly relaxing experience. The district offers a lot to its tourists in terms of natural beauty and picturesque sights. Of the various places of natural beauty located here, the most refreshing sites are the various lakes and gardens located here. There are beautiful lakes in the district, such as Khindsi, Ambazari surrounded by lush gardens. Pench National Park and Totladoh are among the other beautiful parks in the district. One of the popular sites is the Maharaj Baug and Zoo, which is a garden that has been converted into a botanical garden and zoo.
Nature tourism in Nagpur District is a truly relaxing experience. The district offers a lot to its tourists in terms of natural beauty and picturesque sights. Of the various places of natural beauty located here, the most refreshing sites are the various lakes and gardens located here. There are beautiful lakes in the district, such as Khindsi, Ambazari surrounded by lush gardens. Pench National Park and Totladoh are among the other beautiful parks in the district. One of the popular sites is the Maharaj Baug and Zoo, which is a garden that has been converted into a botanical garden and zoo.
The various places of nature tourism offered by the district of Nagpur are discussed below.
Ambazari
The Ambazari Lake is spread over 15.4 sq. kms on the western outskirts of the city. The lake is surrounded by a picturesque garden. The garden has been developed as a model garden by the Nagpur Municipal Corporation. Interesting outdoor activities can be availed of here in the form of boating facilities. There is a beautiful musical fountain at this place too which adds to the charm of the place.
Totladoh
The Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru National Park is situated in this area. It is surrounded by the Satpura mountain range which provides for a rather pleasant climate. This National Park is best known for animal viewing, bird watching and trekking. There is also situated a hydroelectric project here, a joint venture of the Government of Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
 Khekranala
Khekranala
Khekranala is a dam site situated in the Khapra range forest. This area is palm green and provides a view of the finest natural beauty. It has a bracing climate and healthy environment round the year. The water reservoir surrounded by thick forest on two sides.
Nawegaon bandh
Nawegaon, Vidarbha`s most popular forest resort, is the ultimate adventure spot. It is said to have been built by Kolu Patel Kohli in the beginning of the 18th century. There`s a picturesque lake set in the midst of hill ranges with watch towers that enables the tourists to view wildlife. A must-visit when on a trip here are the deer park, the Dr. Salim Ali Bird Sanctuary, the three beautiful gardens and the Children`s Park. Almost 60 percent of the bird species found in Maharashtra have been recorded in Nawegaon. Animals include the leopard, sloth bear, gaur, sambar, chital and the langur.
Ambakhori
Situated around 60kms from Nagpur, it is a beautiful site of natural beauty. Waterfalls and a forest are the main attractions. The place is best-visited in winter.
Pench National Park
Situated around 86kms from Nagpur, this National Park is a place good for a day`s visit. It is built around the Pench Irrigation project, a joint venture of the Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh Governments .This park is also known as the Jawaharlal Nehru Udyan.
Khindsi
It is famous mainly for its large and picturesque lake. Boating facilities are also offered. Khindsi is very close to Ramtek, in fact you can combine the two places in a single trip.
Maharaj Baug and Zoo
The erstwhile Bhonsle rulers laid a beautiful garden, which is now known as The Maharaj Baug. It has been converted into a botanical garden housing a zoo containing some rare species of birds and animals.
These are the many places of leisure tourism offered by the district of Nagpur to its tourists.



















