 Slugs are lung-breathing gastropods. They live on land and are almost worldwide in distribution. They are symmetrical animals with a well-defined head and an elongated body narrowing behind into a pointed tail. They have no spiral shell like snails. Slugs are the most common form of mollusc, with over 60,000 species alive today.
Slugs are lung-breathing gastropods. They live on land and are almost worldwide in distribution. They are symmetrical animals with a well-defined head and an elongated body narrowing behind into a pointed tail. They have no spiral shell like snails. Slugs are the most common form of mollusc, with over 60,000 species alive today.
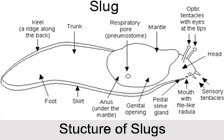
General Features of Slugs
The outside structure of a slug includes the following:
•Tentacles: Like other pulmonate land gastropods, the common of land slugs have two pairs of `feelers` or tentacles on their head. The higher pair is light sensing and has eyespots at the ends, while the lower pair offers the sense of smell. Both pairs are retractable.
•Mantle: On top of the slug, behind the head, there is the saddle-shaped mantle, and under this there are the genital opening and anus. Almost always on the right hand side of the mantle is a respiratory opening, which is easy to notice when release, but difficult to see when closed. This opening is known as the "pneumostome".
•Tail: The part of a slug behind the mantle is called the `tail`.
•Keel:Some species of slugs have a top ridge running over their back along the heart of the tail. This ridge is called a `keel`.
•Foot: The flat bottom side of a slug is called the `foot`. A slug moves by rhythmic waves of muscular contraction on the underside of its foot. It concurrently secretes a layer of mucus that it goes on, which helps stop damage to the foot tissues.
•Vestigial Shell: Most slugs keep remains of their shell, which is usually internalized. This organ usually serves as storage space for calcium salts, often in combination with the digestive glands.
Structure of Slugs
 The bodies of Slugs are made up mainly of water and, without a full-sized shell. Their soft tissues are flat to aridity. They produce protective mucus to stay alive. They cover in damp places in drier conditions. They go through the "torsion" (a 180° twisted of the inner organs) in development. Slugs create two types of mucus - one is skinny and watery, and the other solid and sticky. Body mucus gives some shelter against predators, as it can make the slug solid to pick up and cling to by a bird`s mouth.
The bodies of Slugs are made up mainly of water and, without a full-sized shell. Their soft tissues are flat to aridity. They produce protective mucus to stay alive. They cover in damp places in drier conditions. They go through the "torsion" (a 180° twisted of the inner organs) in development. Slugs create two types of mucus - one is skinny and watery, and the other solid and sticky. Body mucus gives some shelter against predators, as it can make the slug solid to pick up and cling to by a bird`s mouth.
Slugs are "hermaphrodites", having female and male reproductive organs together. Once a slug has placed a mate, they enclose each other. A few days later, the slugs lay about 30 eggs in a hole in the ground.
The largest land snail is the African Achatina achatina. The largest freshwater snails, Pomacea from South America, reach nearly 10 centimetres in diameter, and the largest naval snail, the Australian Syrinx aruanus. It occasionally grows to more than 0.6 metre (two feet). The longest snail perhaps is Parenteroxenos doglieli, which lives as a leech in the body cavity of a sea cucumber: it grows to be almost 130 centimetres (50 inches) in length.
Food Habits of Slugs
Slugs eat rotting plant material and fungi. Most carnivorous slugs on occasion also eat dead specimens of their own type. They can feed on a broad range of vegetables and herbs, including flowers and fruits. They also feed on carrots, peas, apples and cabbage that are offered as a one and only food source. Other species pertaining to different genus, such as Agaricus, Pleurocybella and Russula are also eaten by slugs. Depending on the species and other aspects, slugs eat only fungi at precise stages of development.
Nature of Slugs
 Slugs can contract their body, making themselves harder, more compact and still and round. By doing this, they become firmly attached to the substrate. By doing this, they become firmly attached to the substrate. Some slugs can self-amputate a part of their tail to help the slug run off from a predator. Some slug species hole up underground during the winter in temperate climates, but in other species, the adults die in the autumn. Slugs are more active by night than by day, and they seek moisture.
Slugs can contract their body, making themselves harder, more compact and still and round. By doing this, they become firmly attached to the substrate. By doing this, they become firmly attached to the substrate. Some slugs can self-amputate a part of their tail to help the slug run off from a predator. Some slug species hole up underground during the winter in temperate climates, but in other species, the adults die in the autumn. Slugs are more active by night than by day, and they seek moisture.
Slugs are sensitive to smell. Any putrid vegetable or decaying animal at once attracts them. Sea slugs are highly elastic. They can shrink to half a centimetre and expand up to 8 centimetres. Most of them are far more richly coloured than any of the land slugs and some are of truly remarkable appearance. Their ornamental and colourful appendages serve the purpose of protecting them from their enemies by harmonizing with their surroundings.
Along the Indian shores, especially in the waters of Pamban, Krusadi and Shingle Islands, several attractive and curious species of sea slugs are very common. They are found attached to the underside of stones and rocks in shallows abundant in seaweeds and corals. The more interesting among them are; the plumed types - Bornella and Eubronchus, the filamentose Hervia and the star-marked Dendradoris and Trippa.



















