Trataka is used in yoga for enhancing concentration. In this practice, the practitioner gazes at the smallest object comfortably with steady eyes until tears roll down. Moreover, trataka cures eye diseases and prevents laziness and it is one of the six cleansing processes (Kriyas) of hatha yoga. It is performed with the eyes.
Trataka is used in yoga for enhancing concentration. In this practice, the practitioner gazes at the smallest object comfortably with steady eyes until tears roll down. Moreover, trataka cures eye diseases and prevents laziness and it is one of the six cleansing processes (Kriyas) of hatha yoga. It is performed with the eyes.
Traditionally, there are three types of trataka available for the practice. They are Antar trataka, Madhya trataka and Bahya trataka.
Antar Trataka
In this trataka, one has to experience as if he is gazing in between the two eyebrows (Bhrumadhya drishti) or heart, navel or any other such internal organ with closed eyes.
Madhya Trataka
In Madhya trataka, the practitioner still gazes on bhrumadhya or nasagra (tip of nose) or any near object made of metal or stone or even on Aum written on paper, or single dot in black colour, with open eyes.
Bahya Trataka
In this trataka, one has to fix the gaze on the distant object like Moon, rising Sun or illumined planet.
Technique of Trataka
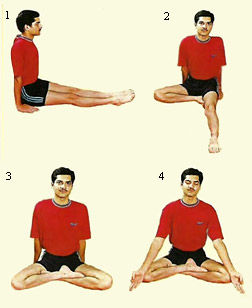
Trataka is done preferably in padmasana (lotus posture) or ardha-padmasana on the ground. It can also be done in sukhasana (comfortable sitting posture) but with the straight back or spinal column. A lamp is placed in the level of the eyes at about one meter distance. Now with the relaxed mind one should gaze at the bright portion of the flame, without blinking, till tears appear in the eyes and roll down on the cheeks. This is the endpoint of trataka. After this, eyes should be closed gently. The practitioner then should sit quietly for 3-5 minutes and then open his eyes slowly. If required, one may repeat the technique once again. It is recommended that after this the practitioner should wash his face and eyes with water.
The duration of trataka from the beginning till the appearance of tears varies from person to person. It also depends on the state of mind of the individual. The duration of trataka is less if the practitioner is relaxed and if the practitioner is tensed or disturbed, he may take more time to finish. Generally, in normal individuals trataka is finished within 3-5 minutes. Some individuals have been observed to take even more than 12 minutes.
Physiology of Trataka
It has been found that soon after trataka is over, the parasympathetic predominance is established as indicated by lowering of heart rate and respiration rate as well as an increase in amplitude of plethysmogram (vasodilatation). That means a peripheral blood circulation is increased after trataka. Emotional balance or stability is restored and a degree of relaxation is increased as indicated by the production of well-modulated train of alpha frequency after trataka.
 Trataka acts as a catharsis, bringing out repressed or suppressed wishes or desires and eliminating them from the subconscious level. This is the process of purification. After this, the practitioner experiences psycho-physiological relaxation and a feeling of calmness and lightness. One pointed concentration is improved, and attention fluctuations are reduced. It has been found that the neurotic tendencies such as anger, short temper, suspicion, irritation and resentment are reduced after trataka practice is done for one month. Anxiety is also reduced. In this way, trataka is a very important practice to remove impurities or blockages in the neural network and to prepare the individual for meditation.
Trataka acts as a catharsis, bringing out repressed or suppressed wishes or desires and eliminating them from the subconscious level. This is the process of purification. After this, the practitioner experiences psycho-physiological relaxation and a feeling of calmness and lightness. One pointed concentration is improved, and attention fluctuations are reduced. It has been found that the neurotic tendencies such as anger, short temper, suspicion, irritation and resentment are reduced after trataka practice is done for one month. Anxiety is also reduced. In this way, trataka is a very important practice to remove impurities or blockages in the neural network and to prepare the individual for meditation.
Benefits of Trataka
Hatha yoga mentions that by performing trataka regularly, the eye disorders are cured and the lethargy is overcome. Such regular practice of trataka facilitates practice of Shambhavi mudra, which leads to the process of Dharana (contemplation) and the practitioner gets the great vision. This description from Gherand Samhita indicates that the trataka is closely concerned with the training of the nervous system in a particular direction. Mental tensions are also reduced after the practice of trataka and one feels very calm and quiet. Peacefulness or pleasantness is the feeling normally experienced by the practitioners after trataka. The sleep pattern is improved within a few days practice of trataka. The period of elimination of emotional tensions as well as the magnitude of relaxation depends upon the basic nature and composition of the person. Sincere and severe practice of trataka is mandatory for those who are desirous of learning hypnosis.
Precautions
•While practicing Trataka, ghee lamp should be used. Trataka should not be performed on flickering flame.
•Hypertensive persons should perform trataka after the practice of Shavasana.
•Persons having too much emotional or mental disturbance should not practice trataka unless they go through other preliminary asanas and kriyas.
•Never rub eyes after Trataka.
•Trataka should not be repeated more than three times in one sitting.
•The practitioner should not try to read or watch TV immediately after Trataka.