 Macaranga Indica is a small or medium-sized evergreen tree with smooth grey bark and stout branch-lets that are marked with leaf scars. The plant is also known as Macaranga flexuosa wt in botany and it reaches a height of up to 20 metres. The plant has different names in various Indian languages. The Kannada name of the plant is Bettadavare and it is called as `Puthata-mara` in Malayalam. The Tamil speaking people call the plant as `Vattathamarei` and `Vuttuttamara`.
Macaranga Indica is a small or medium-sized evergreen tree with smooth grey bark and stout branch-lets that are marked with leaf scars. The plant is also known as Macaranga flexuosa wt in botany and it reaches a height of up to 20 metres. The plant has different names in various Indian languages. The Kannada name of the plant is Bettadavare and it is called as `Puthata-mara` in Malayalam. The Tamil speaking people call the plant as `Vattathamarei` and `Vuttuttamara`.
Macaranga Indica is a native to India and it is distributed southwards and eastwards. The plant is mostly found in moist secondary deciduous forests in the outer Himalayas from Kumaon (northern Uttar Pradesh) in India. The plant is grown at altitudes of 900-1500 m in the states of West Bengal, Bihar and also in the north-eastern states. It is found in the Western Ghats as well. In south-western India, the plant usually flowers and fruits from the month of October to December.
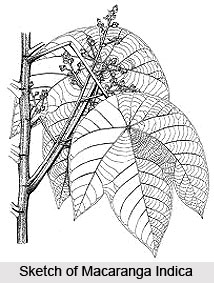
The young parts of the branch-lets of Macaranga Indica are clothed with rusty deciduous tomentum. The plant`s orbicular-ovate leaves are 12-25 cm long and 8-14 cm wide and they are also broadly peltate. The apex is acute or cuspidate-acuminate and the base is rounded. The margins are entire or minutely toothed and the upper surface of the leaves are brown pubescent when young. The leaves are pubescent and thickly covered with minute dark red glands beneath. The plant`s petioles are 7.5-15 cm long and the ovate, acuminate and reflexed stipules are deciduous. The much-branched and densely pubescent male flowers of the plant have a length of up to 12 cm and they are also minute, with a diameter of 0.4 mm. The sessile flowers are fascicled at intervals along axis. On the other hand, the female flowers are longer and denser than the male ones and they are also stalked. The fruit (capsule) of Macaranga Indica is quite small and is less than 0.6 cm. The fruit comprises 2 globose and glandular cocci.
Macaranga Indica has a few medicinal properties and uses. Different parts of the plant are used quite frequently in various traditional medicines. Sometimes, a gum exuded from the cut branches, petiole bases, young shoots and fruits of the plant are applied externally to get relief from venereal sores. The other parts of the plant are also used in different ways to treat various ailments.



















