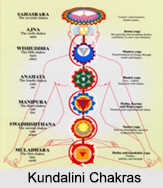
 Kundalini raising that occurs prior to adequate purification and spiritual awareness is considered premature, producing many different symptoms. Symptoms are dissimilar in each individual because each person has blocks, or energy concentrations, in diverse areas. The following are the different symptoms of Kundalini release:
Kundalini raising that occurs prior to adequate purification and spiritual awareness is considered premature, producing many different symptoms. Symptoms are dissimilar in each individual because each person has blocks, or energy concentrations, in diverse areas. The following are the different symptoms of Kundalini release:
•In addition to short periods of intensified awareness and states of paradise or enlightenment, there may be times of extreme dreariness or gloominess, unpredictable behaviour, unexplainable illness, loss of memory, feelings of stupefaction with oneself, friends, work or the world in general.
•If the liver is affected, the skin may take on a yellowish colour, a roughly dirty look, due to the release of negativity; or some areas of the body may take on a reddish or bluish cast. There may be other shadings relating to energy concentrations of different vibrational rates. Each vibrational rate has its own colour.
•A person may look old, tired, or ill but a few hours later, looks younger and full of vivacity, or the reverse.
•Another symptom of premature Kundalini rising is a blackish look to the nails of the big toes due to activated reflexes in the big toes that relate to the pineal gland.
•At times there may be a fluttering feeling as the muscles relax and release more energy into the nerve endings.
•There may be an internal illness or pressure, a wanting to "vomit" out anything in order to eject the extra energy.
•There may be nosebleeds. Kundalini in its stronger states can tear human tissue.
•There may also be involuntary movements or shaking of the body; illness may develop from Kundalini cleansings, many times remedied simply by changing the energy patterns.
A warning is however given, to consult a doctor when changing the patterns does not help; when a problem appears to be medical, there should not be further hesitation to seek medical assistance.
Reactions in Kundalini Release
It is very difficult to know just how a particular person will react. One may compare the Kundalini, when a huge number of waves are released all at once, to a garden hose turned on full force- if the spine is clear and straight, the force flows through to the top of the head unhampered; if distorted, or bent in some fashion, the free flow is stopped or hampered and the energy goes into the nearest area. A very sway-backed person, for instance, will dump this energy into the belly and solar plexus area, causing passionate emotions. A force that continues over a period of time may result in physical injury, stomach disorders, or even ulcers. Obstruction in the brain causes loss of memory and/or mental distortions.
Due to the diverse symptoms and shortage of information about Kundalini, the blame for improper and excessive release is commonly misplaced. People may feel hypochondriacal with all their different aches and pains. At times they may feel ill but not actually be ill. They may feel they do not have long to live, but at the same time feel perfectly all right. Confusion is rampant when unrehearsed people experience unwarranted Kundalini release. Changes of moods, attitudes and dietary, colour and style preferences are common. Some people will experience schizophrenic symptoms as the Kundalini releases energy from strong but un-integrated past-life personalities; it may be that there was little relationship between the soul and the personality and the personality remained separate, to be integrated during another life.
Kundalini will seek to cleanse all locked-in memories, whether physical, emotional or mental, whether of traumatic or ecstatic events. Instinctively or through meditations, people can relieve experiences from childhood or past lives. Power trips, mysterious anger, base or distorted sexual fantasies or feelings these are all part of personal demons, secreted away only to be brought to light by the cleansing of the Kundalini. It helps not to be frightened to face the memories sheltered within. When all blocks are released, the Kundalini flows through unrestrained, polishing the cells and thus allowing the prana or divine and universal energy to come into the system in pure, strong form.