Pilgrimage of Arjuna, Ashvamedhika Parva, Mahabharata
Description: Pilgrimage of Arjuna brought about a number of marriages of this Pandava brother. All the other wives besides Draupadi were acquired by Arjuna during his pilgrimage and by way of marriage Arjuna had established digvijay in almost every part of the world.
Pilgrimage of Arjuna, Ashvamedhika Parva, Mahabharata
Description: Pilgrimage of Arjuna brought about a number of marriages of this Pandava brother. All the other wives besides Draupadi were acquired by Arjuna during his pilgrimage and by way of marriage Arjuna had established digvijay in almost every part of the world.
Pilgrimage of Arjuna is closely associated with several of his marriages in different directions. Arjuna`s marriages occur during the "pilgrimage" he takes after he has violated an agreement with his brothers concerning the proprieties of their relations with Draupadi. Arjuna`s penalty is to undertake five years in exile as a brahmacharin, or religious student. Normally this would require celibacy, but Arjuna`s brahmacharya seems the occasion-even in the Mahabharata- for the development of a humorous folklore on the temptations of this "stage of life." During the time of his pilgrimage time after time he covets an "impossible" match and calls upon Krishna; either or both of them don a disguise and finally Krishna`s last trick works and Arjuna gets the girl.
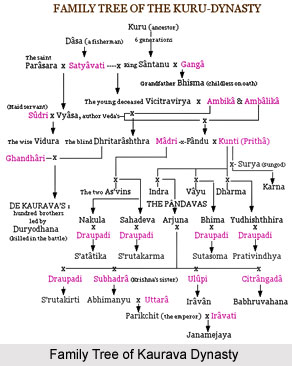
Keeping in the mind the order of Arjuna`s pilgrimage his order of wives were as follows Ulupi, Chitrangada, Subhadra, Pavalakkoti, Bhagavati, and Ellamma. Arjuna thus adds five wives during his pilgrimage. All five, including Ulupi and Subhadra, were from Tamil Nadu.
There is a certain geographical symbolism in the marriages which Arjuna takes place during his pilgrimage. For instance Draupadi is from the centre (Gingee as Hastinapura), Alli is from the south, and Subhadra from a north that is now actually south of Gingee. But beyond this, a cosmic structure is also evident. Arjuna marries Pokavati, a princess from the underworld, to secure the wealth needed for the Pandavas to perform the expensive Rajasuya. His marriage to "Lightning Light," Minnaloli, the daughter of the Cloud King and sister of the Thunder King, is surely a link with the heavenly forces that guarantee prosperous rainfalls. He is thus in effect a symbolic king of Tamil Nadu, of the four directions, and of the resources of the three worlds (heaven, earth, and underworld). Indeed, it is in this expansion of Arjuna`s zones of conquest that the Draupadi cult Mahabharata deals most directly with the theme of movement through the triple world.
Finally it can be said that during the pilgrimage period Arjuna by way of matrimonial alliance made it sure that he establishes control over the triple world so that the Pandvas can have an unperturbed control over their kingdoms.