 Kapalbhati is a technique for purification and a type of Pranayama. The word "Kapala" means the skull, while "Bhati" has been deduced from the Sanskrit word which means to shine. As a whole, Kapalbhati means an exercise that causes the "skull to shine" brightly. It is one of the six cleansing processes of Shatkriyas described in Hatha Yoga. This purification process involves breathing apparatus, nasal passages and the sinuses in the skull that are cleansed effectively.
Kapalbhati is a technique for purification and a type of Pranayama. The word "Kapala" means the skull, while "Bhati" has been deduced from the Sanskrit word which means to shine. As a whole, Kapalbhati means an exercise that causes the "skull to shine" brightly. It is one of the six cleansing processes of Shatkriyas described in Hatha Yoga. This purification process involves breathing apparatus, nasal passages and the sinuses in the skull that are cleansed effectively.
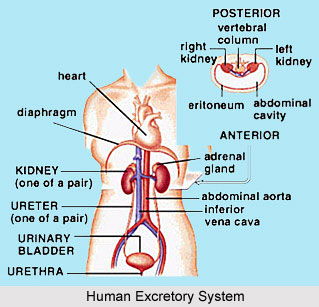
The specific organs or the parts of the body are cleaned by this practice. Yoga believes that there are not only physical but mental or psychological impurities (Malas) also, which cause blockages in the function of the nervous system. If they are not thrown out, they would create imbalance in different functions and ultimately prepare a base for various diseases like asthma, insomnia, acidity and kidney stone.
Types of Kapalbhati
There are total six varieties of Kapalbhati which are mostly practiced by the people in general. In "Gherand Samhita", three diverse varieties of Kapalbhati have been mentioned. All these varieties are commonly categorized according to their capacity of cleansing the nasal passages that are located in the human skull.
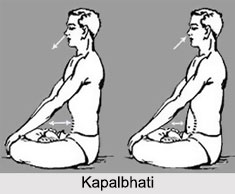
Technique of Kapalbhati
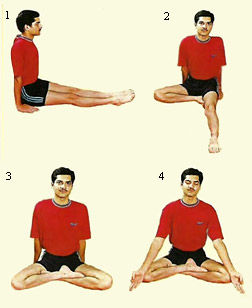
 A vigorous practice of Kapalbhati, even for a few minutes, makes almost every tissue in the human body vibrate. The most preferred posture advised for Kapalbhati exercise is to adopt the "lotus pose" as it has to be practiced vigorously and over a good length of time. The position of the hands must be on the knees making "Jnana Mudra". Sometimes it may even be placed in front of the outer abdomen. Kapalabhati is indeed a breathing exercise where various breathing techniques are moulded to soothe the Yoga practitioners. During Kapalbhati one needs to expel breaths of air as many rounds as one desires and also is competent enough to perform. Kapalbhati, thus, is a breathing exercise of the abdomen or diaphragm in which abrupt ejections of breath are involved.
A vigorous practice of Kapalbhati, even for a few minutes, makes almost every tissue in the human body vibrate. The most preferred posture advised for Kapalbhati exercise is to adopt the "lotus pose" as it has to be practiced vigorously and over a good length of time. The position of the hands must be on the knees making "Jnana Mudra". Sometimes it may even be placed in front of the outer abdomen. Kapalabhati is indeed a breathing exercise where various breathing techniques are moulded to soothe the Yoga practitioners. During Kapalbhati one needs to expel breaths of air as many rounds as one desires and also is competent enough to perform. Kapalbhati, thus, is a breathing exercise of the abdomen or diaphragm in which abrupt ejections of breath are involved.
Benefits of Kapalbhati
There are some physiological effects of Kapalbhati which are as follows;
•The respiration obviously becomes shallow in nature.
•The tidal volume decreases. In normal breathing it is 450-500 ml per breath while in Kapalbhati the tidal volume has been found to be only 150-200 ml per breathing cycle.
•Minute ventilation (MV), increases about three times more than that in the normal breathing due to increased breathing rate. In normal breathing MV is 7.5 litres per minute, while in Kapalbhati MV is about 20.5 litres per minute.
•The Oxygen consumption increases due to increased work of breathing and consequently, Carbon dioxide is eliminated in large quantity from the blood.
•Kapalbhati not only clears the respiratory passage and keeps it free from impurities and mucous etc., but also stimulates the nerves in the abdominal (navel) region and in the skull.
•It produces a peculiar awareness in the forehead region and enhances the effects of Bhrumadhya Drishti (gazing between the two eyebrows).
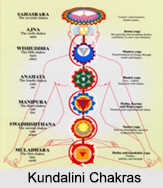
•It also helps in awakening the Kundalini power.
•It gives excellent massage to the abdominal organs and improves digestion.
For all these reasons it seems very practical that the practice of Kapalbhati precedes the Kumbhaka phase of Bhastrika Pranayama. A practitioner feels more energetic and fresh even after a short practice of Kapalbhati.
Precautions for Kapalbhati
A hypertensive or a heart patient is advised not to practice Kapalbhati. The heart rate increases slightly by 15-20 beats per minute and systolic blood pressure also increases by 7-10 mmHg. During Kapalbhati the peripheral blood flow is also reduced.