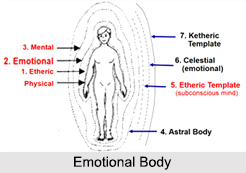
 Emotional Body, the second body has a vibratory rate by which one feels and conveys emotions; it is also a passageway to the divine and when fully developed, serves as a channel for feelings of divine love. The second body is connected to the second chakra, i.e. the Sacral Chakra. This too has two possibilities. One of its natural potential is fear, hate, anger and violence; and the other is the directly opposite conditions of transformation - love, compassion, fearlessness and friendliness.
Emotional Body, the second body has a vibratory rate by which one feels and conveys emotions; it is also a passageway to the divine and when fully developed, serves as a channel for feelings of divine love. The second body is connected to the second chakra, i.e. the Sacral Chakra. This too has two possibilities. One of its natural potential is fear, hate, anger and violence; and the other is the directly opposite conditions of transformation - love, compassion, fearlessness and friendliness.
Fear, violence and anger are all necessary on the second plane; otherwise man could not survive or protect himself. Fear protects him, anger involves him in struggle against others and violence helps him to save himself from the violence of others. All these are qualities of the second body and are necessary for survival. If a person understands the nature of fear he attains fearlessness, and if he understands the nature of violence he attains non-violence. Similarly, by understanding anger he develops the quality of forgiveness. These are the potentials of the second body. Thus, the meditator has to bring about a transformation in the qualities given to him by nature.
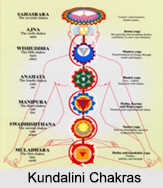
The following illustrations portray the locations of the seven chakra levels of the Emotional Body:
1. Physical Level
Location: stomach.
Function: absorption of emotions.
Too open: susceptible; unwarranted emphasis on feelings.
Blocked: incapability to stomach or digest emotions; incapability to act properly with emotions.
2. Emotional Level
Location: navel.
Function: strongest of the emotional chakras; connecting link with other people on feeling level.
Too open: too emotional; incapability to think distinctly, because of the unnecessary pressure of the emotions.
Blocked: less processed or developed feelings; may be volcanic in nature; though energies may be blocked here, a person would still be exceedingly obsessed with feelings.
3. Mental Level
Location: in the lower back above the root chakra and below the back.
Function: thinking or reasoning about feelings; humour and approval of life.
Too open: overly inattentive with feelings.
Blocked: no humour; taking feelings and self too critically.
4. Intuitional/Compassionate Level
Location: xiphoid process (attached to bottom of breastbone).
Function: classifying what is right or wrong for the person; beginning of conscience energy.
Too open: unnecessary guilt feelings; always trying to rationalise or explain one"s stance or feelings.
Blocked: blocked guilt feelings; may take on others potential without understanding them.
5. Will/ Spirit Level
Location: below the waist on the spine in the back.
Function: emotional strength; helps to equalise emotions; helps in the feeling of having backbone.
Too open: pushing one"s will on others through emotional means; terribly forceful.
Blocked: weak willed; easily influenced emotional about others.
6. Soul Level
Two Locations: both sides of compassionate heart chakra.
Function: helps reinforce one"s ability to give and receive love and to be aware of one"s own “I Amness†in the loving process.
Too open: may feel an extravagant need to love others or be loved by others.
Blocked: not daring to love or not feeling worthy to love or be loved; blocks on the right side pertain to attitudes about loving; blocks on the left side pertains to feelings about loving.
7. Divine Level
Location: compassionate heart chakra (middle of upper chest).
Function: feeling unity of all levels; consolidation of emotions for balance; equilibrium; love, compassion and understanding of others.
Too open: exceptionally concerned about loving enough; about doing enough for others; a person may feel wiped out.
Blocked: hard hearted; closed; afraid to love.