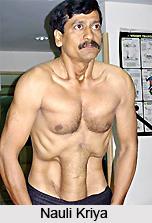
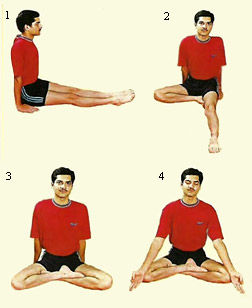
The different kinds of Kumbhaka are an extension of the basic breathing exercise. While doing Surya bhedana air should be drawn in slowly, through the right nostril. Thereafter it should be let out through the left nostril. This asana cleans forehead, removes disorders of Vata as well as worms.
The different kinds of Kumbhaka are an extension of the basic breathing exercise. While doing Surya bhedana air should be drawn in slowly, through the right nostril. Thereafter it should be let out through the left nostril. This asana cleans forehead, removes disorders of Vata as well as worms.
While performing Ujjayi air should be drawn in such a way that it goes touching from the throat to the chest thereby making noise while passing. It should be controlled and then let out through the left nostril. This removes phlegm in the throat as well as increases the appetite. The defects of nadi are destroyed.
Sitkari is performed by drawing air through the mouth and the tongue is between the lips. It is believed that the practitioner becomes the destroyer of creation. They are not affected by hunger, thirst sleep or laziness.
In Sitali the tongue is slightly protruding out of lips when the air is drawn inwards. It goes out through nostrils. This is effective in curing enlarging spleen, fever, disorders of bile, hunger and thirst.
In Bhastrika first one needs to sit in Padma asana posture after which the feet is crossed and placed on both thighs. The mouth is closed so that the air passes through the nostrils.
It should be filled up to the lotus of the heart, making noise and touching the throat, the chest and the head. It should be expelled again and filled again and again. The air should be drawn through the right nostril by pressing the thumb against the left side of the nose, thereby closing the left nostril; and when it is filled it should be closed with the fourth finger and kept confined. This should go out through the left nostril. Bhastrika destroys Vata, pitta and phlegm and increases the digestive power.
In Bhramari the air is filled with force and making a peculiar noise and expel it slowly, making noise in the same way.
The Murchha is a process that involves closing the passages with Jalandhar Bandha firmly at the end of Puraka, and drive out the air slowly that gives the mind great comfort.
In Plavini the belly is filled with air and the inside of the body is filled with air, the body floats on the deepest water, like a leaf of a lotus.