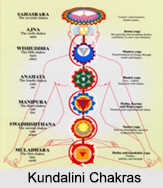
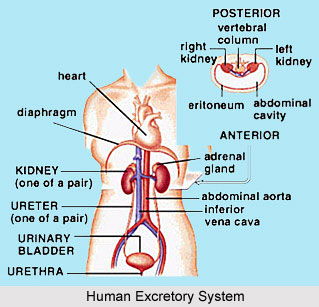
The third brain comprises both the left and right hemispheres. It pertains to the mental body and is concerned with reason, logic, thinking and creativity, acting much like a computer, in that it works with information it has received through experiences and learning. The development of this brain is based moderately on the healthy development of the first and second brains. With an underdeveloped third brain, a person has complexity using reason and logic to apprehend complex situations. He or she may be limited to one point of view and subject to rigidity or prejudice.
It has been mentioned several times that an individual uses about ten percent of their mental capacities. This may be due to underdeveloped first and second brains, inadequate stimulation and laziness (defined as always taking the easy way, not using full perceptive and creative abilities). The outcome is that, people think they are not in touch with all of their mental potentialities, that something is holding back their brain power.
When the first two brains are adequately developed, but the third is not, a person will be excessively concerned with feelings and territory, there will therefore be slight interaction with others. In such a state a person may spend time withy others, but not attentively (the attention is focused on the self). Of course, the identical problems may happen when the first two brains are underdeveloped.
Exceedingly mentally developed people may portray a lack of good old common sense, as in "how can anyone so smart be so dumb?" Each brain has its own consciousness, intelligence, and agenda, each its own perception of how the world operates and its relationship and position proportional to these functions. Each brain may act either independently of or cooperatively with the other brains. Kundalini purification and enhancement not only develops these brains, but also increases their communication.
Children will not function well in school without good reptilian development; they incline either to be more aggressive and quarrelsome, or introvert. Children, who lack a sound sense of survival, possess low-self esteem. Their poorly developed limbic system may cause pitiable study habits, or they may be overly concerned with relationships.