Supta Virasana is a cultural yoga asana that is essentially a supine version of Virasana, a major meditative yoga asana mentioned in several classic yoga texts. It has therapeutic applications in various diseases and intensifies the stretch in the thighs and ankles of its upright version.
Supta Virasana is a cultural yoga asana that is essentially a supine version of Virasana, a major meditative yoga asana mentioned in several classic yoga texts. It has therapeutic applications in various diseases and intensifies the stretch in the thighs and ankles of its upright version.
Meaning of Supta Virasana
Supta means supine or lying down in Sanskrit, and Virasana means hero`s pose. The posture is essentially a supine form of Virasana, hence the name. It also creates new stretches in the groin and the deep hip flexors. The therapeutic applications of the asana includes arthritis, asthma, headache, high blood pressure, respiratory ailments, menstrual discomfort, insomnia and infertility This reclining variation of Virasana is an intermediate pose.
Practice of Supta Virasana
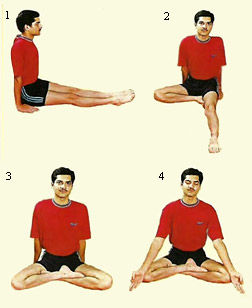
To start with the procedure, one must acquire the posture of Virasana.
* Exhale and lower the back torso toward the floor.
* Lean onto the hands, then the forearms and elbows.
* Once on the elbows, place the hands on the back of the pelvis and release the lower back and upper buttocks by spreading the flesh down toward the tailbone.
* Then finish reclining, either onto the floor or a support.
* If the front ribs jut up sharply toward the ceiling, it`s a sign of tight groins, which pulls the front pelvis toward the knees and causes the belly and lower back to tense.
* Use the hands to press the front ribs down slightly and lift the pubis toward the navel. This should lengthen the lower back and lower it toward the floor. If it doesn`t, raise oneself onto a higher support. Then lay the arms and hands on the floor, angled about 45 degrees from the sides of the torso, palms up.
* Sink the heads of the thighbones deep into the back of the hip sockets. It`s alright to lift the knees a little away from the floor to help soften the groin; in fact, raise the knees a few inches on a thickly folded blanket. One can also allow a little bit of space between the knees as long as thighs remain parallel to each other.
However, do not allow the knees to splay apart wider than the hips - this will cause strain on the hips and lower back. In the beginning, stay in this pose for 30 seconds to 1 minute. Gradually extend the stay to 5 minutes.
To come out, press the forearms against the floor and come onto the hands. Then use the hands to lift the torso into Virasana. While coming up, lead with the sternum, not the head or chin. Come out of Virasana in the recommended manner.
If unable to recline fully on the floor, set one or more folded blankets behind the body to fully support the spine and head. Use as much height as needed to make the position reasonably comfortable.
If the thighs insist on sliding apart in this pose, try one of two short-term solutions: bind the thighs together with a strap positioned around the mid-thighs; or squeeze a 2- to 3-inch thick book between the thighs. In either case be sure to draw the inner groin sharply up into the pelvis. A partner can also help get a feel for the proper movement of the top thighs in this pose.
Effects of Supta Virasana
* Stretches the abdomen, thighs and deep hip flexors, knees, and ankles.
* The arches are strengthened.
* Relieves tired legs.
* Improves digestion.
* Helps relieves the symptoms of menstrual pain.
Precautions
If the practitioner has any serious back, knees, or ankle problems, he or she should avoid this pose unless they have the assistance of an experienced instructor. It is not advisable to perform this pose unless one can sit on the buttocks relatively easily on the floor between the feet.