Introduction
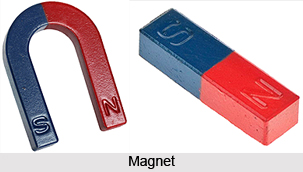 Magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. Magnetism is a common term in the fields of physics, industry and commerce. Although invisible, it is the most significant property of a magnet. There is a simple way to detect a magnetic field by scattering iron filings and observing their pattern. Ferromagnetic substances are referred to the substances that are strongly attracted by a magnet or in which the properties of a magnet can be effectively induced.
Magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. Magnetism is a common term in the fields of physics, industry and commerce. Although invisible, it is the most significant property of a magnet. There is a simple way to detect a magnetic field by scattering iron filings and observing their pattern. Ferromagnetic substances are referred to the substances that are strongly attracted by a magnet or in which the properties of a magnet can be effectively induced.
Etymology of Magnet
The magnet is known by various names in different languages. The original iron-ore, which possessed the attracting power and was natural magnet, was named "Magnetite". It was also known as Loadstone or Lodestone. In Hindi, magnet is known as "Chumbak" or a kissing stone.
Types of Magnets
 The natural and artificial magnets are the two broad types of magnets.
The natural and artificial magnets are the two broad types of magnets.
Natural Magnets
Natural magnets are composed of the substances created by nature, which have the property of attraction. The earth itself is considered to be the biggest natural magnet. Some other natural magnets are iron ore, magnetite and other iron-pyrites, etc. These magnets are composed of iron and oxygen and also have the property of attracting iron filings.
The force of these natural magnets cannot be increased or decreased as per one`s wish or requirement. It remains the same always. Therefore, the use of the natural magnets is very restricted.
Artificial Magnets
The man-made magnets are known as artificial magnets. The force of the artificial magnets can be increased or decreased at different degrees and can be manufactured in various designs. The artificial magnets can again be divided into two main categories: Electromagnets and Permanent magnets.
 Electromagnets- The electromagnets work when electricity is applied to them and without electricity they have no power of their own to act. These magnets are extremely strong as they are composed by placing a metal core inside a coil of wire carrying an electric current. Electromagnets are most useful when a magnet must be switched on and off. The ideal example is the large cranes used to lift cables and rods in construction.
Electromagnets- The electromagnets work when electricity is applied to them and without electricity they have no power of their own to act. These magnets are extremely strong as they are composed by placing a metal core inside a coil of wire carrying an electric current. Electromagnets are most useful when a magnet must be switched on and off. The ideal example is the large cranes used to lift cables and rods in construction.
Permanent Magnets - The permanent magnets remain permanently magnetised once they are charged with electric current and can be used without electricity applied to them every time they are put to use. The permanent magnets do not lose their magnetism if they are properly preserved with keepers attached to them for many years. These magnets are usually composed of ferromagnetic material that comprises of atoms and molecules that each have a magnetic field and are positioned to reinforce each other. An everyday example is the magnet on refrigerator which is used to hold notes on a refrigerator door.
Permanent magnets are further classified into four types based on their composition including `Neodymium Iron Boron`, `Samarium Cobalt`, `Alnico` and `Ceramic` or `Ferrite`.
There are some commonly used shapes and designs of the permanent magnets which are as follows:
Bar magnets
Cylindrical solid magnet
Cylindrical magnets with holes
Ring magnets
Rectangular magnets with holes and without holes
Chuck magnets
Arc or Crescent magnets
U-shaped magnets
Horse-shoe magnets
Square magnets with holes or without holes
Cup shape covered magnets
The sizes of these magnets differ as per the requirements and the purposes for which they are made.
Ceramic Magnets
 Ceramic magnets are made from synthetic material and are also called ceramic ferrite or graphite magnets. These are manufactured from oxides of Ferric and Barium (or Strontium) with certain doping agents, which differ from manufacturer to manufacturer.
Ceramic magnets are made from synthetic material and are also called ceramic ferrite or graphite magnets. These are manufactured from oxides of Ferric and Barium (or Strontium) with certain doping agents, which differ from manufacturer to manufacturer.
The different uses of Ceramic magnets are:
•These are used in the communicative materials such as in loud speakers, microphones, bells, inductors and receivers.
•The electrical materials like cycle dynamos, D. C. (Small) motors, instruments and toy-motors also use the ceramic magnets.
•The electronics items like the calculators, computers and tabulators uses the ceramic magnets.
•The ceramic magnets are used in transportation items such as car radios, aerial motors and dynamos for autos, magnetoes for motor cycles and scooters.
•Some other miscellaneous use of ceramic magnets can be seen in belts, door-latches, filters, magnetic-chucka mngnetic games magnetic separators, novelties, plastic materials and stationery items.
The Ceramic or Ferrite magnets possess the following benefits:
•These have considerably higher coercive force and retention of magnetism for a very long time.
•The ceramic magnets are highly stable to demagnetising field and temperature changes.
•The ceramic magnets have about 60 per cent weight as compared to metallic magnets.
•These are available at lower costs.
•No `keepers` necessary for long preservation of the ceramic magnets.
But the ceramic magnets are very fragile in nature and can break easily if falls down. Therefore, excellent care should be taken of these types of magnets especially to avoid chipping of sharp edges or corners.
Classification of Magnetic Materials
 The permanent magnets are made from a very wide range of magnetic materials. These materials vary in the nature of their elements and their composition. Each of these magnetic materials has its own values, characteristics and consequently its own uses.
The permanent magnets are made from a very wide range of magnetic materials. These materials vary in the nature of their elements and their composition. Each of these magnetic materials has its own values, characteristics and consequently its own uses.
Alnico is the most commonly used alloy in the manufacture of permanent magnets. It consists of Aluminium, Nickel, Iron and Cobalt. The cobalt is costlier than the others and Iron is the cheapest of all.
The magnetic materials or magnetic substances are the different metallic alloys from which magnets are made. Depending on their nature and content, the magnetic materials are broadly classified in three main categories:
* Ferromagnetic material
* Paramagnetic material and
* Diamagnetic material
Ferromagnetic material:
The ferromagnetic materials have very large values of magnetic permeability. They have the highest degree of magnetisation. These are the magnetic materials, which are found to be attracted by magnets or magnetic fields. Iron, Steel, Nickel and Cobalt are ferromagnetic materials.
Again these ferromagnetic materials have their own different properties. For example, the properties of Iron and Steel are different. Soft iron has far greater retentive than steel, but has far less coercive. Steel can retain magnetism for a long time, whereas soft iron loses it earlier. Therefore, soft iron is used in electromagnets and steel is used for permanent magnets.
Paramagnetic material:
The paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted by the magnets when placed in a magnetic field. The paramagnetic materials feel an attractive force towards the strongest part of the field when they are placed in a non-uniform field. Aluminium, Chromium, Copper sulphate, Manganese, Palladium, Platinum, Potassium and Tungsten, etc are examples of paramagnetic materials.
Diamagnetic material:
The diamagnetic materials are not attracted by magnets. They move from stronger to weaker parts of magnetic field and are characterised by negative susceptibility. The examples of diamagnetic materials are Antimony, Bismuth, Copper, Diamond, Gold, Mercury, Silver, Sulphur, Tin and Zinc.
Gases and liquids are also included to the classes of paramagnetic or diamagnetic materials. Air and oxygen are paramagnetic while Alcohol, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and water are diamagnetic in their nature.
Permanent alloy magnets are generally used for door latches, fans, filter coils, gramophones, loud speakers, magnetos, magnetic generators, magnetic separators, meters, radios, scooters, sugar mills, telephones, television receivers, toy-motors, and other novelties.
Power and Qualities of Magnets
 The exact power of these magnets can be measured by a gauss-meter which is a costly instrument. The power and use of magnet is generally calculated by its capacity to lift iron-weight. The more weight a magnet can lift, it is considered more powerful.
The exact power of these magnets can be measured by a gauss-meter which is a costly instrument. The power and use of magnet is generally calculated by its capacity to lift iron-weight. The more weight a magnet can lift, it is considered more powerful.
The power of a child`s horse-shoe magnet is about 300 gauss. This is sold as toys, and has the power of relieving toothache. The magnets having 3000 gauss power are used in treating chronic diseases. It is said that first of all, bar magnets were made. The power of the bar magnet is not very strong as the poles of a bar magnets are at the extreme ends of the magnet, which are placed distantly and oppositely.
The U-shape or Horse-shoe magnets are more powerful and can lift more iron-weight, as these are designed in a way that both the poles may be close to each other. But there is a gap or open space between the two poles of such magnets. Ring magnets or solid cylindrical magnets were made, so that there is no such gap between the two poles. These magnets are still more powerful and can lift heavier weights.
In his book `Magnet and Magnetic Fields`, Dr. A.K. Bhattacharya of Naihati, West Bengal has said that a magnet is a miniature universe as all the forces operating in the universe are seen operating in this little thing also. The magnet has various qualities and properties, which each pole of the magnet possesses separately.
Application of Magnets
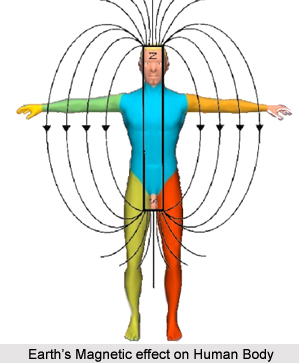
 The magnet has various applications and it works as a medicine and restores the body to its natural state in due course. Its main application is in the healing of various diseases.
The magnet has various applications and it works as a medicine and restores the body to its natural state in due course. Its main application is in the healing of various diseases.
The treatment with the use of magnets effects on body mainly through blood circulatory system. It also effects other systems of the body namely, digestive, nervous, respiratory and urinary. The magnets are also applied in geriatrics, gyneatrics and pediatrics. The application of magnets in treating the different parts of the body for the treatment of different ailments varies from one to another.
After a lot of experiments by the magneto therapists, it is discovered why the magnets failed to show any effect in some cases and even showed adverse effect in some other cases. Actually, the application of different poles on different patients has proved that the two poles of the magnet act in different ways when brought in physical contact with human body. They have different properties, characteristics and effects. If the North Pole is applied then it has a retarding action and controls the bacterial infection and pus and makes ineffective or even kills the cancer cells. The north pole of a magnet also relieves boils, sores, skin rashes, tumours, etc.
On the other hand, the application of South Pole radiates energy, gives warmth and strength to the painful part, increases power of resistance and also reduces swelling and draws pain out of the body. The application of the magnets with low strength or applying them for shorter or longer periods or using incorrect poles may result in negative effect.
Some physicians and scientists believe in applying the use of one single pole of a magnet at a time. The physicians often recommend application of North Pole for 10 minutes and then immediately thereafter South Pole for another 10 minutes like cold and hot packs in Naturopathy. Again others advocate, applying a single pole only where the disease is located in a small portion of the body and to use both the poles when larger parts or whole bodies are affected by any disease. The application of magnet is following the `Single pole theory" which is an old theory while the bipolar application is based on the latest double pole theory of magnetic treatment.
The application of North Pole of a magnet recovers some diseases, which are listed here.
* Arthritis: The application of North Pole of a magnet dissolved the Calcium of joints slowly and thus one can get relief from the disease.
* Bleeding or haemorrhage: The blood loss after birth or due to female weak organs can be decreased by the application of the north pole of a magnet.
* Bleeding of wounds, cuts, bruises due to weak tissues can be relieved by applying the north pole of a magnet in a proper way.
* On applying the South Pole of a magnet on the upper and North Pole on the lower portion ensure best healing from broken bones, broken joints and fractures.
* The North Pole of a magnet can be applied on the burnt portion to get relief. When the pain is less, South Pole is applied to give strength to the tissue and to form flesh over the burnt part.
* Application of North Pole under the right ear down the artery gives relief in high blood pressure.
* If the North Pole of a magnet is applied in infection, it restricts it and heals it naturally.
* Kidney infection or stone can be sometimes removed on applying the north pole of a magnet.
The application of South Pole of a magnet again recovers various diseases, which are given here:
* All kinds of pains, stiffness and weakness in fore limbs, arms, legs, shoulders, hips etc can be relieved by applying the South Pole of a magnet. It also provides strength and life to the limbs.
* Application of South Pole of a magnet helps in poor digestion, gas formation due to more acidity in stomach.
* It also helps in the production of insulin.
* The South Pole of a magnet is applied during prostate enlargement.
* South Pole of a magnet improves hair colouring in limited cases of those persons only whose health is good.
* Application of South Pole of a magnet helps in weak hearts, weak heart muscles, causing murmurs, reduces pulse rate, and heart beats.
* Applying South Pole of a magnet for 10 minutes morning and 10 minutes in the evening strengthens the weak muscles.
* If one is feeling weakness during walking, South Pole of a magnet can be used for a week or 10 days, which provides energy and strength.
The magnetic treatment is usually done in two ways:
Local Treatment:
In this type of magnetic treatment, the selected pole of a magnet is applied to the affected part of the body directly, next to the skin, in close contact with the bare skin. It can be applied over one or two layers of cloth also, without applying pressure on it.
This type of treatment is done if the ailment is localised in a particular part of the body. It may be done when a person suffers from a boil, mumps or in tonsils.
If the patient is suffering from some bacterial action or infection, the North Pole is applied. Again, in the case of pain and swelling where no infection is suspected, the South Pole is used.
In case, a person is having ailments affecting major portion of the body or extending to wider area or covering the whole body, then general magnet treatment is applied. In this type of treatment, two different poles of the magnets of similar shape, size and strength are used.
General Treatment
In general treatment, if the disease is somewhere above the naval, then magnet is applied in the palms of both the hands of the patient. Again, if the disease is in the lower half of the body, then magnets should be applied under the soles of both the feet. If the disease spreads to the whole body, the treatment may be given alternatively under palms and under soles on alternate days or in the morning under the hands and in the evening under the soles if treatment is given twice a day. In this case, the general rule of treatment is to apply the North Pole to the right hand or foot and the South Pole to the left hand or foot.
The extremities of the body, namely, hands and feet, are directly connected with many other important organs of the body. The hands, as well as the feet, have many `Reflexes`. These tie up the different portions of the hands and the feet with various other organs. Hence the palms of hands and the soles of feet are used in general magnetic treatment. Thus, the effect of the treatment goes to all the parts of the body, through internal connections.
Duration of Application of Magnets
 Duration of application of magnets increases in chronic cases of Gout, Paralysis, Poliomyelitis, Rheumatism or Rheumatoid Arthritis, etc. The time of treatment can be gradually increased even up to half-an-hour daily or for 15-20 minutes twice a day.
Duration of application of magnets increases in chronic cases of Gout, Paralysis, Poliomyelitis, Rheumatism or Rheumatoid Arthritis, etc. The time of treatment can be gradually increased even up to half-an-hour daily or for 15-20 minutes twice a day.
The treatment with magnets should be carried out properly or it may not give good result. The application time should be for a particular duration for a particular ailment. Normally, the magnetic treatment should be given for about 10 minutes only once a day.
In the case of the treatments of children, however, the time may be reduced upto 5 minutes a day. It again depends upon the age of the child, the disease and the tenderness and the power of magnets. The magnetic treatment has no fixed course or time-limit. It should be continued till the disease is diminished fully. The disease can be cured in different periods in different cases, depending upon the nature and length of the disease, the age and strength of the patient and the power of magnets to be applied. The effect of the magnetic treatment can be noticed within a few days, in some cases or it may take duration of about two week and in some chronic cases, it may take a few months.
Generally, no irritation is felt in the magnetic treatment. However, if any pain seems to increase in the first instance in any case, it may be due to the fact that the magnet in the process of eliminating the pain draws it out from the internal parts of the body to the skin.
The increase in pain, if felt in any case, settles in a short duration and no separate treatment is considered necessary for reducing it.
Precautions for use of Magnets
 The magnets are applied in the treatment of various diseases among all age groups of patients. But, they should be applied properly with full precaution to get the best effect.
The magnets are applied in the treatment of various diseases among all age groups of patients. But, they should be applied properly with full precaution to get the best effect.
Here, some precautions are given, which should be considered while applying using the magnets.
•The best time for applying magnetic treatment is the morning time. It should be taken after discharging usual routine duties and taking bath but before taking breakfast. In the morning, if it was not taken for some reason, it may be taken in the evening before meals.
•One should not eat or drink anything cold for at least half-an-hour after applying magnets. It is because the magnets create temporary warmth in the body and it is not wise to take anything cold when body is heated. However, hot drinks like milk or tea, etc. can be taken immediately after application.
•Due to the above reason, one should not take bath also for 2 hours after application of strong magnets. Therefore, the magnetic treatment is taken in the morning after taking bath.
•Immediately after taking full meals, strong magnets should not be applied as their application might induce nausea or vomiting in some cases.
•The pregnant ladies and the children should not apply strong magnets. It should not be applied to delicate points in the body such as brain, eyes, heart, etc.
•Application of ordinary magnets does not have any harmful effect. But the application of strong magnets for a long time may result in some trouble, namely, heaviness in head, headache, sleepiness, yawning, tingling in nerves, etc. In that case, the contact of magnets should be discontinued immediately and the patient should take rest.
•If the improper magnet is selected, the resulting sufferings can be permanently removed by laying the outspread hands on a large zinc plate for half-an-hour.
•Homoeopathic medicine `Zincum Metallicum` antidotes the effects of the medicines prepared from the magnet. Therefore, if any adverse effect of application of magnets is noticed, this medicine can also be used as antidote in low potencies.
•The reverse poles of strong flat magnets should never be clapped together. If they are placed somehow face to face, then fingers should not be allowed to come between them as they may get crushed.
•A `keeper` should be kept in-between the two opposite poles of two magnets to join them when they are not being used. Otherwise, the magnetism of them can be lost.
•It is not necessary to remove the gold and other ornaments worn on hands or fingers while using the magnets in palms.
•The watches should be kept away from the contact of the watches unless they are `magnetic proof`.
Magnetisation and Laws of Magnetism
The magnetisation of a material is done by electric current. A material is first magnetised after the magnetic materials are transformed into the required shapes, sizes and designs. Then they can be put to use.
The electromagnetising machines are used these days for magnetising a material, as they are convenient and powerful. By the process of magnetisation, the formed pieces develop North polarity on one end or side and South polarity on the other end or side, in a very short period of time. By the use of a `charger` or `magnetiser`, the magnetisation can be done in few seconds, if one knows the proper operation.
Laws of Magnetism:
After numerous experiments and experiences, the following main principles or laws of magnetism were established:
•Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract eachother:
This is said to be a universal rule. This law of magnets can be experienced by any one by taking two magnets and bringing one marked pole of one magnet near each of the two poles of the other magnet.
•Equality of poles of magnets:
As per this law of magnet, the molecules of magnets are arranged in lines in the magnetised state of a material. There are many like poles on one side of the neutral region as on the other. Therefore, both the poles of every magnet are opposite to each other and have equal and the same strength.
•Inseparability of Poles:
According to this law of magnetism, every bar magnet has two different poles, at its two ends and so has every other type of magnet. If a bar magnet is actually cut into two parts, each part becomes an independent magnet with two opposite poles like the original one. If the smaller magnets are again subdivided still shorter magnets are formed, each having two poles again.
•Retention of Magnetisation:
This law of magnetism says, long bar magnets can retain their magnetism longer than short bar magnets. It is due to the reason of less demagnetising action of the poles on themselves. Again, the Horse-shoe magnets and U-shape magnets retain their magnetisation longer than the bar magnets. Further, the magnets with enlarged pole pieces forming closed rings encased in round or square metal cases retain their magnetisation still longer and become more powerful.
•Demagnetisation and remagnetisation of magnets:
If a magnet is handled very roughly (such as if it is hammered, heated or twisted), then its strength is damaged. It is because such treatment partially breaks down the linear arrangement of molecules. These demagnetised magnets can be remagnetised or recharged to regain their lost strength.
•Safe custody of magnets:
The magnets are usually kept in pairs with two ends of the pieces of soft iron strips placed across them to avoid the automatic demagnetising effect of the poles. These strips are known as `keepers`. The `keeper` completes the magnetic circuit and hence there are no free poles to lose their strength.
Bio-magnetics and Magnetic Effects
 The modern scientific view facilitates verification through proper experimentation. The experimentation does not involve only one time study of a phenomenon. It is done in different laboratories under different circumstances by different researchers. Again, the laboratory experiments are extended to ailing patients in clinics. The conclusion expected is that, every qualified man or woman should be able to duplicate the actual results at any time and location.
The modern scientific view facilitates verification through proper experimentation. The experimentation does not involve only one time study of a phenomenon. It is done in different laboratories under different circumstances by different researchers. Again, the laboratory experiments are extended to ailing patients in clinics. The conclusion expected is that, every qualified man or woman should be able to duplicate the actual results at any time and location.
Countless experiments with magnets have been carried out on plants, bacteria, virus, etc., to ascertain their biological effects. One can also carry out some simple experiments in the home or laboratory or clinic to discern the effectiveness of Bio-magnetism (the biological effects of magnets). Bio-magnetism offers much evidence to prove the claims made regarding its efficacy in health and disease.
Several breakthrough experiments in physical, biological and medical fields have been carried out in the USSR, where the physicists work with engineers, pharmacology`s, chemists and physicians to unravel the facts concerning bio-magnetism. Similarly, several research institutes and research foundations in the USA and Japan have conducted planned research on many important aspects of bio-magnetism. All of these have a vital bearing on magnetic healing.
Several scientists in Japan, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, France, Scandinavia and some places in India and Australia are engaged in active research in this area. As a result, growing number of technical reports are pouring in daily. These studies reveal new bio-magnetic phenomena and also confirm the already existing findings of the researchers on Bio-magnetism. The different effects of magnets can be divided into physical, chemical, biological and purely medical experiments.
Physical and Chemical Effects of Magnetism
It was the use of magnets in the engineering field, which paved way for its extension to the biological and medical fields. It began with a chance discovery when the Russian scientists were confronted with a peculiar and insolvable engineering problem. The boiler feed water pipes carrying the water and the automobile radiators slowly got clogged with the dissolved salts. This resulted in the reduction of their thermal efficiency. In order to increase the lumen of the pipes and the capacity of the radiators, these salts had to be scrubbed off periodically.
The added workload and increased operational cost towards extra consumption of the fuel and lubricants became a matter of concern. Similar problem was confronted by the oil industry, which helplessly watched the deposits of salts in the oil pipes. In order to reach a solution, successful experiments were conducted where; the magnets were employed for dissolution of salts. Almost instinctively, they placed the pipes and the radiators in strong magnetic fields. The reverse process of dissolution of the salts began, which considerably narrowed their burden.
This single and significant discovery of the physical property of the magnets proved to have far-reaching consequences in the medical field where the physicians faced a similar problem of deposition of cholesterol and calcium on the walls of arteries. Arteries are the vessels carrying blood from the heart. The same logic was applied and hypothesis indeed worked in reality. In today`s times, Magnetized water proves to be one of the most effective tools against blood-pressure.
The above experiments led to the conclusion that a magnet brought about some useful changes in fluids. So, the studies were diverted towards the direct effects of magnets on the properties of water and other fluids. A marked change in various characteristics like temperature, density, viscosity, pH, surface tension and electrical conductivity was found considerably.
The magnets were found to cast some favourable effects on properties of water. Some of them were:
* Water acquires more potency
* Conducts magnetism effectively
* Is capable of improved flow, be it in the pipes or the blood vessels.
* The magnetism also favourably affects the sedimentation rate of suspended particles.
The property of electric conductivity is of considerable importance not only in metals and liquids, but also in a number of other substances. Interestingly, the living tissue possesses semiconductor conduction properties. Along with that, sufficient evidence has now been accumulated to show that when a living organism of any species comes into being, the bioelectric phenomenon sets in, which continues until death.
Many scientists consider electrical conductivity an inherent characteristic of vital energy. This is the reason why many scientists are experimenting and establishing the close relation between the phenomenon and human Body. This is where profound physical and chemical effects of magnetism come into play.
Biological Effects of Magnetism:
All possible biological materials like seeds, plants, animals, bacteria, virus, cancer cells, fruits and vegetables, liquors and other fluids such as milk and birds and insects have been the objective of extensive research on Bio magnetism.
The results have again and again established the influence of Magnets in several biological processes. They aid in improving the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by beneficially affecting their enzymatic activity, degeneration of malignant cells and favourably influencing several other biological phenomena. In some or the other degree, all living organisms are affected by magnetism. No living tissue is magnet-proof.
Effects on Animal Life:
The experiments were extended in the higher domain of animal life in order to obtain representative samples. These experiments were significant to evaluate the therapeutic properties of the magnet. Different experiments were conducted to ascertain the effect of magnetic fields on the longevity of different animals. Mice when exposed to the magnetic fields of about 3 to 4 kilogauss daily showed slowing down of the process of aging. In fact, the normal life span of about three years in mice was almost increased by half with the help of the above process. Scientists experimentally doubled the life of the test on houseflies by prolonged feeding with magnetized sugar. Interestingly, experiments on human volunteers brought a hope of longevity possibly upto 400 years through treatment with suitable power of magnetic fields. The observations and the optimism are based on the biochemical changes that occur in the human organism as a result of the exposure to magnetic fields.
The magnet has finally generated the possibility of an answer to the intriguing problem of aging. The favourable biochemical changes brought about by the magnet are closely related to similar effects obtained by other scientists on extraction of the juvenile hormone from the silk-worms as it almost stopped the process of aging in the caterpillars. The subject of experimentation with mice and the intensive studies on the effect of magnets on benign and malignant tumours assumes considerable significance. Several scientists have carried out experiments with different poles of magnets and emerged with a positive assertion that cancer cannot exist in a magnetic field.
The experiment with this outcome of verification was conducted in which white mice were implanted with cancer cells and were allowed to grow. When the manifestations were seen, experiments were conducted by the application of the two poles, separately. With the application of the north pole of the magnet, it was found that the cancerous tumours gradually minimized in size and later disappeared entirely. The exact opposite effect was noticed when the South Pole was applied. The tumours increased rapidly, thereby killing the mice. This opens a new way of treatment. In a foresighted and interesting experiment, the Russians exposed cows to magnetism daily for a certain period and found to their astonishment that they yielded more milk than the normal cows. The magnet thus helps enhance the mammary secretion among mammals.
Effects of Bio Magnetism on Human Beings
Experiments with human volunteers have been conducted to discover the effect of magnetic fields on their body systems. Scientists have also left no stone unturned to detect any ill effects of such exposure.
The Japanese have principally concentrated on the effects of magnets on blood pressure, stiff-shoulders, constipation, and fatigue in both the sexes and preservation of beauty and charm in women. They have been convinced to an extent that a number of companies in Japan are exclusively manufacturing various magnetic articles like bands for blood pressure; bed-pads against constipation, fatigue and dullness; necklaces for women in order to maintain young, freshness and charm; and belts against stiffness and pain in the lumbar region.
The deliberations of one of the bio magnetic symposia held in Japan published in the form of an abstract volume elicit the importance and efficacy of the magnetic bands in relieving stiff shoulders and blood pressure. Though the magnetic tools employed did not yield an immediate or 100% results, still a majority of patients showed remarkable improvement, enough to set magnetic therapy as a mainstream therapy in Japan.
Clinical researches obtained exceptional results in relieving arthritis, pains and muscular fatigue in sports players. Most of the athletes out of the 86 cases showed, marked relief in the symptoms. The experiments were carried out with pairs of permanent magnets used for other healing purposes.
The Russian scientists experimented with magnetized water on dissolution of kidney stones and gall-bladder stones in human beings. The sure results obtained by them in the painful affliction have led to the introduction of magnetized water in many Leningrad clinics where the unfortunate sufferers flock to undergo this simple and promising treatment. The magnetized water helps them in washing out the morbid salts and stones from their bodies.
Utilizing the affinity of Magnets towards Iron, Scientists in the UK have recently found a simple method of separating red blood cells from blood plasma and other blood cells. This has considerable medical implications and has replaced the earlier tedious method of separation of the Red Blood Cells (RBC).
The red blood cells show great affinity towards magnets as they contain about four percent iron in their composition. The notion that a magnet can attract only metallic iron can be broadened by including the property of iron in the ionic form towards magnet. The method of separation of the RBCs comprises the use of a special steel wool filter (fine magnetized wire) over which the entire blood is passed. Standard magnetic field of 17.5 kilogauss was used. The greater paramagnetic susceptibility of the red blood cells helps them to settle down, while the blood plasma and other blood components freely pass over.
This discovery of the effects of magnetism on human blood has paved the way for greater application of this potent tool in therapeutics.
Apart from this, numerous biological experiments have been carried out throughout the world, which give further parameters and proofs of magnetic effects in our body.
Magnets in Vedas
Magnet is said to have very ancient origin and its properties were known to the very ancient Aryans. They have the belief that the magnet, besides having the power of attracting iron, was also gifted with many mystical and curative powers. The Vedas which are the most ancient religious scriptures of the Hindus, also mentioned about the treatment of some diseases with special sand and stones at several places in India.
Among the four Vedas, the Atharva Veda is the basis of the Ayurvedic system of treatment. This particular Veda deals with the treatment of several types of diseases. Some of the mantras of the Atharva Veda can demonstrate well these facts. The use of some articles made of sand and stones (which are thought to be magnets) in the treatment for stoppage of bleeding is cited in the mantras 3 and 4 of Sukta 17 of Kand 1 of Part I of the Atharva Veda.
Again, mantras 2 and 3 of Sukta 35 of Kand 7 of Part 3 of the Atharva Veda deal with the treatment of women with the help of stones and are as discussed below:
The Dictionary meaning of the word `Siktavati` used in the mantras of Sukta 17 and of the word `Ashman` used in the mantras of Sukta 35, mentioned above, are :
As per the Sanskrit-Hindi Dictionary, the word `Sikta` means `sand` and `Siktavati` means `full of sand`. Again the term `Ashman` referred in the Atharva Veda means `stone, Chamak Patthar` and `Ashmana` means `with the stone`.
The Sanskrit-English Dictionary gives the meaning of `Sikta` to be sand, gravel and stone and that of `Ashman` is `stone, rock, precious stone and any instrument of stone. From these discussions, it is obvious that the mantras of Sukta 17 of the Atharva Veda explain about the stoppage of bleeding with some material made of sand and the mantras of Sukta 35 mention about the treatment of women with some kind of stone.
Prof. Friedrich Max Muller of Germany has given the English translations of these Vedic mantras, from where the presence of magnets in the treatment of ailments can be traced. He is one of the most eminent orientalists, who have translated all the four Vedas and many other Sanskrit and Hindi religious books of India. As per his translation of the Vedic mantras, the meaning of mantras 3 and 4 of Sukta 17 respectively goes like below:
•`Of the hundred arteries, and the thousand veins, those in the middle here have indeed stood still, at the same time the ends have ceased to flow`.
•`A great sandy like has passed around you, stand yet still, pray take your case`.
The Mantras 2 and 3 of Sukta 35 are translated like this:
•`Of these hundred entrails of thine, as well as of the thousands canals, of all these have I closed the openings with a stone`.
•`The appeared part of the womb do I place below, there shall come to thee neither off-spring nor birth, I render thee sterile and devoid of off-spring, a stone do I make into a cover for thee`.
All these mantras of Atharva Veda discussed above are related to the treatment of human diseases. From these mantras, it is clear that the treatment was not possible by means of ordinary sand or simple stones and it was done with some special sand and stones having specific therapeutic properties. The usual metallic magnets are made from iron alloys and the ceramic magnets are manufactured from sand, clay, barium and iron oxide. Therefore, the words mentioned in the Vedas like the `Siktavati` (meaning sandy) and `Asitma` (meaning chakmak patthar) are enough to verify that the magnetic stone and its properties were known during Vedic period also. The magnetic elements were used for therapeutic purposes in India since times immemorial.