 An organism requires not only nutrients but also oxygen and respiration is the process by which oxygen is absorbed in the blood, food material is metabolized with oxygen and carbon dioxide and the end-product of this oxidation is eliminated from the body. The transportation of the gases takes place through the circulating blood. The exchange of gases between blood and tissue is known as `internal respiration` and the exchange of gases between the blood and the environment (in lungs) is known as `external respiration.` To keep the respiratory system in healthy condition yoga can be a lot of help. Yoga has pointed out the relationship between the irregularities in the breathing and disturbances or disorders of physical and psychological functions and vice versa. Number of yogic practices, including Pranayama, have a significant influence on the functioning of the respiratory system. Researches are being carried out to find out the relationship between the nasal cycle and various physical and psychological functions, which has been explained to a great extent in the yogic text Shiva Swarodaya.
An organism requires not only nutrients but also oxygen and respiration is the process by which oxygen is absorbed in the blood, food material is metabolized with oxygen and carbon dioxide and the end-product of this oxidation is eliminated from the body. The transportation of the gases takes place through the circulating blood. The exchange of gases between blood and tissue is known as `internal respiration` and the exchange of gases between the blood and the environment (in lungs) is known as `external respiration.` To keep the respiratory system in healthy condition yoga can be a lot of help. Yoga has pointed out the relationship between the irregularities in the breathing and disturbances or disorders of physical and psychological functions and vice versa. Number of yogic practices, including Pranayama, have a significant influence on the functioning of the respiratory system. Researches are being carried out to find out the relationship between the nasal cycle and various physical and psychological functions, which has been explained to a great extent in the yogic text Shiva Swarodaya.
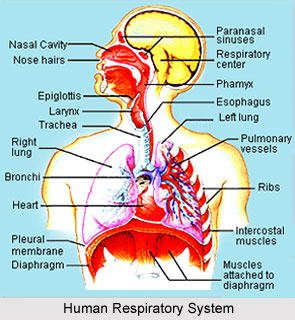
The respiratory passage in a human body begins from the two nostrils. Nostrils lead to right and left nasal cavities that open into the pharynx. This is the upper part of the throat. Buccal cavity or the mouth also opens into the pharynx. Thus, it is a common passage for both, food and air. The larynx or the voice box is a short passage that connects the pharynx with trachea. Larynx also acts as a protective sphincter to prevent solids and liquids from entering into the bronchi and lungs. Its major function is production of the sound. The trachea or the windpipe is a tubular air passage starting from the larynx. At the length of about 12 centimeters, it splits up into right and left branches called bronchi. Trachea lies anterior to the esophagus. The wall of the trachea is composed of smooth muscles; elastic connective tissue and C-shaped horizontal rings of cartilage placed one above the other on the anterior side. Thus, the trachea cannot collapse inward or the air passage is never obstructed mechanically. The bronchi open up into the lungs on right and left sides and divide several times like branches of a tree. The smallest division is bronchiole. This is the end of the conducting portion and starting of the respiratory portion. The air way ends into air sacs called alveoli. Numerous alveoli look like clusters of grapes. Alveoli are in close contact with the microscopic blood capillaries.
Lungs, an important part of the respiratory system, are made up of a spongy substance. Left lung is divided into two lobes and, right lung is divided into three lobes. Two thin membranes cover the lungs. The outer membrane, which is attached to the wall of the thoracic cavity, is called parietal pleura. The inner membrane, which encloses lungs is called visceral pleura. A lubricating fluid between the two membranes prevents friction of the membranes with each other when the lungs expand or reduce to normal during inhalation and exhalation. Thus, lungs are well protected in a cage made up of ribs and a diaphragm.
Composition of the Inspired and Expired Air
| Air | Oxygen | Carbon dioxide | Nitrogen & other gases |
| Inspired air | 0.2013 | 0.0004 | 0.7903 |
| Expired air | 0.163 | 0.04 | 0.797 |
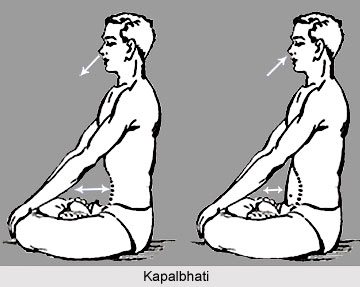 The lungs cannot be empty completely even at the end of maximum and forceful expiration and what remains behind is known as Residual volume (approximately 1 litre). In quiet breathing the amount of air taken in and out of the lungs in known as tidal volume (approximately 500cc) while the maximum amount of air which can be taken in and out of the lungs is known as vital capacity, (approximately 3399 ml). Practicing yoga can increase the vital capacity significantly from 3399 ml to 3443 ml. The amount of the air breathed in one minute is known as minute ventilation. It depends on the respiration rate and the tidal volume. According to researches minute ventilation can be increased by practicing Kapalabhati.
The lungs cannot be empty completely even at the end of maximum and forceful expiration and what remains behind is known as Residual volume (approximately 1 litre). In quiet breathing the amount of air taken in and out of the lungs in known as tidal volume (approximately 500cc) while the maximum amount of air which can be taken in and out of the lungs is known as vital capacity, (approximately 3399 ml). Practicing yoga can increase the vital capacity significantly from 3399 ml to 3443 ml. The amount of the air breathed in one minute is known as minute ventilation. It depends on the respiration rate and the tidal volume. According to researches minute ventilation can be increased by practicing Kapalabhati.