 Haveri district is exactly in the centre of Karnataka equidistant from Bidar District in the far north to Kollegal in the far south. It is bounded by Dharwad district on the north, by Gadag District on north east, by Bellary district on the East, by Davanagere district on the south, by Shimoga on southwest and by Uttar Kannada district on west and north-west. The district is spread across an area of 4848 Sq.Kms, which is 2.53 percent of the area of Karnataka state.
Haveri district is exactly in the centre of Karnataka equidistant from Bidar District in the far north to Kollegal in the far south. It is bounded by Dharwad district on the north, by Gadag District on north east, by Bellary district on the East, by Davanagere district on the south, by Shimoga on southwest and by Uttar Kannada district on west and north-west. The district is spread across an area of 4848 Sq.Kms, which is 2.53 percent of the area of Karnataka state.
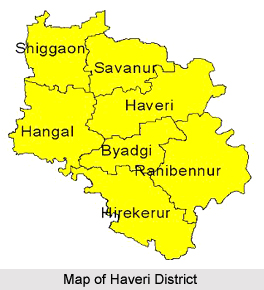
Haveri district along with Gadag district was earlier part of undivided Dharwad district. Owing to the demands of the people, Haveri district was carved out of old Dharwad district and was formed on 24.08.1997. Haveri district has, for decentralized administration, two sub-divisions namely Haveri and Savanur with seven taluks namely Hanagal, Shiggaon, Savanur, Haveri, Byadagi, Hirekerur, and Ranebennur. Haveri being an administrative and political Head Quarters of the District is 335 Kms. from Bengaluru by road and 394 Kms. by rail.
The main rivers flowing through the district are the Varada River, Kumadhvati River, Dharma River and Tungabhadra River. Agriculture forms the main occupation of the district. Consequently, of the total geographical area of 485000 hectares of the region, 360030 hectares are cultivated. The main crops grown here are jowar, cotton, rice, chillies, gram, groundnut, sunflower, sugarcane, maize, wheat, bajra, ragi, pulses and oilseeds. The crops are irrigated from a number of different sources, which forms 11 percent of the total covered area.
Haveri District is known for chilli area and National Level chilli marketing at Byadgi taluk. It has a suitable climatic and soil condition to grow various horticulture crops like mango, sapota, banana, and the vegetables like chilli, tomato, brinjal etc and plantation crops like coconut, betel wine and cashew, flowers like jasmine and chrysanthemum. Ranebennur, Byadgi and Hirekerur taluks are known for vegetable seed production. Apart from this, development and poultry are major activities. Sheep and goat rearing is one of the important allied activities providing supplementary income to the economically weaker sections.



















