 Diagnosis is a very vital aspect of Ayurvedic treatment. Diagnosis according to Ayurveda is to find out the root cause of a disease. Unless the proper diagnosis is done, it is difficult to provide medicine and cure the disease. It is not always necessary that the root cause is internal. Many times the cause may be external. To give permanent relief the root cause has to be removed. Ayurveda not only treats the physical aspect of the disease but it cures the total disease.
Diagnosis is a very vital aspect of Ayurvedic treatment. Diagnosis according to Ayurveda is to find out the root cause of a disease. Unless the proper diagnosis is done, it is difficult to provide medicine and cure the disease. It is not always necessary that the root cause is internal. Many times the cause may be external. To give permanent relief the root cause has to be removed. Ayurveda not only treats the physical aspect of the disease but it cures the total disease.
Disease is a state of disturbed equilibrium of the Doshas, Dhatus, Agnis and Malas. All causative factors of disease internal or external directly or indirectly create an imbalance in these doshas first and only then do the symptoms of the disease manifest. The causative factors can be the food, life style or other activities. Factors affecting the health could be ones diet, life style or daily activities.
In Ayurveda, the diagnosis and treatment of disease is always individual to each patient. All diseases are caused by aggravation of the three doshas i.e. Vata, Pitta and Kapha. This aggravation is caused by the intake of improper diet and an improper lifestyle.
Types of Diagnosis in Ayurveda
The art of diagnosis in Ayurveda can be divided into 2 parts: the inspection of the individual and their constitution and the examination of the progression of the disorder. A very important aspect is the determination of the constitution, which is described as ones ultimate state of health and indicates hereditary tendencies to particular ailments. The constitution is diagnosed by determining the individual"s inherited blueprint and proportion of the elements at the time of birth.
A skilled Ayurvedic Practitioner uses several techniques to determine the current condition as well as any imbalances in the doshas. These are used to augment the questions he or she asks during consultation to determine the dosha type.
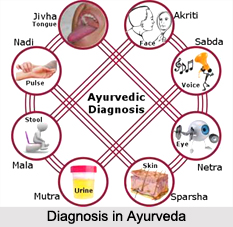
The auxiliary diagnostic techniques employed in Ayurveda are:
•Pulse Diagnosis
•Tongue Diagnosis
•Facial Diagnosis
•Nail Diagnosis
•Lip Diagnosis
•Eye Diagnosis
Ayurvedic practitioners also employ other diagnostic techniques such as palpation, percussion, auscultation along with examination of the heart, liver, spleen, kidney, urine, stool, sputum, sweat, and speech.




















