 Cabinet Secretariat is one of the most important institutions required for the efficient functioning of the Cabinet. It is the duty of the Secretariat to prepare in a meaningful way the agenda of the Cabinet meeting, to provide information and material necessary for its deliberations, and to draw up records of the discussions and decisions both of the Cabinet and its Committees. It keeps the President, the Vice-President and all the Ministries informed of the major activities of the government.
Cabinet Secretariat is one of the most important institutions required for the efficient functioning of the Cabinet. It is the duty of the Secretariat to prepare in a meaningful way the agenda of the Cabinet meeting, to provide information and material necessary for its deliberations, and to draw up records of the discussions and decisions both of the Cabinet and its Committees. It keeps the President, the Vice-President and all the Ministries informed of the major activities of the government.
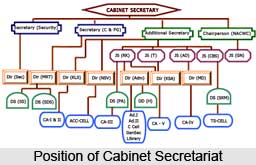
Structure of Cabinet Secretariat
The Cabinet Secretariat has total of 500 posts. This department is organized in three wings - the civil wing, the military wing and the intelligence wing. The main civil wing provides secretarial machinery for the cabinet. It provides secretarial services for the various standing committees and ad hoc committees of the cabinet as also to a number of committees of secretaries which function under the chairmanship of the cabinet secretary. It also deals with the framing of the Rules of Business of the union government.
The military wing is responsible for all secretarial work connected with the meetings of the Defence Committee, National Defence Council, Military Affairs Committee and a number of other committees concerned with defence matters.
The intelligence wing is concerned with matters relating to the joint intelligence Committee of the Cabinet.
Functions of Cabinet Secretariat
The various functions of the Cabinet Secretariat are briefly listed below.
Role as Secretariat of the Cabinet: The cabinet secretariat in the first place performs the necessary secretariat work pertaining to the meeting of the cabinet and its committees.
Role as an originating department: The item of work relates to the appointment of Ministers, Ministers of State, Deputy Ministers and Parliamentary Secretaries and the allotment of portfolios to the Ministers. Also related to this are certain aspects of coordination and expedition in the implementation of the policies of government.
Role as a co-ordinating department: In any administrative system, it is essential to secure coordination in the process of laying government policies and in their efficient execution. Over the years various types of mechanism have been evolved for the purpose of having quick and efficient inters departmental consultations and for securing coordination of activities of different ministers and departments. The department of cabinet affairs is one of the agencies charged with the duty of securing effective coordination.
Role in implementing the decisions of the cabinet: The Cabinet has a very important role to play in the implementation and progress of the decisions of the cabinet and its committees. In keeping with the instructions of the Cabinet Secretariat, a monthly statement showing the progress on the cases relating to each ministry is sent to the Cabinet Secretariat. These statements are scrutinized in the context of the decisions taken. If in any case it is noticed that the ministries are not making substantial progress in the implementation of the decision of the cabinet, the matter is taken up with them at a higher level with a view to speeding up the implementation action.
Thus, it is seen from the above discussion that the Cabinet Secretariat has a most important role to play in governance.




















