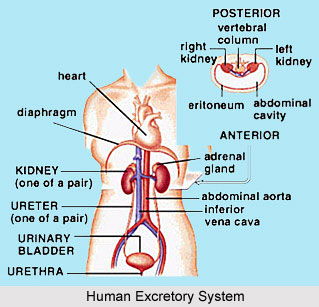
Breathing and concentration in Yoga Asanas form a vital part of asana practice, as Asanas are devised to help both one`s mental equilibrium and physical well being. Several Asanas cannot be performed without a breathing sequence specific to them, and all Asanas must be practiced with an attentive mind observing the accuracy of one`s posture.
Breathing and concentration in Yoga Asanas form a vital part of asana practice, as Asanas are devised to help both one`s mental equilibrium and physical well being. Several Asanas cannot be performed without a breathing sequence specific to them, and all Asanas must be practiced with an attentive mind observing the accuracy of one`s posture.
Breathing should be done only through the nostrils for all Asanas, and several Asanas have their own unique breathing patterns, which should be followed scrupulously.
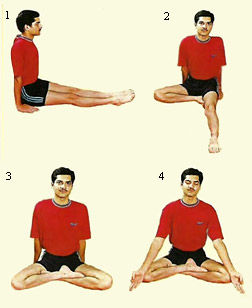
The mind must be kept passive, alert and watchful during the practice of Asanas, so that one can observe one`s mistakes. It is also advisable to practice in front of a mirror in the early stages, as this will help one observe the accuracy of one`s postures. When practiced regularly for a sufficient period of time, the mind will automatically meld itself to the body`s motions.
Center of Attention in Asana
It is useful to perform the exercises in front of a mirror (at least in the initial stages) in order to create an appreciation for the body`s muscular movements. This will help concentration of the mind on particular parts of the body, and the faults can be corrected better. Later this distraction may be avoided to keep the mind free from any object. When practised with regularity, one`s mental processes will meld perfectly with each muscle that moves in every posture, and the exercise will itself grow habitual. This habituation (Abhyasa) leads to uniformity in one`s postures. However, concentration and meditation is required if the greatest good is to be gained through the medium of physical training.
Emotional restraint in practice of Asanas
Yogis have long observed the varied influences and effects of emotions on the body and the mind, and believed that the proper execution of asans will eventually lead to emotional stability. However, it is not denied that no matter how emotions are restrained, they cannot fail to affect the mind, which should remain free of all distractions till complete spiritual detachment (Kaivalya) is to be realized.
If the temperament is not kept calm before and during the practice of Yoga exercises, the attainment of salvation becomes a vague concept and thus emotional shut off is insisted upon by the authorities.
Asanas ideally should not be performed during periods of violent emotions, and as far as possible, with an evenness of feeling and an undisturbed mind. This will help the mind attain a steadiness that paves the way for Kaivalya.