Introduction
 History of Ayurveda is long, copious and loaded with a rich past, deeply seated in the antiquities. Nearly 5,000 years ago the great sage, Vyasadeva for the first time penned downs the Vedas. The Vedas also included a branch called Ayurveda meaning "The Science of Life". Thus began the journey of Ayurveda as an oldest and most holistic treatment method. The history of Ayurveda states that steeped in mystic antiquity this ancient wisdom of curing, preventing disease and long life was a part of the spiritual tradition of a universal religion in India even before it was penned down.
History of Ayurveda is long, copious and loaded with a rich past, deeply seated in the antiquities. Nearly 5,000 years ago the great sage, Vyasadeva for the first time penned downs the Vedas. The Vedas also included a branch called Ayurveda meaning "The Science of Life". Thus began the journey of Ayurveda as an oldest and most holistic treatment method. The history of Ayurveda states that steeped in mystic antiquity this ancient wisdom of curing, preventing disease and long life was a part of the spiritual tradition of a universal religion in India even before it was penned down.
 Ayurveda constitutes not just science but also the philosophy and religion. Religion implies the disciplines and beliefs which contribute towards a state of being in which one can perceive all the aspects of life. According to the concepts of Ayurveda, the entire journey of life is considered sacred. Philosophy indicates the love for truth and truth in Ayurveda is the pure existence of a person. Thus the science of truth constitutes Ayurveda which finds its expression in life.
Ayurveda constitutes not just science but also the philosophy and religion. Religion implies the disciplines and beliefs which contribute towards a state of being in which one can perceive all the aspects of life. According to the concepts of Ayurveda, the entire journey of life is considered sacred. Philosophy indicates the love for truth and truth in Ayurveda is the pure existence of a person. Thus the science of truth constitutes Ayurveda which finds its expression in life.
Samkhya philosophy of creation forms the basis of all the Ayurvedic literature. The term Samkhya is formed of two Sanskrit words `sat` which means truth and `khya` which means to know. The readers of Ayurvedic literature are advised to cultivate an open mind and heart to grasp the philosophy of Samkhya owing to its intimate connection with Ayurveda. In ancient times the truth were discovered by sages with the help of religious practices and disciplines. They had inculcated truth in their daily lives through intensive meditation. Ayurveda encompasses the science of daily living which has evolved from religious, philosophical and practical illumination. This system of knowledge is enrooted in their understanding of the creation. On the basis of the intimate relationship between the man and the universe they had also developed an understanding about the manifestation of cosmic energy in all living as well as non living organisms. The sages had also realized that cosmic consciousness is the source of all existence, the manifestation of which is male and female energy known as Shiva and Shakti.
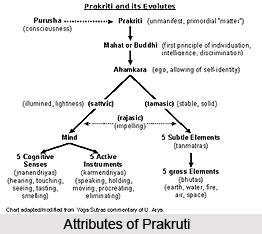 The Samkhya philosophy of creation was realized by Rishi Kapila who had also discovered twenty-four elements or principles of universe. The most basic of these is Prakruti, also known as creativity. Prakruti signifies the female energy while Purusha is the male energy. The latter is colourless, formless and devoid of attributes. It also does not take any active part in the creation of universe. It is a passive awareness devoid of choice. In contrast, Prakruti has colour, form as well as attributes and implies awareness with choice. It indicates a divine will which desires to become many. It is believed that the universe is a child which has taken birth from the womb of Prakruti, also known as the Divine Mother. All forms of universe are created by Prakruti whereas Purusha witnesses the creations.
The Samkhya philosophy of creation was realized by Rishi Kapila who had also discovered twenty-four elements or principles of universe. The most basic of these is Prakruti, also known as creativity. Prakruti signifies the female energy while Purusha is the male energy. The latter is colourless, formless and devoid of attributes. It also does not take any active part in the creation of universe. It is a passive awareness devoid of choice. In contrast, Prakruti has colour, form as well as attributes and implies awareness with choice. It indicates a divine will which desires to become many. It is believed that the universe is a child which has taken birth from the womb of Prakruti, also known as the Divine Mother. All forms of universe are created by Prakruti whereas Purusha witnesses the creations.
Prakruti is primordial physical energy which comprises three attributes, also known as gunas, which is existent in all nature. These three gunas constitute tamas (inertia), rajas (movement) and satva (essence) which forms the foundation of all existences and are duly balanced. With the disturbance of this balance the gunas interact, endangering the evolution of the universe. Cosmic intellect is the first manifestation from Prakruti. Ego or Ahamkar originates form Mahad or intelligence and the former, with the aid of satva, then manifests into the five senses, called tanmatras, and the five motor organs and create the organic universe. This ego also manifests five basic elements, called bhutas, with the aid of tamas for creating the inorganic universe.
Another vital active force in the body is Rajas which moves both inorganic and organic universes to tamas and satva respectively. Thus the tamas and satva can be considered as inactive potential energies which require the active, kinetic force of rajas. Satva signifies creative potential (Brahma), rajas denotes a kinetic protective force (Vishnu) and tamas corresponds to the potential destructive force (Mahesha). These three are believed to be the three manifestations of `aum`, the first cosmic soundless sound that continuously operates in the universe.
Origin of Ayurveda
Ayurveda is the most ancient Indian medical science and the origin of ayurveda can be traced back to even more than five thousand years. Ayurveda is the science based on ancient Indian philosophy and can therefore appropriately be called as `The Science of Living`. Ayurveda traces its etymology to Ayush, meaning `life`, and Veda, which originates from `vid` or knowledge. Popularly ayurveda can actually be defined as a medical science that helps the human body to keep fit, while providing cures from indigenous plants, animal products and minerals for ailments.
Steeped in antiquities the origin of ayurveda has two discrete dominions, one is the folk wisdom and the other is the scientific knowledge. Tradition attributes the origin of ayurveda from the creator itself. According to Mythology the creator Brahma whilst creating the universe, clutched knowledge from the four directions and created Vedas. Brahma then carried the knowledge of Ayurveda to Prajapati Daksha. Daksha passed it on to the Ashwinikumaras, the twins who were the physicians of the gods. The Ashwinikumaras then proffered this knowledge to Lord Indra. Dhanwantari was instructed by Lord Indra to spread this priceless science of longevity on the earth. Thus the legacy of Ayurveda initiated on earth as a holistic treatment procedure. The origin of ayurveda thus claims that the deity of this celestial science is indeed Lord Dhanwantari, an incarnation of Lord Vishnu.
Although ayurveda put across antiquity, legitimacy and usefulness, yet the tradition does not determine the source of knowledge, nor does it implies any specific date of origin. Vedas, the ancient Indian testimonials contain references to illness, cures and other health-related issues. The cures are both magical and medicinal. However, the references do not add up to a theory of medicine but to a great extent signifies the deep seated relation of Vedas with ayurveda whilst marking the origin of ayurveda. Ayurveda is treated as Upaveda of Rigveda and Antharveda (internal part) of Atharvana veda.
Quite ideally therefore Ayurveda is not just merely a medical system on the contrary an entire medical kit offering the secrets of the sacred science of life. Ayurveda therefore supports the human being to lead a happy life with pure mind. The paramparas of ayurveda like the Daiva parampara, Siddha parampara and Rishi paramparas which are deeply entwined with this mystic science further points out the origin of ayurveda. The Daiva parampara states that ayurveda was revealed by the creator Brahma and was then transformed from Lord Brahma to Ashwini kumar through Prajapati, the son of Brahma. Ashwini Kumar taught Ayurveda to Indra and then from Indra ayurveda was gradually revealed to the Saint, Bhardwaj.
The rishi parampara of ayurveda however offers another saga in regard to the origin of ayurveda. According to the Rishi parampara, Dhanvantari received the divine knowledge of ayurveda and pass it on to Sushruta. After this followed an entire Rishi parampara like from Sushruta to Vaitarana then Bambrha and after that Poshka bhavara received the knowledge. He then passes it on to Gopura rakshita and Karaveera who again pass it on to Kasyapa - Atri. It was much later Kasyapa muni passed the divine knowledge to Bhrugu and Vasistha. Laced with antique mysticism the origin of ayurveda marks this holistic treatment procedure as an ancient and higher knowledge to support human being in leading a happy life in natural way.
Ancient Texts on Ayurveda
There are two main re-organizers of Ayurveda whose works still exist intact today - Charaka and Sushruta. According to the history of Ayurveda, Charaka was the first man who based his Samhita on Agnivesha Samhita and further elaborated it with his interpretations and annotations. Precisely, "Charaka Samhita" integrated the external as well as the internal cause of illness. Sushruta based his Samhita on the Dhanvanatri school of Ayurveda. In "Sushruta Samhita" there is details discusses about various surgeries, burns, fractures, wounds and amputation. The complete discussion on human anatomy marks Sushruta Samhita as a contemporary treatise on Ayurveda. The history of Ayurveda however uncovers the third major treatise which is called the "Ashtanga Hridaya". This is basically a summarizing version of the works of Charaka and Sushruta which was compiled by Vagbhata.
Development of Ayurveda
 Development of Ayurveda hints back to the practice of medicine and medications by the contemporary sages and saints. Ayurveda has intense mythological association with the creation of cosmos and preservation of life- force. It is said in "Ayurvedavatarana"(the descent of Ayurveda) that Lord Brahma sung these life- giving slokas to other deities who would together relieve human race of severe suffering. Dhanvantari was one among those deities who propagated Ayurveda in the mortal sages; the elixir of life thus came to be known as the divine science of revelation .It equalizes the worth of deep perception, inner vision and realization with empirical observation. Ayurveda is hence, crowned as the "Mother of all healing".
Development of Ayurveda hints back to the practice of medicine and medications by the contemporary sages and saints. Ayurveda has intense mythological association with the creation of cosmos and preservation of life- force. It is said in "Ayurvedavatarana"(the descent of Ayurveda) that Lord Brahma sung these life- giving slokas to other deities who would together relieve human race of severe suffering. Dhanvantari was one among those deities who propagated Ayurveda in the mortal sages; the elixir of life thus came to be known as the divine science of revelation .It equalizes the worth of deep perception, inner vision and realization with empirical observation. Ayurveda is hence, crowned as the "Mother of all healing".
The birth of Indian medicine can be traced back to the days of the famous Indus -Valley civilization of 2700-1500B.C. One notes Sanskrit writings of mythic-religious hymns related to the civilization in Vedas. Atharva Veda and Rig Veda definitely provide us with data of medical practices. The Golden Age of Ayurveda is from 800-1000B.C marked by the evolution of medical texts like Charaka Samhita, Sushruta Samhita, Madhava-nidana, Sarangdhara Samhita,etc.
Ayurveda flourished significantly, during the times of Buddha(520B.C.). The Ayurvedic practitioners of that period invented the unique formula of mixing mercury, sulphur and different metals with beneficial herbs in medicinal compositions. Nagarjuna, the Buddhist herbologist was the greatest exponent of medical science, then. Also big names like Nagbodhi, Yashodhana, Govinda, Vagbhatta worked with him.
The tradition of Ayurvedic medicine, as a chief medical practice, in the rule of Chandragupta Maurya was also present in Emperor`s Ashoka`s paradise of peace. Moreover, the prevention of bloodshed, as a must, inspired the Ayurvedic doctors of that era to innovate new and advanced treatment techniques to avoid surgery. With the Islamic invasion in India (1100-1800A.D.), Ayurveda lost its appeal. However in 1800A.D, a revival was attempted. Ayurveda as a course was introduced in the academics of Sanskrit College, Kolkata in 1827.But unfortunately in 1833 all efforts went in vain. British stopped the educational enterprise.
Western colonisation invited allopathic medicinal method in India which reduced the glory of native Ayurveda.
Nevertheless, Indian National Congress did a lot to retrieve it`s prestige by referring it as a National Healthcare System in 1920. Mahatma Gandhi inaugurated Ayurvedic and Unani Tibia College in Delhi in 1921. In 1927 Madan Mohan Malviya opened an ayurvedic branch in BHU. In 1940 acts were enforced for ayurvedic medicines.
Finally the scenario became better after 1947. Ayurvedic Universities in Jamnagar, Gujrat, BHU and few started conducting research and higher education in Ayurveda. The pharmacopoeia laboratory in Ghaziabad in 1970 was an important establishment. National Institute Of Ayurveda in Jaipur, Rajasthan in 1972-73 is a move ahead. Then the publication of ayurvedic formulary took place. Progress has become the order of the day for Ayurveda. Ayurveda has gained international recognition as well.
Legends of Ayurveda
 The history of Ayurveda also points out the celestial origin of this ancient science, which was once communicated to the Indian saints and sages. Myths unfold that Dhanvanatri, who later penned down Ayurveda, taught it to the sages. While according to another legend, the knowledge of healing originated from Lord Brahma who taught it to King Daksha, who further taught Lord Indra.
The history of Ayurveda also points out the celestial origin of this ancient science, which was once communicated to the Indian saints and sages. Myths unfold that Dhanvanatri, who later penned down Ayurveda, taught it to the sages. While according to another legend, the knowledge of healing originated from Lord Brahma who taught it to King Daksha, who further taught Lord Indra.
It was the time of restlessness when disease and death were creating havocs and human had no answer. It was this time when all great sages in order to find solution to this problem gathered. During this meeting Sage Bharadvaja came forward and learnt the ancient science of Ayurveda from Lord Indra. He then taught this science to Atreya, who further transmitted this knowledge throughout world. The history of Ayurveda states that later, it was Agnivesha, the disciples of Atreya wrote "Agnivesha Samhita" which is still considered as the most comprehensive form of Ayurveda.
Reformation of Ayurveda
 During the Vedic and earlier Buddhist period "Ayurveda" was at its pinnacle. Ashoka also boosted up the contemporary Indian medicine by his official authority. Starting from the Maurya period the repeated Scythian invasions into India, Indian science suffered a lot. The research on Ayurveda gradually ceased to occur when the Turkish invaders came to India; it suffered further more.
During the Vedic and earlier Buddhist period "Ayurveda" was at its pinnacle. Ashoka also boosted up the contemporary Indian medicine by his official authority. Starting from the Maurya period the repeated Scythian invasions into India, Indian science suffered a lot. The research on Ayurveda gradually ceased to occur when the Turkish invaders came to India; it suffered further more.
When the Muslim rule in India became stable in the later Middle Ages, religious discrimination affected Ayurveda as a science of the Kafirs (non-believers of Islam). It is said Bakhtiyar Khalji destroyed thousands of books of the Nalanda University Library written on palm leaves. He also burnt the Vikramshila University which was located near modern Bhagalpur. The library of Vikramshila was also destroyed. The earlier Muslim rulers imported Unani physicians from their homeland. Some prudent Indian scholars spirited away valuable Indian texts to Tibet and China some of which are still extant.
During the Mughal period, particularly during the reign of Akbar, attempts at the reintroduction of Ayurveda were made which though very meagre still helped Ayurveda to live for the posterity. With entry of the Portuguese into India in the 15th century and later the British settlement of India during and after the reign of Jahangir, Ayurveda gradually eclipsed from the scene of India. From the 18th century onwards European medicine or Allopathy boarded the stage of Indian medicine.
Western Thoughts on Ayurveda
 Western thoughts on Ayurveda differ considerably from the East. Individuality is greatly generalized and categorized as per the thoughts and concepts of Western medicine. The Western concept of normality states that the common features found in the majority of people becomes the norm. However as per the concepts of Ayurveda, every individual differs in terms of normality and the varied constitution of every human being affects the spontaneous as well as particular functioning and temperament of his or her body.
Western thoughts on Ayurveda differ considerably from the East. Individuality is greatly generalized and categorized as per the thoughts and concepts of Western medicine. The Western concept of normality states that the common features found in the majority of people becomes the norm. However as per the concepts of Ayurveda, every individual differs in terms of normality and the varied constitution of every human being affects the spontaneous as well as particular functioning and temperament of his or her body.
The key for understanding in the Eastern medicine lies in observation, experience and acceptance, whereas in the West it all depends on logical deduction, analysis and questioning. Objectivity gets greater emphasis in the Western mind while in the East, the subjectivity forms the foundation. In fact the teachings of the Eastern science go beyond the division between objectivity and subjectivity. This significant difference in terms of approach creates difficulty for the Westerners for comprehending the concepts and methodologies of Ayurveda.
In the study of Ayurveda many questions of `How` and `Why` arise which are often unanswerable. The phenomenon is also common many a time in Western medicine. Often certain concepts are proven effective but the reasons behind them remains shrouded in mystery. For instance, many antibiotics are known to destroy the toxin producing bacteria in the body however there is still a considerable lack of explanation for why and how these toxins are produced by the bacteria. Ayurveda is in fact a holistic approach. It is a science, the foundation of which lies in the sum of several elements. Thus a strong overview of the complete science of Ayurveda is essential before questioning its details; otherwise the practice becomes unsatisfactory and unproductive.
Ayurveda in Later Vedic Period
 Ayurveda took a concrete shape in the later Vedic period. Knowledge about medicines was acquired from the Vedas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas, Upanishads and Sutra literature. The sages and scholars worked dedicatedly to compose several medical texts in all the eight branches of Ayurveda i.e.
Ayurveda took a concrete shape in the later Vedic period. Knowledge about medicines was acquired from the Vedas, Brahmanas, Aranyakas, Upanishads and Sutra literature. The sages and scholars worked dedicatedly to compose several medical texts in all the eight branches of Ayurveda i.e.
* Salyatantra
* Salakya
* Kayachikitsa
* Bhutavidya
* Kaumarabhrtya
* Agadatantra
* Rasayana
* Vajikarana
Apart from these ayurveda also deals with general surgery, internal medicine, paediatrics, toxicology, geriatrics and aphrodisiac. During this period ayurveda also developed for the treatment of diseases of animals and even plants. Texts on ayurveda such as Hastyayurveda and Gavayurveda relate to the treatment of horses, elephants, cattle and trees. Ayurveda not only developed for curing of diseases but also to prevent them. It is believed that it gained importance before the time period of the Sanskrit grammarian Panini. It also finds mention in Mahabharata.
Texts of Ayurveda
The Charaka School of ayurveda was known as the `school of medicine` and Sushruta School as the `school of surgery`. A classical text of the ancient ayurvedic literature known as Charaka Samhita deals with the compilation of ancient Indian medical art. It states about the discourse of Atreya Punarvasu on diseases, method of diagnosis based on some careful observations of the clinical symptoms, the pathology as well as the personal nature of the patient and his constitution. The text is in the form of dialogue between a teacher and a student. Charaka Samhita is chiefly a treatise on ayurvedic therapeutics.
Another important classical text of ayurveda is Sushruta Samhita. It deals with essential information regarding the objective and scientific approach of the ancient physicians, pharmacological, the knowledge of the diseases and surgical therapies. Sushruta Samhita also mentions about many instruments that are similar to some of the modern instruments that are used today. The modern acupuncture system owes its origin to the Sushruta Samhita. It also deals with types of therapy in connection with Marmas i.e. `vital points`. It is for this point that the sensitive parts or the `vital points` are known as `marmasthanas`. According to ayurveda the marma points are linked through bio energy channels known as Nadis. It is through these underlying channels that the bio energy known as prana is passed from one point of the body to other another. These `marmasthanas` become sensitive when pressed or touched by needles, finger tips etc and gives some sort of relief. In the old tradition of Sushruta the marma treatment was used for therapeutic purpose. Sushruta was also translated into Arabic language and deals elaborately and systematically with the surgical operations of ancient India. It describes ways of removing stones from uterus, methods to undertake a plastic surgery of the nose, cataract couching, cauterization, application of leaches in high blood pressure, treatment of Alkali etc.
Another important ayurvedic text Astangahrdaya, written by Vagbhata was studied by the Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang. The book was translated into Arabic and Persian language in the court of the Persian emperor Harun-AI-Rashid in the 8th century. It has been composed in both prose and poetry. One more ayurvedic book Astangahrdaya is largely known in foreign countries and has been translated in several languages.
Ayurveda in Buddhist Period
 In the Buddhist period reached to great heights. Centres for Indian medical studies were established during this period and ayurvedic medicine was taught at the universities of Kashi, Taxila and Nalanda. This period is regarded as the golden era of Ayurvedic treatment. The term `Ayurveda` was replaced by the term `tigiccha-satta` in early Buddhist literature.
In the Buddhist period reached to great heights. Centres for Indian medical studies were established during this period and ayurvedic medicine was taught at the universities of Kashi, Taxila and Nalanda. This period is regarded as the golden era of Ayurvedic treatment. The term `Ayurveda` was replaced by the term `tigiccha-satta` in early Buddhist literature.
Gautama Buddha was regarded as a great physician as well as a surgeon. During the early Buddhist period medical treatment and surgery developed to a greater extent. The great physician and renowned surgeon Jivaka belonged to this period. There are several anecdotes that mentions about his expertise. Jivaka had completed seven years of medical training under Bhiksu Atreya at Taxila University. After that he became a famous surgeon. Buddhism propagated outside India helped in the growth and development of ayurvedic medicine. The merits of ayurveda spread over to Tibet, Central Asia, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Java, Sumatra and to many other countries.
Ayurveda in Early Buddhist Period
In the early Buddhist period ayurveda flourished considerably. The Ayurvedic practitioners during this period commonly used mercuric-sulphur combination based medicines. They usually used sulphur, mercury and other metals along with herbs to prepare the different types of medicines. Nagarjuna was a famous Buddhist herbologist and an ayurvedic practitioner of this period. He was known for inventing different types of new drugs for the treatment of diseases. Many rulers following the teachings of the Gautama Buddha promoted healing activities. They constructed hospitals and established free dispensaries. Emperor Ashoka after the Kalinga War was highly influenced by the Buddhist teachings. He banned bloodshed in his kingdom. Hence many Ayurvedic practitioners who practiced surgery left their surgical intervention and adopted new medicinal treatments.
Ayurveda in Later Buddhist Period
In the later Buddhist period Ayurveda however received a blow when the doctrine of `ahimsa` or non-injury was preached. It changed the viewpoints of the common masses who looked upon surgical operations as causing injury (himsa) and pain to patients. Thus, surgery was highly discouraged during that period. The extensive study of the eight branches (astanga) of ayurveda suffered great loss. Only the branch of Kayacikitsa i.e. inner medicine and Rasayana survived. Thus, the practice of the surgery during this period slowly died out.
Ayurveda in Muslim Period
 Ayurveda is a traditional health care system being practiced in India for more than 5000 years. It is as sub section of the Atharva Veda. According to history several Indian saints propagated this form of medication. Ayurveda focuses on the use of natural herbs, yoga therapy and massages. For the development and progress of ayurveda two schools were established. One was meant for the physicians and another one was for the surgeons. Ayurveda also progressed significantly under the rule of influential rulers at different periods of time.
Ayurveda is a traditional health care system being practiced in India for more than 5000 years. It is as sub section of the Atharva Veda. According to history several Indian saints propagated this form of medication. Ayurveda focuses on the use of natural herbs, yoga therapy and massages. For the development and progress of ayurveda two schools were established. One was meant for the physicians and another one was for the surgeons. Ayurveda also progressed significantly under the rule of influential rulers at different periods of time.
The advent of Muslim rule in India in the 10th and 12th centuries A.D. significantly influenced Ayurveda. The Islamic medicine or the Unani system of medicine was introduced during that period. It was a combination of Islamic medicine and Greek medicine. It enjoyed the royal patronage of the Muslim rulers. During the period of Khiliji Dynasty and Tughluq Dynasty the Unani system of medicine got its official recognition. The Mughal rulers also invited several Muslim physicians and surgeons from Persia. As per historical report there were almost twenty-nine eminent physicians in the court of Emperor Akbar. They came from Arab countries to pay homage to the king. Akbar also had few ayurvedic scholars in his court.
The development of Unani medicine in India significantly hampered the growth of traditional ayurvedic medicine. However, it still maintained its popularity being practised by few eminent people. Unani medicine and ayurveda mutually influenced each other and are still practiced in India.
Ayurveda in British Period
 In the first two decades of the 19th century Ayurveda was taught in a traditional way. The British rulers did not bother much as the British East India Company employed their English doctors. They remained indifferent towards the health and physical condition of the Indians.
In the first two decades of the 19th century Ayurveda was taught in a traditional way. The British rulers did not bother much as the British East India Company employed their English doctors. They remained indifferent towards the health and physical condition of the Indians.
The British hospitals employed few Indians as `subordinate health-workers.` The Indians who possessed high skills in medical service served at regiments and civil stations under the name of `native doctors`. Slowly the demand for medical service increased; hence in 1822 the Calcutta Native Medical Institution was established. It was set up under the supervision of Jamison, Breton, and Tytler.
Earlier the British rulers tried to popularise the western medical science among the Indians but the rising demands for indigenous medicines forced them to built medical colleges. They established the Sanskrit College in 1824. Here the prospective doctors were given training in Indian medicines. Ayurvedic classes were also introduced in Sanskrit College in 1827. Professors gave lectures on both Indian and western medicines. Dr. Tytler was one of the professors of the college. Lectures on classical texts of Ayurveda were also given. However, this friendly co-existence of European and Indian medicine did not last for a long time.
In 1935 the ayurvedic classes in Sanskrit College was discontinued under the advice of Lord Macaulay. A new medical college was established in West Bengal where European medicine was the only recognized system of medical study. Dr. Tytler and Dr. Jamison tried hard to curb their actions by sending their famous Memorandum to the Educational Secretary of India. They however, did not succeed in their mission.
The British in order to accomplish their mission started granting free studentship and scholarship to the students. They also gave free of cost medical training materials, such as books, charts and models etc. The government supported the students who chose the European system of medicine.
Students who passed the final examination of the Medical College successfully obtained certificates and were designated as native doctors. They were regarded as the first class of `Native Doctors`. The second class was accorded to the students who passed from the Calcutta Native Medical Institution and the third class was those who had got their training in the British Hospitals. Thus, the growth and development of Indian medicine was restricted during this period. It was thought that the allopathic medicine would soon replace the traditional Indian medicine. During this crisis period Kaviraj Gangadhara Roy, a well known Indian personality lifted up the position of ayuryedic medicine in West Bengal.
Development of Ayurveda in British Period
Ayurveda was elevated to its prestigious position by the vital contribution of Kaviraj Gangadhara Roy. Throughout the 19th century and also in the first two decades of the 20th century, he worked hard for the development of ayurveda. He worked as an ayurvedic physician and also established a medical school to impart education to students from different parts of India. He earned popularity for his skill in the therapeutic use of medicine. His commentary on Charaka Samhita named as Jalpakalpatar was one of his vital contributions. He elaborately studied the Indian medical system and sent them to different parts of Bengal and India. Ganga Prasad Sen, a junior contemporary of Gangadhara Roy also contributed significantly for the growth of ayurveda. He was from Kumartulle in Calcutta (now Kolkata). Gangadhara Roy fought for the cause of Ayurveda outside Kolkata while Ganga Prasad Sen tried to compete with western medicines in the market. The later also edited several ayurvedic journals, made Ayurvedic medicines at home and sold them to the general public.
India passed through a phase of national awakening from 1920. Several schools, colleges and universities were established that imparted education on ayurveda. Several ayurvedic scholars and practitioners also came forward for the development of indigenous medicine. Many committees such as Chopra Committee, Osman Committee etc., were formed to suggest ways and means for national improvement.
After India`s independence in 1947, the Government of India, as well as the state governments, allotted funds to boost up research work in ayurvedic medicine. State dispensaries and hospitals were also established in the districts.




















