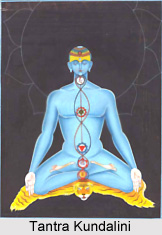
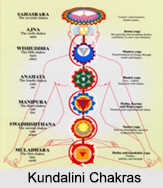
 The mental body contains matter, which can vibrate at a rate similar to that of the creative force in the cosmos. It is where a person starts to think, to reason, to know, to create. Through the mental body one gathers knowledge, through reason and logic, one applies that knowledge. It is also through this body that one sets up severe attitudes or structures in the system. It is here that prejudices are formed. The more inflexible the matter in the mental body becomes, the more complicated it is to flow with life, to learn new ways of living and to develop fresh ideas.
The mental body contains matter, which can vibrate at a rate similar to that of the creative force in the cosmos. It is where a person starts to think, to reason, to know, to create. Through the mental body one gathers knowledge, through reason and logic, one applies that knowledge. It is also through this body that one sets up severe attitudes or structures in the system. It is here that prejudices are formed. The more inflexible the matter in the mental body becomes, the more complicated it is to flow with life, to learn new ways of living and to develop fresh ideas.
Cleansing the Mental
While the Kundalini releases the mental body, a person may find strong, formerly unknown preconceptions or become conscious of life-governing attitudes, which have long influenced actions and reactions.
Clearing the Brain
Firstly, one should concentrate on breathing through the nose, up into the head. Then, it is advised to look into the head as one would look up into the heavens and survey stars in the sky. However, what colours, what energy patterns can one observe?
Truth
Firstly, it is advised to do the Deep, Peaceful Breathing, concentrating on the centre of the forehead; then,. The word `truth` needs to be visualised in that area. Breathing in can help feel truth enter the whole system, flooding each cell. It is best advised to hold this system, while doing Deep, Peaceful Breathing, for at least two minutes.
During Kundalini purification, it is especially easy for untruths and misconceptions (which block growth) to enter the thoughts. If one has mental work to do, but the energy will not flow, it is best to try dancing. Dancing is an exceptional exercise for releasing Kundalini flow and assists in thinking and perceptive processes. Since mental work is often done in a way that is not advantageous to superior Kundalini flow- at a desk or a table, curved over the work, shoulders rounded and hunched, head lowered- it is advised to try to change the posture and take breaks, where one may walk, dance or exercise.
Kundalini flow to the brain is slowed when one is caught in emotional situations and relationship problems (common, in this age). Having trust that "this too shall pass", and gaining linear perspective on the situation, helps keep energy flow open to the brain.
The Ultimate
One shall think and create in fresh ways and work with higher magnitudes. Manifestation and other mental powers will be considered normal.