 Leeches have been employed by the Hindus from a very remote period to treat many illnesses and diseases through bloodletting. Leech Therapy is sometimes the best alternative in treating illnesses and even surpasses pharmacological treatments. Because of its healing effects to the human body, this traditional method of curing diseases is still thriving today. The Leeches have been used to treat a variety of ailments including nervous system abnormalities, dental problems, skin diseases and infections.
Leeches have been employed by the Hindus from a very remote period to treat many illnesses and diseases through bloodletting. Leech Therapy is sometimes the best alternative in treating illnesses and even surpasses pharmacological treatments. Because of its healing effects to the human body, this traditional method of curing diseases is still thriving today. The Leeches have been used to treat a variety of ailments including nervous system abnormalities, dental problems, skin diseases and infections.
Types of Leeches
Sushruta gives a detailed account of their varieties, habits, mode of application, etc. There are 12 varieties of leeches, 6 of which are venomous and 6 useful. The venomous leeches are found near putrid fish or animals in foul, stagnant and putrescent water. Such leeches are consequently to be avoided. The good leeches are found in clear and deep pools of water which contain water lilies and are surrounded with sweet smelling plants.
Preservation of Leeches for Treatment
The middle sized leeches are the best. These leeches are to be caught on a piece of leather or cloth, and placed in a new water pot in which some clay and pure water has been put. Some grass or leaves of aquatic plants are to be placed in the pot for them to lie upon, and the roots of water lilies and dry flesh are to be given to them for food. The water is to be changed every third day, and the water pot every seventh day.
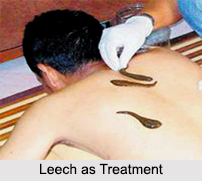
Use of Leech as Treatment
If the leeches do not fix quickly, apply a drop or two of milk or blood to the part, or make one or two very slight scarifications, which will induce them to fix themselves more readily. When the leeches are sucking, sprinkle a few drops of cold water upon their bodies. When the leeches have removed the necessary quantity of blood, sprinkle a small quantity of salt upon their heads to make them drop off. Put the gorged leeches upon some dry bran, put a little oil and salt upon their mouths and then strip them. Put them next in fresh water and, if they are lively, they will live and may be used again; but if they are languid, they will soon die and they should therefore be at once thrown away. The part upon which the leeches have been is to be smeared with honey, cold water and astringent substances. In other cases poultices may be applied.




















