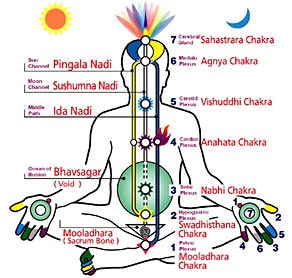
Vipassana meditation is the process of self -transformation through self-observation. Deeply focusing on the interconnection between the body and the mind Vipassana meditation is as if the journey to the inner self. The techniques of Vipassana Meditation further supports in this eternal self-exploratory journey to the common root of mind and body that dissolves mental impurity whilst promising a balanced mind filled with compassion, love and other finer feelings.
Vipassana meditation is the process of self -transformation through self-observation. Deeply focusing on the interconnection between the body and the mind Vipassana meditation is as if the journey to the inner self. The techniques of Vipassana Meditation further supports in this eternal self-exploratory journey to the common root of mind and body that dissolves mental impurity whilst promising a balanced mind filled with compassion, love and other finer feelings.
The technique of vipassana meditation calms the mind and also instills simple moral conduct. These can be broadly categorised into three basic parts. These parts aid in the overall spiritual development of the yogis.
The three parts are:
•Watching the belly
•Watching the coolness in the nostrils
•Watching the breathing like a river
Watching the belly
Belly plays an important part in meditation and in Vipassana meditation, watching the belly is indeed an important technique. Belly part is reckoned as the location of the hara centre. Just behind and below the navel or the belly button lies the hara, which is the point of consciousness and is considered as the center of the subtle body. By focusing the attention on the hara centre, one can easily attain a meditative state of mind. As one meditates upon hara, his thinking process automatically slows down. This is the state of "choice less awareness". The `belly watching` form of Vipassana meditation involves the idea of focusing the attention on the breathing process, felt around the belly. The movement of the belly and watching it carefully can aid in attaining a meditative state. It is first advised to sit quietly at a comfortable and peaceful place. With closed eyes one should take few deep breaths. Now the focus and attention should be shifted on the area around the belly. It is important here to watch the movement of the belly how it goes up and down along with the breath. The whole attention should be shifted towards the belly movement.
As one keeps watching the belly movement within no time he feels that his thoughts have gradually started disappearing from his mind and a state of increased awareness is felt. Daily practice of this meditation supports in recognizing the presence of a hara centre. It feels as if a sort of ball of consciousness around the belly. This feeling further increases the awareness of the inner self which is the indeed main aspect of the Vipassana Meditation.
Watching the coolness in the nostril
Careful watching of the coolness in the nostril is the second technique of Vipassana meditation. The technique involves focusing the attention on the coolness during breathing. Breathing is a continuous process which goes on. Along with the breathing, the soothing coolness of the nostrils supports in emanating itself. If one focuses the attention on the coolness then the meditative state is achieved. This technique of Vipassana meditation can be followed while sitting in a comfortable and peaceful place. With eyes closed the deep breathings are to be exercised. The concentration then needs to be shifted on the comforting sensation of slight coolness that one feels whenever breath goes in. Repeatedly engaging the mind in feeling this coolness relaxes the mind.
Watching the breathing process
This is the third technique of Vipassana meditation. The central idea of Vipassana meditation is to focus on the breath itself. Quite ideally therefore watching the breath is indeed the most basic form of Vipassana meditation. Watching the breath as it comes inside the body and then watching it as it goes outside is the fundamental idea of this third technique of Vipassana meditation. This third technique of Vipassana meditation involves two requirements like a comfortable sitting position and indeed a peaceful place. After this the first step is to sit silently in a comfortable position with closed eyes, whilst shifting the entire focus to the flow of the breath as it travels inside your body and comes out. Following the breath in its entire route of inhalation and exhalation is thus the crux of breath watching. In this technique the focus is in watching the breath while remaining completely detached. Watching the breath like a river is important to gain the maximum benefit of vipassana meditation.
The techniques of vipassana meditation supports in quieting the mind whilst turning observation inside to lead a harmonious life filled with love and compassion.