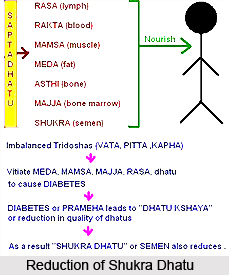
 Shukra Dhatu is considered to be the supreme body tissue because it has the power to produce life.
Shukra Dhatu is considered to be the supreme body tissue because it has the power to produce life.
Shukra dhatu comprises the spermatozoa (male sex cell) in the male human body and ovum (female sex cell) in the female human body. The spermatozoa are a specialised cell and differ from an ordinary cell in various aspects.
It is much smaller compared to the ovum and its length is more or less equal to that of the nucleus of the ovum. The mature spermatozoa can be commonly divided into head and tail. The tail in turn consists of a neck, middle piece, main piece and end piece on the basis of slight differences in thickness along its length. The head is a condensed nucleus and contains about 40 percent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid, the basic genetic factor) and is rich in a substance called arginine.
The head has a head cap whose posterior part is absent in human spermatozoa. The neck is a weak portion, which connects the head with the middle piece. The middle piece is also called the engine room of the spermatozoa because in it various reactions take place. The ATP ase, an enzyme present predominantly in the main piece of the tail and it helps in the movement of the spermatozoa. Before puberty, mature spermatozoa are not formed. It takes place actively from the start of puberty and is maintained with advancing age, although the rate declines gradually. The exhaustive process of formation of spermatozoa is known as spermatogenesis.
Semen is the reproductive fluid present in male human body, which is a suspension of spermatozoa secreted by different associated reproductory parts like `epididymis`, `prostrate`, `seminal vesicle` and `Cowper`s glands`. There are 100,000 sperms per cubic millimeter of healthy semen. Ovum, the female component of shukra is found in the matured stage after undergoing a series of developmental changes in the female human body.
These changes are collectively termed as the menstrual cycle, which is characterized by a distinct feature called menstruation. Menstruation is the cyclical discharge of blood, mucus and certain other substances from the uterus (female reproductive organ) in the reproductive life of the females, at an average interval of 28 days.
It is absent before puberty, during pregnancy and after the cessation of the menstual cycle. It occurs when the ovum fails to unite with a sperm. The mature ovum has a `germinal vesicle` and has two covering membranes--- the vitelline membrane and the zona pellicuda. The ovum is covered by epithelial cells, which are collectively known as corona radiata.
Shukra dhatu of both males and females take part in the process of fertilisation in order to generate life in the female body. During the act of copulation, semen is deposited in the female genital tract. The penetration of the ovum by the sperm is brought about by enzymes present in the sperm. Only one sperm is allowed to penetrate the ovum. Once the ovum is fertilised, it creates a barrier, which prevents the entry of other sperms. After fertilisation, the structure is known as embryo, which moves into the uterus for implantation and subsequent development.
Ashtang Ayurveda honors shukra as the supreme body tissue because of its generative property. Therefore, for intimate satisfaction and for better progeny the shukra dhatu should be in good state. Vajikaran tantra is that branch of Ashtang Ayurveda that is concerned with all types of physical, and psychological sexual problems like impotence, libido, poor erection and early ejaculation in the males as well as sterility and frigidity in the females. The vajikaran drugs help in giving strength and vigour to the shukra dhatu thus strengthening the reproductive potentiality.




















