 Mutras are the substances or waste matters that need to be eliminated from the body. According to Ayurveda only a balanced condition of doshas, dhatus and malas can produce Aarogya (good health or disease free condition) and their imbalance causes ill health or disease.
Mutras are the substances or waste matters that need to be eliminated from the body. According to Ayurveda only a balanced condition of doshas, dhatus and malas can produce Aarogya (good health or disease free condition) and their imbalance causes ill health or disease.
Mutra or urine is a liquid form of mala produced by animals and humans. The water that we consume purifies and cleanses our body and comes out through skin, lungs faeces and urine. Our body`s outer surface is kept dirt free by bathing with water and the blood plasma within our body cleans the inner organs and tissues by the process of osmosis or electrolyte transportation between tissues. This blood plasma is filtered mainly by the kidneys (to a certain extent by the liver) and the waste products thus obtained are eliminated in the form of mutra.
Urine formation is a vital necessity for maintaining the balance of minerals and other substances in the body. If a newborn does not urinate within twelve hours after birth, it should be seriously investigated. Cellular metabolism builds up many toxic nitrogenous substances within the body that are removed through urine. For instance, the body gets rid of excess of calcium through urine. Mutra (urine) also excretes ammonia, ethanol and artificial sweeteners which are harmful if allowed to remain within the body. Moreover, Mutra (urine) helps to maintain the appropriate amount of water in the body.
Mutra is a transparent solution whose colour ranges from clear to amber, and is generally light yellow. Mutra (urine) is actually a watery solution consisting of metabolic wastes (such as urea), dissolved salts and organic materials that come from the blood or interstitial fluid. Normally urine comprises 95 per cent water, and other common constituents like sodium - 0.4 per cent, ammonia - 0.05 per cent, phosphates - 0.6 per cent, urea - 2 per cent, sulphate - 0.2 per cent. Substances like creatine, urobilinogen and casts are also present, but in minute quantities. In a normal human body, soluble substances are excreted in the urine.
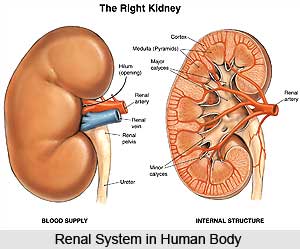
Mutra is formed in the human body by an elaborate process. Millions of nephrons in the kidney filter out the waste products, toxins, excess water and mineral salts from the bloodstream. Kidney, the primary organ of water balance mechanism, eliminates nitrogenous wastes in a non-toxic concentrated form. In order to maintain the body`s fluid balance, it filters, cleans and purifies about 150-180 litres of blood and recycles it daily. The urine formed in the kidney is transported to the bladder by the ureters for storage. Urination is normally controlled by a reflex phenomenon with urinary sphincters, which determines when the urethra will bring out the urine from the bladder. Because of their functional ability, the kidneys also have the potential of controlling the blood volume by manipulating the urine volume, which in turn maintains the blood pressure at an optimum level. When there is dehydration, it reabsorbs the water from distal tubules and balances the blood volume. In case of hypertension or excess fluid intake, it eliminates the water and reduces blood volume and blood pressure. The functions of the kidney are co-ordinated by the endocrinal glands. The urine primarily formed contains a high concentration of glucose, which is returned to the main blood stream by means of the carrier molecules. As a result, the residual fluid contains high concentrations of urea and other such toxic substances which are eliminated during the process of urination. Urine is produced through the three processes of filtration, reabsorption, and tubular secretion.
Various pathological conditions are associated with abnormalities in mutra. These include dysuria, nocturia, uricosuria (gout), diabetes and many more. Urine can also indicate renal excretory disorders, pregnancy in women, adulteration in foods and steroids in the body. It often cautions about the early stage of a diseases before it proliferates.
As we can see, Ashtang Ayurveda rightly considers mutra as the vital excretory product of the body. Any disorder in the formation of urine affects the body`s normal functions. If any abnormality is found in the urine, Ashtang Ayurveda suggests immediate investigation of the source of the disease and the associated treatments.




















