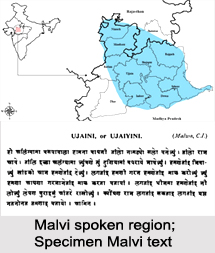
 Amongst various languages prevalent in the western region of the Indian subcontinent, Malvi finds a significant place. Also spelt as Malwi, it is the language spoken and native to the natural region of Malwa in west-central India, politically and administratively encompassing the districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. With over 10 million native speakers of the language, Malvi is closely related to Nimadi, spoken in the Nimar region of Madhya Pradesh.
Amongst various languages prevalent in the western region of the Indian subcontinent, Malvi finds a significant place. Also spelt as Malwi, it is the language spoken and native to the natural region of Malwa in west-central India, politically and administratively encompassing the districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. With over 10 million native speakers of the language, Malvi is closely related to Nimadi, spoken in the Nimar region of Madhya Pradesh.
Malvi language has different dialects pertaining to specific regions. It is spoken in the Ujjaini dialect in the Ujjain, Indore, Dewas, Shajapur and Sehore districts of Madhya Pradesh while prevalent in the Rajawadi dialect in Ratlam, Mandsaur and Neemuch districts of the state. It is spoken in Umathwadi in the Rajgarh district of Madhya Pradesh and in Sondhwadi in the Jhalawar district of south-eastern Rajasthan.
Amongst the different dialects of the language, Ujjaini is regarded the prestige dialect, with the language as a whole sometimes going by that name. Quite a handful of dialects, namely Bachadi, Bhoyari, Dholewari, Hoshangabad, Jamral, Katiyai, Malvi Proper, Patvi, Rangari and Rangri have taken birth from the Malvi language. The lexical similarity of all the dialects of Malvi ranges form about 65 to 89 per cent.
Malvi is a part of the Indo-Aryan group of languages, coming under the Western zone of the same. About 75 per cent of the Malvi speaking population can converse in Hindi, which is the official language of the Madhya Pradesh state, and the literacy rate in a second language, such as Hindi, is about 40 per cent. There are also several unpublished materials in Malvi.
This article is a stub. You can enrich by adding more information to it. Send your Write Up to content@indianetzone.com
Related Articles:
Languages of India
Indian Spoken Languages
Malwa Plateau
Nimadi Language
Indo-Aryan Languages
Hindi Language
Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh
Jhalawar District, Rajasthan
Madhya Pradesh
Rajasthan



















