Introduction
 Tawang district is amongst the 16 districts which are located in the North-East Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The term Tawang is a derivation of the words `Ta` which implies horse and `Wang` which means `chosen`. The ancient Tawang Monastery based here is believed to have been the true inspiration behind the name of Tawang. Tawang district is surrounded by Sela range of West Kameng in the eastern side, Tibet in the northern portion and Bhutan in the south-western part and is based at an altitude of 10,000 feet above mean sea level. The area occupied by this Indian district is a part of Tibetan territory, historically speaking.
Tawang district is amongst the 16 districts which are located in the North-East Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The term Tawang is a derivation of the words `Ta` which implies horse and `Wang` which means `chosen`. The ancient Tawang Monastery based here is believed to have been the true inspiration behind the name of Tawang. Tawang district is surrounded by Sela range of West Kameng in the eastern side, Tibet in the northern portion and Bhutan in the south-western part and is based at an altitude of 10,000 feet above mean sea level. The area occupied by this Indian district is a part of Tibetan territory, historically speaking.
>History of Tawang District
 History of Tawang district is mysterious and uncertain, though it was believed to be a portion of Tibet in the medieval age. Regional tribal kings used to rule the district at times. During 1873, this area was announced as off-limits and the region around Tawang became a cause for political dispute between the countries of China and India, following the Indian independence in the year 1947. In 1962, the Chinese army had invaded the district of Tawan, though eventually they retreated.
History of Tawang district is mysterious and uncertain, though it was believed to be a portion of Tibet in the medieval age. Regional tribal kings used to rule the district at times. During 1873, this area was announced as off-limits and the region around Tawang became a cause for political dispute between the countries of China and India, following the Indian independence in the year 1947. In 1962, the Chinese army had invaded the district of Tawan, though eventually they retreated.
The name Tawang was obtained from the gigantic Tawang Monastery which is based here, on the summit of a ridge, surrounded by tall columns of clouds and mist. This monastery is more than 400 years old and provides shelter to over 700 monks. It is believed to be amongst the most ancient and the grandest monasteries in Asia and supervises 17 Gompas and nunneries. Merag lama Lodre Gyatso had founded this monastery in 1681. The term `Ta` implies horse while `Wang` implies chosen. According to a popular legendary account, the place of this monastery was chosen by Merag Lama`s horse. The legend states that once when the Lama was praying inside a cave seeking divine intervention in aiding him to select an appropriate spot for constructing the monastery, his horse went missing. Finally, the horse was found at the summit of a hill. Believing this to be a divine miracle, the Lama decided to erect the Tawang Monastery at this exact spot. This monastery is also known as Galden Namgey Lhatse.
Before this spectacular monastery had been created, the Monpas were believed to have been the traditional inhabitants of Tawang district. They had ruled the Mon kingdom, which extended till Sikkim, right from Tawang district. However, eventually, the Mon kingdom was grabbed by the administrators of Tibet and Bhutan and included under their jurisdiction. Tawang was separated from Tibet after the independence of India from the British Raj. The army of China attacked Tawang in 1962, and during this time they demolished some parts of the Tawang Monastery. The nationalist troops of China controlled this district for several months. After the withdrawal of the Chinese armies, Tawang was again included under the administrative control of India. In the year 1984, Tawang district was severed from West Kameng District. Presently, Tawang district is an interesting tourist destination in India, particularly due to the existence of the Tawang Monastery.
Geography of Tawang District
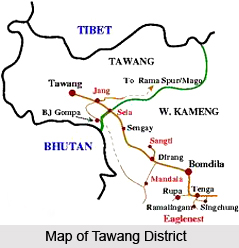 Geography of Tawang District involves some variations in climatic conditions which occur within short distances, on account of the alterations in the local terrain. Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh is located between longitude 90 ° 15 minutes East and latitude 27 ° 45 minutes North. West Kameng District in the south-eastern part, Tibet in the north-eastern part and Bhutan in the south-western portion surrounds the Tawang district.
Geography of Tawang District involves some variations in climatic conditions which occur within short distances, on account of the alterations in the local terrain. Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh is located between longitude 90 ° 15 minutes East and latitude 27 ° 45 minutes North. West Kameng District in the south-eastern part, Tibet in the north-eastern part and Bhutan in the south-western portion surrounds the Tawang district.
Climate of Tawang District
The maximum part of this Indian district is present in the Higher Himalayan Mountain range, which receives snowfall. The other portions of Tawang district are existent on the mountain slopes of the Lesser Himalayan Mountain ranges which mainly experience pleasant and cool climate.
Topography of Tamang District
The total area occupied by Tawang district is 2085 square kilometre and the forest area measures about 1251 square kilometre. Tamang district comprises two important geographical divisions. One of them involves the snowy Himalayan mountains which possess an altitude of about 11,000 feet to 22,000 feet which consists of uninhabited, bare mountains. The higher altitudes contain mountains which have a height of nearly 6000 feet to 11,000 feet. These mountain ranges comprises valleys and plateau regions, which boast of a scanty populace. The texture of the soil found here is loamy, rocky with a shallow depth. The soil existent here is mostly of a skeletal texture.
Demography of Tawang District
The 2011 census states that the population of Tawang district amounts to 49, 950, which imparts it a ranking of 633 in the country, out of 640. During the period 2001 to 2011, this district experienced a population growth rate of 28.33%. The literacy rate of this district is 60.61%. Monpas are the main inhabitants of Tawang, who dwell in the 163 villages situated here. Takpa tribals are found in the western and northern parts of Tawang.
Culture of Tawang District
The Tibetans, Takpas and Monpas who stay in this district follow Buddhism. Shamanist and Pre- Buddhist Bon influence is also noticed. Torgya, Dungyur, Choskar and Losar are the various festivals celebrated in Tawang district. Torgya and Dungyur festivals are observed in the Tawang Monastery with great pomp. The Tawang Monastery belongs to the sect of Gelugpa and is known to be the biggest monastery in the nation. Galden Namgey Lhatse is another name of this monastery. The regional tribes of Tawang are dependent on agricultural activities for earning their livelihood. Due to the cooler climes of this district, yak and sheep are bred by the local farmers. The people of Tawang follow monogamy but polyandry is also prevalent here. They reside in comfortable houses made of blocks of stone and are amicable by nature.
Administration of Tawang District
The district is classified into three major subdivisions known as Jang, Lumla and Tawang. The two administrative circles of this region are Kitpi and Tawang. The subdivision of Lumla is again divided into four administrative circles called Zemithang, Bongkhar, Lumla and Dudunghar. Jang is divided into four administrative circles known as Lhou, Mukto, Thingbu and Jang. Three Arunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly constituencies are existent here called Mukto, Tawang and Lumla. They all belong to the Arunachal West Lok Sabha constituency.
People of Tawang District
 People of Tawang District mainly constitute the Monpas, who are believed to be of a Mongoloid descent and immigrants from Tibet and Bhutan. However, the circumstances which resulted in the migration of the Monpas is veiled in mystery. A Tibetan epic named `Dowa Sangmo`, which is as old as the 7th century has mentioned a region called `Tana Mandegang`, which is said to be the kingdom which was ruled by the king Kala Wangpo.
There exists a popular legend which asserts that Acharya Padmasambhava, an Indian saint had paid a visit to this place in the 8th century.
People of Tawang District mainly constitute the Monpas, who are believed to be of a Mongoloid descent and immigrants from Tibet and Bhutan. However, the circumstances which resulted in the migration of the Monpas is veiled in mystery. A Tibetan epic named `Dowa Sangmo`, which is as old as the 7th century has mentioned a region called `Tana Mandegang`, which is said to be the kingdom which was ruled by the king Kala Wangpo.
There exists a popular legend which asserts that Acharya Padmasambhava, an Indian saint had paid a visit to this place in the 8th century.
The Monpa tribes follow Buddhism and the Tawang Monastery located here is a significant centre of their religious life. Prior to embracing Buddhism, the Monpas practised spirit worship as well as the sacrifice of wild animals. Motivated by the principles laid down by Lord Buddha, the Monpas are generally courteous and compassionate. The major occupation of these people is industrial, trade and cattle breeding. They are also known to breed yaks.
Monpas perform terraced cultivation processes and produce crops like tomatoes. It is said that the cultivation of potatoes commenced in the Tawang District in the 1970`s era, when the `Kufri Jyoti` species of potatoes were quite popular in this area. The local farmers had brought the seeds of potatoes from the North- Indian state of Himachal Pradesh and used to sell these seeds to the farmers belonging to Arunachal Pradesh. Several varieties of horticulture crops like almonds, walnuts, oranges and apples are cultivated by the people of Tawang district. Monpas reside in comfortable double-storied homes which are manufactured from stone and decorated with carved doors, window frames and plank floors. The inhabitants of this Indian district are quite artistic and are known to create excellent artefacts like bamboo utensils, carpets, wood carvings and many other items. `Thangka` paintings and hand-made paper crafts manufactured by the people of Tawang district have earned recognition. While monogamy is the general rule followed by the residents of Tawang, polyandrous marriages are also common in this portion of the country. Numerous people dwelling here are also known to follow the process of marriage though negotiation.
Art and Craft of Tawang District
 Art and craft of Tawang district are diverse and include the manifold innovative artifacts which are manufactured by the local artisans of this portion of the country. Such crafts are unique instances of the outstanding dexterity of the local craftsmen and are immensely popular amongst the local inhabitants. Utensils, carpet weaving, wood carving and bamboo products are the various indigenous crafts made here. They are also engaged in creating magnificent `Thangka` paintings as well as hand made paper.
Art and craft of Tawang district are diverse and include the manifold innovative artifacts which are manufactured by the local artisans of this portion of the country. Such crafts are unique instances of the outstanding dexterity of the local craftsmen and are immensely popular amongst the local inhabitants. Utensils, carpet weaving, wood carving and bamboo products are the various indigenous crafts made here. They are also engaged in creating magnificent `Thangka` paintings as well as hand made paper.
Numerous wooden products are crafted by the local craftsmen of Tawang district for decorative as well as utilitarian products. Wooden spoons like `sheng-khlem`, wooden cups called `gruk` which are utilized for serving tea, `zarku` which is used for serving meals and wooden masks are some of the several wooden items which are made here. The wooden masks are used particularly during the `Torgya Festival`, where the dancers are adorned in these wooden masks and perform in the courtyard of the Tawang Monastery. `Zan Shanpur` is a wooden ladle which is utilized for the purpose of kneading flour regularly. `Dolom` is a beautifully designed eating bowl manufactured of wood, and comes with a lid. Paddy rice is pounded with mortar and pestle, which are locally referred to as `Tun` and `TokTse`. `Zan Gya` is another wooden vessel which is again used to preparing flour paste which is termed as `zan`.
Dances of Tawang District
 Dances of Tawang district are a reflection of the ancient cultures and regional traditions which have been practiced since ancient ages, by the local inhabitants of this Indian district. Yak dance, Aji Lhamu dance and lion and peacock dance are some of the popular traditional dances which are performed in this part of the country.
Dances of Tawang district are a reflection of the ancient cultures and regional traditions which have been practiced since ancient ages, by the local inhabitants of this Indian district. Yak dance, Aji Lhamu dance and lion and peacock dance are some of the popular traditional dances which are performed in this part of the country.
Aji Lhamu Dance
Aji Lhamu dance is practiced by Sherdukpens of West Kameng District and Monpas of Tawang during the Losar festival. This dance is a portrayal of the Tibetan version of the Hindu epic of Ramayana and is practiced by five characters. Lhum and Lhamu are the female characters, while Nyapa is the main protagonist. Gyeli is yet another character in the dance. As per a mythological account, Lhamu is a fairy who had arrived on the earth and became the queen of Gyeli later. The dance therefore depicts the wedding ceremony of King Chhoegay Norzang and Lhamu.
 Yak Dance
Yak Dance
This dance is generally performed by the Monpas of the Eastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The yak dance is done by masked dancers whose dance symbolizes the discovery of the yak with the aide of a magical bird. This dance portrays the joy of the people upon finding the yak and it signifies the presence of health, wealth and happiness of the Monpa tribes, who believe that performing this dance would relieve them of all their complications and anxieties.
Lion and Peacock Dance
There exists an interesting legendary tale which is associated with the lion and peacock dance. According to this story, a saint named Tentelling was once meditating on the summit of Gangrikapro mountain for three years constantly, with severe concentration and abstaining from drinks and food. Two lions resided on the other side of the very same mountain. The legend also states that the snow lions were astonished to notice the saint mediating so austerely and out of compassion for him, offered him some milk. Gradually, the lions and the saint became close friends. News of this extraordinary incident reached the ears of the inhabitants of the place who approached the spot to witness the incident. Watching the sight with their own eyes, they were dumbfounded at the intimacy of man and animal and therefore they started dancing together. Therefore, the lion and peacock dance signifies the importance of harmony and mutual respect and also emphasizes upon the fact that for the survival of all species on this planet, the existence of peace and harmony between all living beings is essential.
Fairs and Festivals of Tawang District
 Fairs and Festivals of Tawang District are an essential part of the lives of the regional tribes of the state of Arunachal Pradesh. A majority of such festivals are influenced by religions and also agriculture of this area. Monpas tribe is engaged in observing most of these local festivals every year.
Fairs and Festivals of Tawang District are an essential part of the lives of the regional tribes of the state of Arunachal Pradesh. A majority of such festivals are influenced by religions and also agriculture of this area. Monpas tribe is engaged in observing most of these local festivals every year.
Losar Festival of Tawang District
The festival of `Losar` is celebrated with pomp in the latter portion of the month of February and the earlier part of March every year. It continues for a period of eight to fifteen days. Lion dances and yak dances are performed by youngsters during this festival. On the very first day of Losar festival, some members of the family follow a ritual of fetching a bucket of water during the early dawn and offer incense near the source of the water. After this is done, a scarf is tied around the water tap. A liquor known as `Chang` is offered, accompanied by `chemar` to please the Nagas, as well as the evil spirit. When they return home, the family members then visit the chapel wherein lamps are lighted and some prayers are recited for seeking blessings for peace and harmony. Everyone is then served hot chang, along with `khabsay` and `looves`, as a gesture of conveying best wishes to all and sundry. During this festival, religious flags are flown from the terraces of several local homes.
`Torgya Festival` of Tawang District
Torgya is a significant Monastic festival which is observed on the 28th day of the 11th month of the lunal calendar. This occurs in January, usually. It is believed that this festival eliminates the evil spirits, ailments and numerous natural disasters. Masked dances, which consist of some gracefully choreographed steps is the major attraction of Torgya. The dances are done inside the courtyard of the Tawang Monastery.
Choekhor Festival of Tawang District
The Choekhor festival is conducted by the entire village in order to bestow divine protection to the regional crops and also to alleviate the ill effects of the evil spirits which are feared to adversely affect the communities residing in the villages. The monks recite prayers for the well-being of agriculture and newly planted crops and religious flags are flown by the monks, in the religious processions which are carried out in this festival. Two `Kong-Yoks`, who are followed by innumerable regional people leads this procession.

Gaden Ngamchoe Festival of Tawang District
Gaden Ngamchoe festival is celebrated on the 25th day of the lunar month to mark the death anniversary of the founder Gelukpa named Tsong Khapa. The Gelukpa is an order of Tibetan Buddhism. Lamps are lit towards the evening on the rooftops of houses and also the verandahs of several homes and monasteries.
Dukpa Tse-She Festival` of Tawang District
The Dukpa Tse-She festival is celebrated to pay tribute to the delivery of religious sermon by Lord Buddha inside the Deer Park at Sarnath. During this festival, residents of this district visit the monasteries and chant prayers. It is observed on the fourth day of the lunar calendar`s sixth month.
`Saga Dawa Festival` of Tawang District
Saka Dawa festival falls on the fourth month of lunar calendar and it is celebrated to mark the attainment of `Nirvana` by Gautama Buddha.
Traditional Games of Tawang District
 Traditional Games of Tawang district include `Majong`, archery, `Sho` or the game of dice and `pongor`, which are played the regional inhabitants of Tawang district.
Traditional Games of Tawang district include `Majong`, archery, `Sho` or the game of dice and `pongor`, which are played the regional inhabitants of Tawang district.
Majong in Tawang District
The game of Majong is played with the aide of small tiles by four people. In this game, the players choose tiles and abandon them, and continue doing so till a unique combination is reached when one of the players win the game.
Archery in Tawang District
Archery is amongst the most interesting games of Tawang district which is practiced by the Monpa men-folk, particularly during the Losar festival which is celebrated in February. The arrows and bows employed in this game are generally made of bamboo. They are placed at about 50 to 100 metres during this game.
`Sho` or Dice Game in Tawang District
The game of Dice, locally referred to as `Sho`, is usually played by the Monpas and participated by three persons. Two dices are used, which are shaken inside a wooden bowl. Thereafter, the bowl is turned and placed on a strip of leather, with a thumb. Seashells are utilized to count the scores of the players.
Pongor in Tawang District
Pongor is yet another game which is played by the men of the district and is a certain type of shot put.
Tourism in Tawang District
 Tourism in Tawang District is gaining popularity due to the presence of the renowned Tawang Monastery and picturesque tourist locales which tempt nature lovers all across the nation. Innumerable tourists throng Jang Waterfalls, which is located here. The snow covered Sela Pass in Tawang district is another major tourist attraction in this Indian district. There exists a handicrafts centre in Tawang district which encourages the production of small-scale industries based on the regional handicrafts.
Tourism in Tawang District is gaining popularity due to the presence of the renowned Tawang Monastery and picturesque tourist locales which tempt nature lovers all across the nation. Innumerable tourists throng Jang Waterfalls, which is located here. The snow covered Sela Pass in Tawang district is another major tourist attraction in this Indian district. There exists a handicrafts centre in Tawang district which encourages the production of small-scale industries based on the regional handicrafts.
Visitors who aim to pay a visit to this portion of the country must possess an Inner line Permit from the government which can be availed from New Delhi, Tezpur, Guwahati and Kolkata. Travellers approach Tawang along a steep road journey, and cross Sela Pass which is located at an altitude of nearly 13, 701 feet. One might also access Tawang from the Tezpur area of Assam by road. Visitors from Kolkata can reach Tezpur with the aide of a direct flight. In June, 2008, the government of Arunachal Pradesh had initiated a regular helicopter service from Guwahati till Tawang.
Private and shared taxis and buses are some of the readily available modes of transport for visitors who are looking forward to traveling from Tawang to Tezpur in Assam. One can enjoy the spectacular natural beauty as one approaches Tawang, particularly when he passes the Bomdila Pass which is located at a height of 8, 000 feet, Sela Pass and Jaswant Garh. The entire journey spans for a time duration of about 12 hours. One can gorge on the local delicacies like cream buns, vegetarian momos and non-vegetarian items.
Tawang district also includes some of the most beautiful waterfalls, lakes and mountains are capable of charming all its visitors. The regional Monpa tribes of this place are known to be hospitable and generally welcome tourists warmly. The best time one should visit Tawang is between the months of September and November. From December to March, one would experience the thrilling sight of snow covered mountains and landscape.
Monasteries of Tawang District
Monasteries of Tawang District include the Buddhist monasteries like Tawang Monastery, Regyaling Monastery, Urgelling Monastery and many other monasteries. These monasteries are located on the top of the Eastern Himalayan Range or in the foothills of the Shivalik Hills.
The experience of Buddhism developed within the Buddhist tradition over thousands of years has shaped an unrivalled resource for all those who wish to follow a path which ultimately culminates in Enlightenment. An enlightened one sees the nature of reality absolutely clear, and lives fully and naturally in accordance with that the inward vision. This is the goal of the Buddhist spiritual life, representing the end of suffering for anyone who attains it. And these doctrines are developing in these monasteries.

Tawang Monastery
Tawang Monastery in Tawang District of Arunachal Pradesh is one of the largest monasteries of Mahayana sects and the second oldest monastery in the world after Lhasa Monastery. Tawang Monastery, which is also known as Galden Namgey Lhatse, is housed with more than 500 monks. It has also a centre of Buddhist Cultural Studies where the Buddhist monks and the young Buddhist students are provided the basic philosophical education besides the traditional monastic education. This monastery was founded by a Mahayana Buddhist monk named Mera Lama Lodre Gyatso a contemporary of His Holiness Fifth Dalai Lama in 17th century AD. The complex of the Tawang monastery is comprised of more than 65 residential buildings meant for monks. The Monastery also houses the establishment of the Head Priest, living chambers of the Lamas, an ancient library and antique museum.
Regyaling Gonpa
Regyaling Gompa was constructed by the former Rigya Rinpoche. This monastery is located at a distance of one kilometre from Tawang Town, located ion the midst of Tawang District. However, after the death of Regyaling Gonpa, the charge of the Gompa was taken over by his secretary, Chang-sey. The monastery of Regyaling is surrounded by a lush green pine forests. The monastery of Regyaling Gompa is surrounded by a lush green pine groove enhancing the beauty of the Monastery.
Urgelling Gonpa
Urgelling Gonpa is one of the main attractions of the tourists; which is believed to have been in existence since medieval times. It was one of the first three monasteries built by Urgen Sangpo, the youngest brother of Terton Pempalingpa, the famous Treasure-Revealer. It was here in 1683 Tsangyang Tashi, His Holiness the sixth Dalai Lama was born. He was the son of Lama Tashi Tenzin of Urgelling village a descendent of Terton Pempalingpa. The Urgelling Gonpa is about 3 kilometers away from Tawang.

Taktsang Gonpa
Taktsang Gonpa whgich is better known as Tiger`s Den, is located at the distance of 45 kilometers from Tawang. The Tawang Township is located in Tawang District. It is believed to have consecrated by the visit of Guru Padmasambhava in the 8th century AD. The Monastery of Taktsang is perched on the ridge of the hillock surrounded by a dense coniferous forest and lofty mountains of eastern Himalayas. The visitors can also conduct a pilgrimage visit round about the places nearby Taktsang Gonpa where Guru Padmasambhava had meditated. It is place where one can really feel the ecstasy of solitariness and tranquillity.
Gorsam Chorten Stupa
The Gorsam Chorten Stupa is situated ninety kilometres from Tawang town. This Stupa is the largest Stupa of Tawang Township. The Gorsam Chorten Stupa is believed that Lama Pradhar, a Buddhist monk of Monpa Tribe constructed in this Stupa in the early phase of 12th century. The semi-circular dome of this Stupa touched the sky and rests upon a three-terraced plinth. There are four miniature Stupas are also set on the four corners of the lower most terraced of the plinth. The base of the stupa is squared with each side about 170 feets in length with a niche running along its whole length and 120 Manis are set in wooden frames. A well-paved footpath goes around the Stupa for pilgrims to go round about praying, which in Pali Language says Kora.



















