Introduction
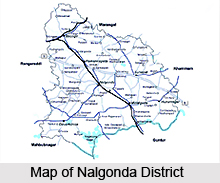 Nalgonda district is located towards the southern part of Telangana, a newly formed state in India with the capital Hyderabad for 10 years. Previously the district was known by the name Nilagiri, the meaning of which is `blue hill`. Later on the district was named after Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah after he had conquered the region. Other famous dynasties which had reigned over the district were the Satavahana Kings, the Kakatiyas and the Mughal Rulers.
Nalgonda district is located towards the southern part of Telangana, a newly formed state in India with the capital Hyderabad for 10 years. Previously the district was known by the name Nilagiri, the meaning of which is `blue hill`. Later on the district was named after Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah after he had conquered the region. Other famous dynasties which had reigned over the district were the Satavahana Kings, the Kakatiyas and the Mughal Rulers.
Nalgonda district has been divided into 59 mandals under 4 Revenue Divisions. As far as the history of the district is concerned it dates back to the Paleolithic Age. Gradually with passing time Nalgonda has moved towards advancement and development. As such Nalgonda has been influenced by a number of rulers and the district has strongly survived the ravages of time and human vandalism and till today has retained its pristine glory. The district of Nalgonda became a part of Telangana on 1st November 1956.
History of Nalgonda District
History of Nalgonda deals with the glorious rule of Satavahana Dynasty, Chalukya Dynasty, Maurya Empire, Pallava Dynasty and Vishnukundini Dynasty.
During ancient period, the people fashioned tools and weapons by chipping hard stones of convenient size and shape. This feature is testified by the findings of unifacial Paleolithic implements of the Sloan type at Yellowhammer. The traces of Neolithic culture were found at Chota Yelupu, where chuck stones and other objects of interest were unearthed.
Ancient History of Nalgonda
History of Nalgonda commences with the rise of Maurya Empire. Mauryas, during the reign of Ashoka the Great held their sway over this region. Later, the region came under the lordship of the Satavahana Dynasty who ruled between 230 BC - 218 BC. It was during this period the region established trade contacts with the Roman Empire. The Ikshvakus Dynasty attained control over the region of Nalgonda and ruled with their capital Vijayapuri. During this period, the Sakas reigns this region. Buddhism flourished during this period. After the Ikshvaku Dynasty, Pallava Dynasty and Yadava Dynasty fought for supremacy over the region. A major portion of Nalagonda appears to have passed from the Chalukyas of Badami to the Rashtrakuta Dynasty. Rashtrakutas fell in 973 and gave room to the Chalukyas of Kalyani. The sway of the Chalukyas continued until the end of the 12th century.
 Medieval History of Nalgonda
Medieval History of Nalgonda
Nalgonda came under the control of the Kakatiyas from the western Chalukyas in the early phase of middle ages. During Prataparudra`s time the kingdom was annexed to the Tughluq Empire in 1323. During Muhammad bin Tughluq`s period, Musunuri chief Kapayanayaka ceded a part of Nalgonda to Ala-ud-din Hasan Bahman Shah. During Ahmad Shah I`s period the region was annexed to Bahmani kingdom. Jalal Khan in 1455 declared himself king at Nalgonda, but it was a short-lived affair. The region was brought back to the Bahmani kingdom. During the time of the Bahmani Sultan Shihabud-din Mahmun Sultan Quli was appointed as tarafdar of Telangana region of present-day Telangana . From him the region was taken by his son Jamshid.
Modern History of Nalgonda
Nizam-ul-Mulk defeated Mubasiz Khan at Shaker Khere in Berar (now Berar District) and ruled the Deccan in an autonomous capacity. This district, like the other districts of Telangana, passed under the Asaf Jahis and remained under them for a period of nearly two hundred and twenty five years. After the Asaf Jhah Dynasty rule, British gained autonomous power and Nizams became their feudal members.
Geography of Nalgonda District
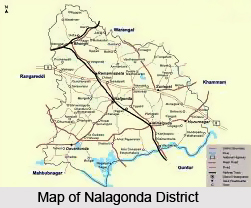 Geography of Nalgonda District in Telangana covers with the variant landforms and pleasant landforms. Nalgonda district is situated in the State of Telangana, between 16-25 degree and 17-50 degree of the Northern Latitude and 78-40 degree and 80-05 degree of Eastern longitude covering an area of 14,240 Sq. Kilometres.
Geography of Nalgonda District in Telangana covers with the variant landforms and pleasant landforms. Nalgonda district is situated in the State of Telangana, between 16-25 degree and 17-50 degree of the Northern Latitude and 78-40 degree and 80-05 degree of Eastern longitude covering an area of 14,240 Sq. Kilometres.
Extension of Nalgonda District
Nalgonda District is located in the Southern part of the Telengana region, Nalgonda district became part of Telangana with effect from 2014 that is after reorganization of Telangana after bifurcated from Andhra Pradesh. It was formerly known as "Nilgiri"
Nalgonda District is bounded by the Medak district and Warangal district in the North, Guntur district and Mahbubnagar district in the South, Khammam district and Krishna district in the East and Mahabubnagar district and Ranga Reddy district in the West.
Climate of Nalgonda District
The geographical area of Nalgonda District is 14,217 Sq. Kilometres. The region experiences a hot and dry summer throughout the year except during the South West Monsoon season. The year may broadly be divided into four seasons. It experiences cold season from December to Mid February, summer season from Mid February to first week of June. South West monsoon season from June to September and retreating monsoon or the past monsoon season during October to November. Cold season, extending from December to February, is followed by summer when both day and night temperatures increase sharply. May being the hottest month, the mean daily maximum temperature is about 40 degree Celsius and the mean daily minimum is about 28 degree Celsius sometimes the day temperature crosses 44 degree Celsius during this period. On some days, afternoon thundershowers come as a blessing and though temporarily they bring relief from the oppressive summer heat. By about the beginning of October day temperature decreases steadily signalling the withdrawal of monsoon. The day and night temperature decrease rapidly during November. December is the coldest month with the mean daily maximum and minimum temperatures being 35 degree C and 20 degree C respectively. Sometimes during the cold season, night temperature may drop down to about 10 degree C. The skies are generally clear or lightly clouded throughout the year except during south west monsoon season when heavy clouds cast the skies.
Annual Rainfall of Nalgonda District
The average rainfall in the district is 772 mm. 71% of the annual rainfall is received by the district during south west monsoon (i.e. June to September). September is the rainiest month. During summer and retreating monsoon season some amount of rainfall is received in the form of thunder showers. The variation in the annual rainfall in the district from year to year is large. On an average there are 46 rainy days. (i.e. days with rainfall of over 2.5mm or more).
Soils of Nalgonda District
The soils of the district are mainly `red earth`s` comprising loamy sands, sandy loams and sandy clay loams. In the areas of flat topography and along side the Krishna River and its tributaries, regur or black cotton soil is found.
Agriculture of Nalgonda District
The increased Irrigation facilities have given a boost to agricultural activity in the district. Out of a total of 14, 23,423 hectares of land utilisation in the district, more than 50% is cultivable land. The terrain of the district is very suitable for irrigation development. The government has taken all measures to increase the percentage of land under cultivation by expending irrigation facilities. The emphasis was not only on major irrigation projects but area specific and need specific minor and lift irrigation projects were also given predominant importance. The main crops grown in the district are Paddy, Jowar, Bajra, Ground Nut, Red gram, Green gram, Castor and Sugarcane is being grown in command areas to the extent of about 1,50,000 acres. The practice of mixed cropping is limited to dry crops. Jowar is grown mixed with red grams or bajra. Red gram is also grown mixed with groundnut or bajra or green gram.
Population of Nalgonda District
According to the census of 2001, the district has a population of 3,238,449. The density of population in the district is equal to 242 persons per square kilometre and the literacy rate in the region is 58 percent. As far as vegetation is concerned around 7 percent of the land in Nalgonda is covered by forests. The types of forests which are commonly found in the region are mixed deciduous forest and tropical thorn forests.
Culture of Nalgonda District
 Culture of Nalgonda district lies in the traditions and customs that have been passed down through the generations. Over centuries, these have found expression in the art, language, dance, music and social customs of the place, unique to that region alone. The performing arts, particularly the theatre, are especially significant in preserving and transmitting the culture of a place. The culture of Nalgonda district finds expression through all these various means. Nalgonda district is famous for its religious, linguistic and traditional diversities.
Culture of Nalgonda district lies in the traditions and customs that have been passed down through the generations. Over centuries, these have found expression in the art, language, dance, music and social customs of the place, unique to that region alone. The performing arts, particularly the theatre, are especially significant in preserving and transmitting the culture of a place. The culture of Nalgonda district finds expression through all these various means. Nalgonda district is famous for its religious, linguistic and traditional diversities.
In the field of drama and theatre, plays dealing with mythological themes from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata are greatly enjoyed and appreciated. The Harikatha is another popular art and provides enjoyment and edification particularly to the elderly and devoutly inclined. Veedhinatakam or street drama in which the characters sing and dance throughout the night is another traditional art which has retained its popularity. The Burrakatha which is a ballad sung by a minstrel to the tune of a single - stringed Tambura and tiny drum grips both the urban and the rural people so wonderfully that its popular appeal has been exploited by the Government to spread the meaning and message of the plans and also by the political parties to spread their ideologies.
There are also a number of rural dances and games, of which Kolatam by girls is a popular dance. Among the classical arts, confined largely to urban life are the Bharatnatyam and Kuchipudi styles of dance and Carnatic music. The musical instruments largely in use are the Violin, Flute, Veena and Mridangam. Hindustani music, an art which was introduced into the district during the time of the Peshwas is also practised in many parts of the district. The lambada dance and the hand-clapping dance are very popular in rural areas. The Holi Dholandi is the traditional dance of the Lambada women. They sing quite gaily and dance prettily; the songs are in their own language and mostly in praise of Lord Krishna. In some places Pigeon flying is a popular pastime. In some place where important public offices are located, the employees have their recreation clubs.
 In the community life of the region, there is seen a in diversity though the external pattern of life of all the communities is becoming increasingly uniform under the Socio-economic stresses of modern living, each community has its own particular way of life, distinguished by varying manners and customs. All the communities co-exist in harmony and follow their beliefs and customs. Pilgrimages to holy shrines is a custom common to all three major religious groups.
In the community life of the region, there is seen a in diversity though the external pattern of life of all the communities is becoming increasingly uniform under the Socio-economic stresses of modern living, each community has its own particular way of life, distinguished by varying manners and customs. All the communities co-exist in harmony and follow their beliefs and customs. Pilgrimages to holy shrines is a custom common to all three major religious groups.
The culture of a place is also inherent in the dressing style of the people belonging to that place. Among the Hindus and Christians men commonly sport a Dhoti and Kurta. The younger folk of all communities, however, wear pants and shirts, The Muslims normally wear pyjamas and instead of dhoties and Kurta and the fez cap which however is not so common now. The women of all communities including Muslims wear saris and blouses (Ravikulu). Salwar Kameez are also worn by some Muslim women. The Lambada men have adopted the regional dress but the women folk have to this day retained their attractive colourful and heavy garments.
Hindu women wear the Bottu, The vermillion mark on the forehead. Some of the Christian women, particularly, the Catholics also put on the Bottu. Among the most treasured ornaments of married Hindu women are the Tali and Mattelu (Silver rings on the toes) because these ornaments are the seal and symbol of married status and are discarded only in the unfortunate event of widow-hood. The Lambada women are laden with ornaments, the horn bangles and the peculiar shaped anklets, which are heavy, attractive and most characteristic.
There is seen a comfortable harmony existing between the various communities living in the district. Almost all the festivals typical to the different communities, such as Diwali, Sankranti, Id ul Fitr, Bakrid, Christmas and Easter are celebrated here. A festival typical to the Telegus is the Ugadi. It is celebrated as the New Year Day of the Telugus usually occurring in March - April (Chaitra Suddha Padyami). Ugadi festival is characterised by the reading of significant passages from the New Years Panchangam (almanac). Feasting, common to all festivals is of course there.
Jatra and fairs are held in all parts of the district. These are annual occasions celebrated in reverence to a local God or Goddess. Urs are also organised on certain religious occasions. All these make the festivals and celebrations a much awaited affair of mirth and joy.
Education in Nalgonda District
 Education in Nalgonda district in Telangana is taken care of by the District Education office of Telangana State. It takes care to see that education is imparted to all children below the age of fourteen years. District Education Officer is the Head of the Department. He is responsible for the entire academic monitoring from 1st Class to 10th Class and administrative control of educational institutions up to 10th Class.
Education in Nalgonda district in Telangana is taken care of by the District Education office of Telangana State. It takes care to see that education is imparted to all children below the age of fourteen years. District Education Officer is the Head of the Department. He is responsible for the entire academic monitoring from 1st Class to 10th Class and administrative control of educational institutions up to 10th Class.
There are certain aims and objectives District Education Office, in keeping with which it carries out its functions. These aims are-
•To achieve 100% enrolment in 5-14 age group children
•To ensure 100% retention i.e. who are enrolled in the school.
•To reduce the dropout rate.
•To improve the quality of education and results of VII and X Class.
•Provide schooling facility to every habitation.
A number of steps have been taken by the Government and administrative authorities in order to improve the quality of education in the Nalgonda district. During the academic year 2001-02, the Government had sanctioned 416 new primary schools in school-less habitations in the district. Out of these, 20 were supposed to be Urdu medium schools. They were all opened with the help of Vidya volunteers. 396 Secondary Grade Teachers Telugu Medium 20 and Secondary Grade Urdu Medium Posts have been sanctioned posts are to be filled by the candidates.
The Govt. had also permitted to upgrade 109 Primary Schools into Upper Primary Schools by opening Class - VI. Apart from this, the Government also took measures to provide audio-visual education to the students for improving their power of absorption and intellect. For this purpose, the Government has provided TVs. V.C.Ps and R.C.C.Ps to the District for development of Primary Education. The scheme of Vocational Education Scheme was introduced during the year 1985-86 in the then 15 secondary schools in the district. As a result of this, 7 Vocational Educational Trades are being run in the above 15 Secondary Schools and around 5931 students are being benefited in the trades.
In 2001, the State Project Director, DPEP, A.P., Hyderabad, the twin capital of both Telangana and Andhra Pradesh had communicated G.O.Ms.No.52, Education Department for the implementation of Education Guarantee Scheme and Alternative and Innovation Education in Nalgonda. As per the guide lines of the G.O. a district level committee had been constituted with the following members to receive and review the proposals emanating in the district under the Chairmanship of the District Collector.
Vidya Volunteers of Nalgonda District
As per the instructions of Commissioner and Director of School Education, A.P., Hyderabad total (1489) Vidya Volunteers were engaged by the School Education Committees in their respective Schools as against the district requirement of (1904) Vidya Volunteers.
In the year 1997-98 the Open School Scheme was introduced in Nalgonda district. The basic aim of the scheme is to provide alternate system of education to the dropouts who have missed the benefits of Formal Schooling. According to the scheme, any one who has completed the age of 12yrs and dropped out at V, VI, and VII Classes is eligible for the course. The courses conducted are S-2, equal to class VI education and S-3, equal to class VII education. The division of the course has been done according to the trimester system, i.e., 10 months in a trimester equals 3 trimesters. The passed learners in Stage-II (S2) and Stage-III (S3) are admitted in 7th & 8th Class in formal Schools. Study Centres are identified where 20-30 learners are available in a village.
A.P.Open School Society, Hyderabad has sanctioned 150 Open Schools Centres during the academic year 2001-02. Out of 150 Centres, 138 study centres are opened in 54 Mandals. 87 Cluster centres are identified for the conduct of contact Classes and Trimester Examinations to the learners.
Child Labour Residential Schools of Nalgonda District
The child labour survey was conducted at village level by the teachers and name wise lists of never enrolled, drop-out, working children prepared and read out in Janmabhoomi Program. Lists are available with the Head Masters and Mandal Education Officers concerned. The village wise campaigns were conducted for enrolment. Government Organizations meetings were conducted to run the bridge course centres one for each Mandal.
Economy in Nalgoda District
As far as economy is concerned most of the people in Nalgonda district are engaged in agriculture and hence it is obvious that most of the revenue earned in the region is from agriculture.
Tourism in Nalgonda District
Leisure Tourism in Nalgonda District
 Leisure tourism in Nalgonda district in Telangana is a pleasurable experience as the district has a variety of places to offer to the interested tourist. Forts, dams and places of historical worth are among the prime spots of leisure situated in the Nalgonda district.
Leisure tourism in Nalgonda district in Telangana is a pleasurable experience as the district has a variety of places to offer to the interested tourist. Forts, dams and places of historical worth are among the prime spots of leisure situated in the Nalgonda district.
Bhongir Fort
Among the historical monuments located here, the Bhongir fort is a popular destination. It was built on an isolated rock by the western Chalukya ruler Tribhuvanamalla Vikramaditya VI and was thus named after him as Tribhuvanagiri. This name gradually became Bhuvanagiri and subsequently Bhongir. The splendid historical fort with the awe-inspiring rock and the aesthetically fortified courts which have stood the ravages of time stir the imagination of the tourists. The Bala Hisar or citadel on the top of the hill gives a bird`s eye view of the neighbouring area. The fort is associated with the heroic queen Rudramadevi and her grandson Prataparudra`s rule. At the foot of the fortified rocks, 609.6 meters above the sea level, stands the town of Bhongir.
Devarakonda Fort
Another fort situated here is the Deverakonda Fort. Once a formidable stronghold of the Recherla Chiefs, this fort now stands in ruins. It is surrounded by seven hills and is connected with Nalgonda, Mahbubnagar, Miryalguda and Hyderabad by road.
Nandi Konda is a small village on the bank of Krishna River where several Buddhist structures like monasteries and pillared halls were unearthed and preserved in a Museum of Central Archaeological Department.
Pochampalle
Of great historical interest is Pochampalle, the place of origin of the popular Bhoodan movement led by Acharya Vinoba Bhave in 1950, when offerings of land were donated to the landless poor on his plea. The impetus to a great movement led by Vinobaji has a humble but a noble beginning at this place. It so happened in 1951 that during Vinobhaji`s tour, 2 Harijans complained that they did not have any land at all. Then a local Deshmukh readily offered 100 acres of his own land for the distribution among the poor. This is said to have given Vinobaji the idea of propagating Bhoodan Yagna. Out of 13,100 acres of donated land nearly 8,290 acres have been distributed among the landless poor. Pochampalle is situated at a distance of about 14.48 kilometres from Bhongir and 9.66 kilometres from the Bibinagar railway station.
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
Located at a distance of 150 kilometres from Hyderabad, Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is an important irrigation dam on river Krishna. This is the tallest and biggest masonry dam in the world. It creates the third largest man-made lake in the world. Apart from this, some remains of the Buddhist civilization dating back to the 3rd century A.D, are seen on an island called Nagarjunakonda located in a man-made lake on the other side of the river Krishna. These relics of Buddhist civilization found during excavation unveiled the traces of Mahachaitya, the most sacred of the stupas. An inscription in the Brahmi script states that the sacred relics of Lord Buddha lie within the Mahachaitya. Similar excavations of the surroundings have brought to light the remains of a university, vihara and monasteries. This University flourished under Acharya Nagarjuna, the great Buddhist saint, scholar and philosopher who migrated to Nagarjunakonda from Amaravati to spread the message of the Buddha. An "Ashwamedha" sacrifice altar and tools from Paleolithic and Neolithic times were also found here. The remains of a Buddhist University were found during an excavation while constructing the Nagarjuna.
Excavations near Nagarjuna Sagar Dam
The foundation stone of the Sagar Dam was laid by the late Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister of India on 10-12-1955. Excavations conducted at the Sagar Dam have revealed several Brahmanical temples. Now though the actual site of the excavations have been flooded with the waters of the mighty river, the relics of the ruins have been reconstructed and kept in an island museum, the largest of its kind in the world and are in an excellent state of preservation-thanks to the efforts of the Archaeological Survey of India. Today Nagarjunakonda along with Nagarjunasagar attracts many tourists from South East Asian Countries and also from all over India.
Pilgrimage Tourism In Nalgonda District
 Pilgrimage Tourism in the Nalgonda district comprises a visit to the various beautiful temples located here. A number of magnificent temples are found located at the Nalgonda district which are not just of religious significance but also of great historical work due to the era of their construction. Some of the prime spots of pilgrimage tourism in the Nalgonda district are discussed below.
Pilgrimage Tourism in the Nalgonda district comprises a visit to the various beautiful temples located here. A number of magnificent temples are found located at the Nalgonda district which are not just of religious significance but also of great historical work due to the era of their construction. Some of the prime spots of pilgrimage tourism in the Nalgonda district are discussed below.
Sri Laxminarsimha Swamy Temple, Yadagirigutta
Yadigirigutta, also known as the second Tirupati, is said to be the abode of Lord Narsimha Swamy. It is believed that the son of the great sage Rishyatunga, Yadarshi, did tapas here once upon a time and pleased by his devotion the Lord Narsimha Swamy appeared before him in his five forms, archa purams. The hill which Narsimha Swamy appeared before Yadarshi has hence came to known as Yadagiri. The temple attracts a number of tourists and pilgrims all throughout the year. The pujas held here begin at four and the day ends at 9 pm. Brahmotsavam of the Lord is celebrated from Suddha Vidiya of Palguna Masam to Dwadasi and Narasimha Jayanthi from Suddha Dwadasi of Vyshaka Masam to Chaturdasi. The Kshetram is situated at a distance of 60 km from Hyderabad on the Secunderabad-Khajipet rail-road. It is situated at a distance of 6 km from Raigir Railway station and distance of 15 Kms from Bhongir. A number of buses are also available from Hyderabad to Yadagirigutta and Bhongir to Yadagirigutta.
Sri Meenakshi Agastheswarw Swamy, Wadapally
 6000 years ago sage Agastya Maharshi installed the idols of Sri Meenakshi Agasteswara and Sri Laxmi Narsimha at the holy Sangam of Krishna River and Musi river in Wadepally village of Miryalguda Mandal. For thousands of years the temple remained hidden in a dense forest. During the time of excavation the idols of Lord Shiva were found in the temple and reinstalled. There are holes on the Siva Lingam in which 10 figures can be inserted. Even after taking large quantities of water from the holes, the level of water does not go down.
6000 years ago sage Agastya Maharshi installed the idols of Sri Meenakshi Agasteswara and Sri Laxmi Narsimha at the holy Sangam of Krishna River and Musi river in Wadepally village of Miryalguda Mandal. For thousands of years the temple remained hidden in a dense forest. During the time of excavation the idols of Lord Shiva were found in the temple and reinstalled. There are holes on the Siva Lingam in which 10 figures can be inserted. Even after taking large quantities of water from the holes, the level of water does not go down.
Sri Laxmi Narsimhaswamy, Wadapally
Located at the confluence of the Krishna River and the Musi River there is a very old temple of Sri Narasimha Swamy. According to the Indian Puranas, Vyasa Bhagavan knowing the piousness of the place meditated for a long time for the manifestation of Sri Narasimha Swamy. Consequently, Sri Narasimha Swamy manifested there to bless the devotees and to alleviate their difficulties. It is believed that even now that idol breathes in and let it out. The temple authorities have arranged two lamps. One of the lights of the lamp used for showing the face of the Lord will be quivering to testify the fact that the Lord is taking breath and letting it out. The light of the other lamp, which is kept below remain resolutely.
Sri Jain Mandir, Kolanpak
The Jain Shrine at Kolanupak village in Nalgonda district is more than 2000 years old and was renovated very recently by employing more than 150 artisans from Rajasthan and Gujarat. Found at the temple near Alair are three holy idols of Lord Adinath, Lord Neminath and Lord Mahavira and 21 other "Theerthankars". The Kolanupaka temple has a great history. Lord Vrishaba Deva populary called Adinath Bhagvan was the first "Theerthankara" in the Jain religion. It is believed that the original idol of Lord Adinath, known locally as Manikya Deva has made Kolanupaka its abode. It is believed that Jainism was prevalent in Andhra Pradesh before 4th Century and Kolanupaka was one of the prominent centres of Jainism.
 Sri Seetharamachandra Swamy Devasthanam
Sri Seetharamachandra Swamy Devasthanam
Sri Seetha Rama Chandra Swamy Devasthanam was originally situated at Malbouli. It was later shifted here when the lord appeared to Kammamettu Shesha Charyulu and his brothers in their dreams and asked them to install him at any other place. They installed the idols and named that area as Ramagiri. All this happened more than 200 years ago. Over the years of development, Godadevi (Andalamma) idol was installed in the same premises. The Andalu Kalyanam is celebrated here on a grand scale.
Pillalamarri
Historically significant, this ancient village consists of many splendid temples is maintained by State Government. The temples stand testimony to the architectural style of the Kakatiya period. The intricately carved stone pillars add grandeur to these archaeologically significant temples. Frescoes and inscriptions tell the tales of the rulers of the Kakatiya dynasty. There is a Kannada, Telugu inscription dated S. 1130 (A.D 1208) on a stone referring to king Ganapati. Another inscription of S.1117 (A.D 1195) found on a stone in the temple mentions the rule of Rudradeva. Ancient coins have also been discovered at this place. Pillalamarri, being the birth place of the famous Telugu poet Pillamarri Pina Virabhadrudu, is not only historically but also culturally and religiously significant. The sanctorum of Lord Chennakesavaswami is much revered and the annual celebration of the deity, held during February - March is waited to be attended by thousands of devotees.
Panagal
 The shrines of Panagal constitute perhaps the finest examples of the medieval Deccan temples. The temple complex consists of the main shrine dedicated to Lord Shiva with the Nandi mandapa in front. It has 66 pillars. The four central pillars of the mandapa are highly ornate at the bottom and, on them, the scenes from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata are depicted. The perfected-screen pattern on the flanks in various dancing poses displays the supreme workmanship accomplished during that period. These are specially noted for their graceful carving which reveal the high perfection reached by the sculptors and architects of that age. The Kakatiya Stapati mastered the idioms of the earlier Chalukya style.
The shrines of Panagal constitute perhaps the finest examples of the medieval Deccan temples. The temple complex consists of the main shrine dedicated to Lord Shiva with the Nandi mandapa in front. It has 66 pillars. The four central pillars of the mandapa are highly ornate at the bottom and, on them, the scenes from the Ramayana and the Mahabharata are depicted. The perfected-screen pattern on the flanks in various dancing poses displays the supreme workmanship accomplished during that period. These are specially noted for their graceful carving which reveal the high perfection reached by the sculptors and architects of that age. The Kakatiya Stapati mastered the idioms of the earlier Chalukya style.
The Chayala Somesvara temple is yet another temple near Panagal. The temple is known for the Chhaya (shadow) of Siva Linga which is said to be stationary from sunrise to sunset. The temple contains valuable inscriptions of Rudramba`s time. The most conspicuous feature of the Pandya style was the emergence of the monumental gateway or Gopuram which is the dominant point of temple complex. The walls of the temples imposed an ornamental appearance. The gateways are treated with rich plastic decorations
Mellachervu
The village of Mellachervu has still restored the glimpses of Kakatiyan architecture which is manifested in one of most celebrated temples of Swayambhu Sambhulingeswara Swami. A notable feature of the temple is that on the top of the lingam there is a hole of about 2 inches in circumferance which is full of water in all seasons and the place therefore came to the known as Dakshina Kasi (Varanasi of the South). There is a legend associated with this lingam which is 1.83 metres in height and 0.34 metre in diameter. day `Pooja` is celebrated in the temple where devotees in large number visit the temple to receive the blessings of the Lord. Every year, during the season of Mahashivratri festival, the Kalyanotsavam of the diety is celebrated with devotion and this event forms one of the greatest instances where people gather in thousands. Mellachervu is situated at a distance of 9.6 km from Huzur Nagar and 67.6 km from the Khammam railway station. This village is connected to the important commercial city of Vijayawada by a canal way.
 Yadagirigutta Temple
Yadagirigutta Temple
This temple is at a height of 300 feet on Yadagiri hill. At the foothill there is Vaikuntha Dwara entrance. At the entrance there is a shrine dedicated to Hanuman with a gap in the rock representing Ghandabheranda Narasimha. There is also a temple to Shiva on the Yadagiri hill.



















