 Sylheti language is the spoken in certain North Eastern Indian states like Assam and Tripura. It is basically the language of Sylhet, which is situated in the north-eastern area of Bangladesh. Sylheti language is spoken by a considerable population north eastern India. Interestingly, Sylheti language is often considered as a dialect of Bengali Language and Assamese Language. There are many similarities between these two languages and Sylheti language. However, there are noteworthy differences too between them. Sylhet was a branch of the ancient kingdom of Kamarupa; Sylheti language has various common features with Assamese language. It includes the existence of a bigger set of fricatives as compared to other East Indian languages. The script of Sylheti Language is not broadly known. This language was previously written in its own script that is Sylheti Nagari, but presently it is almost written in Bengali script. Sylheti language is spoken across the border in several districts of Assam like Cachar District, Karimganj and Hailakandi.
Sylheti language is the spoken in certain North Eastern Indian states like Assam and Tripura. It is basically the language of Sylhet, which is situated in the north-eastern area of Bangladesh. Sylheti language is spoken by a considerable population north eastern India. Interestingly, Sylheti language is often considered as a dialect of Bengali Language and Assamese Language. There are many similarities between these two languages and Sylheti language. However, there are noteworthy differences too between them. Sylhet was a branch of the ancient kingdom of Kamarupa; Sylheti language has various common features with Assamese language. It includes the existence of a bigger set of fricatives as compared to other East Indian languages. The script of Sylheti Language is not broadly known. This language was previously written in its own script that is Sylheti Nagari, but presently it is almost written in Bengali script. Sylheti language is spoken across the border in several districts of Assam like Cachar District, Karimganj and Hailakandi.
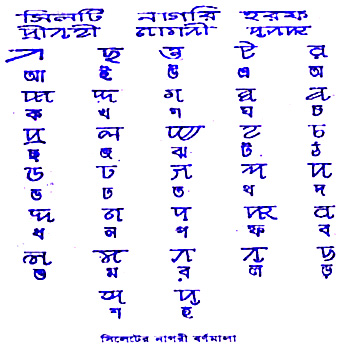
There is a prosperous heritage of literature in Sylheti Nagri script that dates back to around 200 years. The script of Sylheti language comprises five independent vowels, five dependent vowels associated with a consonant and 27 consonants. The alphabets in Sylheti Nagri script differs from Bengali alphabet. In Bangladesh, during the 1971 Liberation War, writing structure came to a stop. Efforts for establishing Sylheti language as a modern language were strongly opposed in Bangladesh by political and cultural forces. However, campaigns began in order to recognize Sylheti language as an independent language.
Sylheti language is distinguished by huge range of fricative sounds. These fricative sounds of Sylheti language match up with the aspirated stops in some closely connected languages like Bengali language. This language is also distinguished by the deficient in breathy voiced stops, which are generally common in other Indian languages, amount of stress given on words, and also by a moderately large set of borrowed words from Arabic language, Hindi language, Persian, Bengali language and Assamese language. Sylheti language is presently considered as an independent language and not a dialect of Bengali and Assamese languages. There are a huge number of speakers of Sylheti Language across the globe.



















