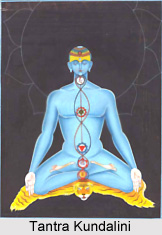
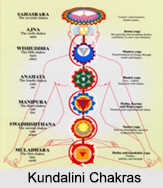
Parichaya Avastha is the third stage of Siddha Yoga. During the Third Stage, the Kundalini Shakti moves to his Sahasrara Chakra or the spiritual centre in the brain and unites with it. This leads to the practitioner"s Awareness uniting with the Kundalini. It is done in the following manner:
Parichaya Avastha is the third stage of Siddha Yoga. During the Third Stage, the Kundalini Shakti moves to his Sahasrara Chakra or the spiritual centre in the brain and unites with it. This leads to the practitioner"s Awareness uniting with the Kundalini. It is done in the following manner:
Vayu through difficult practice pierces the Kundalini, along with Agni and enters the Susumna without any interruption. When one`s Chitta enters the Susumna along with Prana, then it reaches the high seat along with Prana. When the Yogi acquires power of action and pierces through the Six Chakras and reaches the secure condition of Parichaya. The Yogi is then able to see threefold effects of Karma. Then Yogi destroys the multitude of Karmas by the Pranava. Then he accomplishes Kaya-Vyuha, a mystical process of arranging the various Skandhas of the body as well as taking them, in order to exhaust all his previous Karmas without taking rebirth. The Yogi practise the five forms of concentration by which one can have command over the five elements and fear of injuries is removed.
With Parichaya Avastha, the Yogi begins to achieve complete peacefulness of mind and gradually his perspective of the universe changes. He constantly observes the universe as nothing but a manifestation of Prana. He finds that oneness in everyone and everything around him.
Owing to the above mentioned consequence, the practitioner reaches the status of Siddha. This status enables him to gain extraordinary powers like the ability to awaken the inactive Kundalini Shakti in others. He achieves his aim of Self-Realization which transforms him from an "aspirant" to a true "Yogi". Now he can decide to continue living in this world as long as he aims or to free himself from it at will. Some yogis choose to stay in this state for extended periods while others move on to the next stage of Liberation i.e., Mukti.