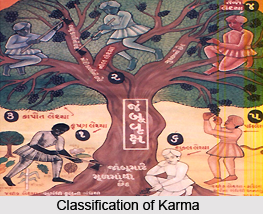
 According to Bhagwan Mahavir of the Jaina dharma, the world is full of misery and sorrows. Therefore, the fundamental object of religion should be to help the worldly souls to cross the river of sorrows and attain liberation from the cycles of births and deaths. The actual reason behind the soul`s worldly career is its own actions, which relate it with different types of external material particles called karma.
According to Bhagwan Mahavir of the Jaina dharma, the world is full of misery and sorrows. Therefore, the fundamental object of religion should be to help the worldly souls to cross the river of sorrows and attain liberation from the cycles of births and deaths. The actual reason behind the soul`s worldly career is its own actions, which relate it with different types of external material particles called karma.
There are mainly two classifications of Karma:
• Destructive and
• Non-destructive karma
Destructive karma is to get bound with the soul and destroy its natural qualities. There are of four types of destructive karma.
• The perception- obscuring (darshanavarni) karma
• The knowledge- obscuring (jnanavarni) karma
• The deluding- (mohaniya) karma
• The obstructing- (antaraya) karma
These destructive karma are again divided into two parts-
• All-destructive karma: This type of karma destroys the natural qualities of a soul completely. This karma again has 20 sub-types.
• Partially destructive karma: This karma destroys the natural qualities of soul partially. There are 25 sub-types of this karma.
Non-destructive karma does not harm the main qualities of the soul. These are again four types:
• The feeling- producing (vedaniya) karma
• The life-span- determining (aayu) karma
• The physique-determining (naam) karma
• The status- determining (gorta) karma and
 All these again have many sub-types of karma.
All these again have many sub-types of karma.
It is believed that all living in this world come under the influence of these eight types of karma. Again, as per another classification, karma is of two kinds:
• Physical (dravya) karma, which are material particles and
• Abstract or Psychical (bhava) karma, which is impure mental dispositions.
The karmic body is constituted of the physical karmic particles, which is linked with the soul. The gross material body is built through nutrition from the environment. The abstract karma is said to be responsible for attracting material karmic particles to the soul. The physical karma has its influences the psychological disposition. In this way, a psycho-physical cycle is maintained between the physical karma and abstract karma.
The Physical Karma is the substance of karmic variform that attracted by the activity of mind; speech and body are unified with the soul.
The Psychical karma is the passions, attachment, jealousy and aversion that are constantly attached to the soul. It can be said a type of mental condition.
The four non-destructive karmas are again divided into two types:
• Meritorious karma and
• Demerit karma
The results of which karma yield sensuous, physical and worldly pleasures are known as merits. The demerits karma results or cause physical pains, worldly sorrows and displeasure to senses.
There are total 158 sub-groups of the basic eight karma available in Jaina philosophy. These are:
• Knowledge obscuring karma 5 sub groups
• Intuition obscuring karma 9 sub groups
• Feeling producing karma 2 sub groups
• Deluding karma 28 sub groups
• Life span determining karma 4 sub groups
• Body making karma 103 sub groups
• Status determining karma 2 sub groups
• Energy obstructing karma 5 sub groups
• 158 sub groups



















