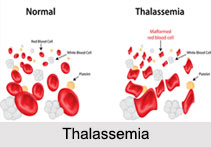
 Thalassemia is an inherited blood related disorder in which the body makes an abnormal form of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. A person with Thalassemia will have too few red blood cells and too little haemoglobin. The impact can range from mild to severe and life-threatening. The disorder results in excessive destruction of red blood cells, which leads to Anaemia.
Thalassemia is an inherited blood related disorder in which the body makes an abnormal form of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. A person with Thalassemia will have too few red blood cells and too little haemoglobin. The impact can range from mild to severe and life-threatening. The disorder results in excessive destruction of red blood cells, which leads to Anaemia.
Types of Thalassemia
There are two main types of Thalassemia:
•Beta Thalassemia
•Alpha Thalassemia
Causes of Thalassemia
Thalassemia occurs when there is an abnormality or mutation in one of the genes involved in haemoglobin production. The mutations associated with Thalassemia are passed from parents to children.
Symptoms of Thalassemia
The symptoms of Thalassemia vary depending on its type. Symptoms will not show until the age of six months in most infants because new borns have a different type of haemoglobin, called Foetal Haemoglobin. After six months "normal" haemoglobin starts replacing the foetal type and symptoms may begin to appear. Some of the most common ones include:
•Bone deformities, especially in the face
•Dark urine
•Delayed growth and development
•Excessive tiredness and fatigue
•Yellow or pale skin
Not everyone has visible symptoms of Thalassemia. Signs of the disorder also tend to show up later in childhood or adolescence.
Diagnosis of Thalassemia
The doctor will do a physical exam to look for an enlarged spleen. A blood sample will be sent to a laboratory to be tested. A test called Haemoglobin Electrophoresis shows the presence of an abnormal form of haemoglobin. Mutational analysis can help detect alpha Thalassemia. Most children with moderate to severe Thalassemia receive a diagnosis by the time they are 2 years old.
Treatment of Thalassemia
The treatment for Thalassemia depends on the type and severity of disease involved. It often involves regular blood transfusions and foliate supplements. People who receive a lot of blood transfusions need a treatment called Chelation Therapy. This is done to remove excess iron from the body. A bone marrow transplant may help treat the disease in some people, especially children.