The distinctive style of Mohiniattam is the complete absence of heavy stamping and rhythmical tension, where the footwork is gentle, soft and sliding. The movements are never abrupt, they are dignified, easy and natural, but the vertical line of the body is never broken. Hence, among the styles detailed by Bharata Muni in the ancient Indian treatise on dance, the Natyashastra, Mohiniattam resembles the Kaisiki type meaning graceful. The dance is romantic in nature and is characterized by graceful movements, wide swinging steps and swaying of the upper body from side to side.
The distinctive style of Mohiniattam is the complete absence of heavy stamping and rhythmical tension, where the footwork is gentle, soft and sliding. The movements are never abrupt, they are dignified, easy and natural, but the vertical line of the body is never broken. Hence, among the styles detailed by Bharata Muni in the ancient Indian treatise on dance, the Natyashastra, Mohiniattam resembles the Kaisiki type meaning graceful. The dance is romantic in nature and is characterized by graceful movements, wide swinging steps and swaying of the upper body from side to side.
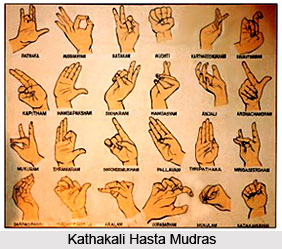
Mohiniattam is renowned for its grace, flow, simple looking footwork and rotating rhythmic movement. The eyes play an important role in emphasizing the direction of the movement. The basic dance steps are the Adavus, which are of four kinds: Taganam, Jaganam, Dhaganam and Sammisram. These names are derived from the nomenclature called Vaittari. Mohiniattam like much other form follows the Hastha Lakshandeepika, which is a classical text, the basis for the expressive gestures of the hands and arms in Mohiniattam. This Indian classical dance has flavours of Bharatnatyam and Kathakali in it.
 The technique of Mohiniattam emphasizes lasya and sringara or romance is the prominent rasa. Rasa means the dominant emotion. Basically, it is the Nayika (heroine) a devotee pining for the Deva or Nayaka (hero), Chari (special type of movement) and Nritta Mudra (hand movement without any special meaning) are special to Mohiniattam. The hasta mudras used in this dance are Asamyukta (single hand), Samyuktra (both hands) and in Misra (either way) positions. The bobbing gait forward - backward or side ways and the graceful swaying of the trunk or head are special to this style. The basic sitting posture with the feet apart is reminiscent of Kathakali.
The technique of Mohiniattam emphasizes lasya and sringara or romance is the prominent rasa. Rasa means the dominant emotion. Basically, it is the Nayika (heroine) a devotee pining for the Deva or Nayaka (hero), Chari (special type of movement) and Nritta Mudra (hand movement without any special meaning) are special to Mohiniattam. The hasta mudras used in this dance are Asamyukta (single hand), Samyuktra (both hands) and in Misra (either way) positions. The bobbing gait forward - backward or side ways and the graceful swaying of the trunk or head are special to this style. The basic sitting posture with the feet apart is reminiscent of Kathakali.
This article is a stub. You can enrich by adding more information to it. Send your Write Up to content@indianetzone.com