The origin of Indian alphabets can be traced through well preserved inscriptions in different parts of the country. Apart from these many scholars and researchers have their vital contribution towards its development. Different scholars have opined different thoughts about its origin.
According to Professor Wilson, Indian alphabets originated after the Greek or Phoenician model whereas Sir William Jones along with others like Weber, Westergird, Buhler, Max Muller, F Muller, Sayce and Whitney opines that it has a Semitic origin. Another researcher Dr Burnell is of the view that the Indian alphabet was derived from the Aramaean alphabets which were once followed in Persia and Babylonia.
Benfey speaks of the Phoenician origin to which Dr Taylor objects. The latter is of the view that if the Phoenician alphabet had evolved in Solomon`s time, then in 700 years many alphabets would have developed in India. Hence no alphabet has originated in India before the sixth century BC.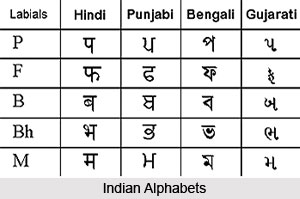 Further, there is no similarity between the Phoenician alphabets and the Indian alphabets. Dr Taylor says that the Indian alphabet originated from the Sebian alphabet which was an off spring of the Phoenician alphabet. The Indo-Bactrian alphabet came to northwest India by the Khyber Pass while the source of alphabets in western India was from the sea. Yemen of Arabia became a centre of trade from 1000 BC. Different countries participated in the barter system and exchanged goods with each other.
Further, there is no similarity between the Phoenician alphabets and the Indian alphabets. Dr Taylor says that the Indian alphabet originated from the Sebian alphabet which was an off spring of the Phoenician alphabet. The Indo-Bactrian alphabet came to northwest India by the Khyber Pass while the source of alphabets in western India was from the sea. Yemen of Arabia became a centre of trade from 1000 BC. Different countries participated in the barter system and exchanged goods with each other.
Earlier the Sebians were the leaders and till 2500 BC trading between Yemen and Egypt was in full swing. With India it continued till 1000 BC. Even under the Ptolemies, the Egyptians never traded with India but with the beginning of the second century AD, Indian goods were exchanged at Diocoridus Islands near the Somali coast. Thus, the Sebian alphabet got the opportunity to enter India.
Thus it can be concluded that before sixth century BC Indians has not adopted the art of writing. It was first brought in by the merchants of western India from the West during the seventh or eighth century BC. It was later adopted by the Brahmans in an altered form. They named it as Brakmi Lipi and in course of time it became the parent of the various Indian alphabets.



















