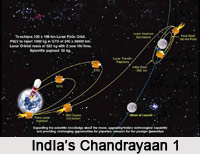
Chandrayan 1 is the first mission of India to the moon. It was India`s first unmanned lunar craft. It was operated by Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008. The lunar craft had started on 22nd October in the year 2008 and had operated till August 2009. Chandrayan was launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota in the Nellore District of Andhra Pradesh. According to Indian Standard Time the lunar craft was launched at 6:22 a.m. The lunar craft was successfully inserted into the lunar orbit on 8th November 2008. The launch of Chandrayan was a giant leap in the field of Indian Astronomy because with the help of this India had developed its own technique and methodology to explore the moon.
Chandrayan 1 is the first mission of India to the moon. It was India`s first unmanned lunar craft. It was operated by Indian Space Research Organisation in October 2008. The lunar craft had started on 22nd October in the year 2008 and had operated till August 2009. Chandrayan was launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota in the Nellore District of Andhra Pradesh. According to Indian Standard Time the lunar craft was launched at 6:22 a.m. The lunar craft was successfully inserted into the lunar orbit on 8th November 2008. The launch of Chandrayan was a giant leap in the field of Indian Astronomy because with the help of this India had developed its own technique and methodology to explore the moon.
India was the fourth country to have implanted its flag on the moon. The Moon Impact Probe was separated from Chandrayan orbiter in the South Pole in a controlled manner. The estimated cost of the project was around rupees 386 crores.
Chandrayan was launched with the help of PSLV which weighed 1380 kg at launch and 675 kilograms in the lunar orbit. The lunar craft had high resolution remote sensing equipment and soft and hard X-ray frequencies. It was intended that the lunar craft would monitor the surface of the moon for a period of two years. It aimed at finding out the chemical characteristics of the surface and the three dimensional topography of the moon. Chandrayan carried along with five ISRO payloads and six payloads from other agencies in order to carry out the study of moon in a more effective manner.
Unfortunately Chandrayan suffered a number of technical difficulties. As a result it had stopped giving radio signals to earth on August 29th at 1:30 a.m. Right at that moment it was declared by Indian Space Research Organisation that the mission had come to an end officially. Chandrayan had operated for a period of 312 days against its intended period of two years. Even within a short span Chandrayan 1 had achieved 95 percent of its objectives.
 A major discovery that was made by Chandrayan 1 was the discovery of abundant of water molecules in the lunar soil. Some of the other objectives of Chandryan 1 were to design, develop, launch and orbit a spacecraft around the Moon using an Indian-made launch vehicle, conducting experiments using instruments of the space craft which would give certain desired results. It was planned that the instruments in the space craft would be used to prepare a three dimensional atlas of the moon both from the near and far side. The instruments would also be used to carry on mineralogical and chemical exploitation of the lunar soil in order to excavate minerals like magnesium, aluminium, calcium, silicon, iron, titanium, radon, thorium and uranium. It was also expected that Chandrayan would increase the scientific knowledge and would also be a fore-runner for future soft-landing missions on the lunar soil.
A major discovery that was made by Chandrayan 1 was the discovery of abundant of water molecules in the lunar soil. Some of the other objectives of Chandryan 1 were to design, develop, launch and orbit a spacecraft around the Moon using an Indian-made launch vehicle, conducting experiments using instruments of the space craft which would give certain desired results. It was planned that the instruments in the space craft would be used to prepare a three dimensional atlas of the moon both from the near and far side. The instruments would also be used to carry on mineralogical and chemical exploitation of the lunar soil in order to excavate minerals like magnesium, aluminium, calcium, silicon, iron, titanium, radon, thorium and uranium. It was also expected that Chandrayan would increase the scientific knowledge and would also be a fore-runner for future soft-landing missions on the lunar soil.
As per as the success of Chandrayan is concerned it can be said that Chandrayan has carried out efficient mineral exploitation on the surface of the moon. On the lunar surface traces of iron have been found. Several rocks bearing composition of iron has been mapped by the Moon Mineralogy Mapper. The lunar craft could also take around 70,000 images of the surface of the moon. With the help of those images the lunar surface could well be estimated. Not only has Chandrayan taken the images of the moon but also has captured the image of the earth in its entirety.
Some of the prominent objectives which had been fulfilled by Chandrayan during its short span was to place the flag of India in the lunar soil and to bring several images home which would assist the detailed the study of the moon. The Moon Mineralogy Mapper in the Chandrayan had also found the traces of water on the lunar surface. It was also found that water is produced by moon in a special way. Moon produces water just like a sponge. It absorbs charged particles emitted by the sun and then those particles interact with oxygen in the lunar surface to produce water.
Chandrayan 1, thus, was an important breakthrough in the field of Indian Astronomy. It made important discoveries regarding the chemical composition and lunar soil. In fact it showed the entire world that India had developed in the field of astronomy in leaps and bounds.